Minsk
Minsk Мінск · Менск · Минск | |
|---|---|
Capital city | |
 Clockwise from top left: Minsk City Hall, the Red Church, Railway Station Square, Independence Square, National Opera and Ballet Theatre and the Church of Sts. Peter and Paul. | |
 Flag  Coat of arms | |
 Minsk Location within Belarus Show map of Belarus  Minsk Location within Europe Show map of Europe | |
| Coordinates: 53°54′N 27°34′E / 53.900°N 27.567°E / 53.900; 27.567Coordinates: 53°54′N 27°34′E / 53.900°N 27.567°E / 53.900; 27.567 | |
| Country | |
| Founded | 1067 |
| Government | |
| • Chairman | Anatoli Sivak[2] |
| Area | |
| • Total | 409.5 km2 (158.1 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 280.6 m (920.6 ft) |
| Population (2018) | |
| • Total | 1,982,444[1] |
| • Density | 4,841/km2 (12,540/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+3 (FET/MSK[3]) |
| Postal Code | 220001-220141 |
| Area code(s) | +375 17 |
| License plate | 7 |
HDI (2017) | 0.824[4] – very high |
| Website | www.minsk.gov.by |
Minsk (Belarusian: Мінск, pronounced [mʲinsk]; Russian: Минск) is the capital and largest city of Belarus, situated on the Svislač and the Nyamiha Rivers. As the national capital, Minsk has a special administrative status in Belarus and is the administrative centre of Minsk Region (voblasć) and Minsk District (rajon). The population in January 2018 was 1,982,444,[1] making Minsk the 11th most populous city in Europe. Minsk is the administrative capital of the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) and seat of its Executive Secretary.
The earliest historical references to Minsk date to the 11th century (1067), when it was noted as a provincial city within the Principality of Polotsk. The settlement developed on the rivers. In 1242, Minsk became part of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. It received town privileges in 1499.
From 1569, it was a capital of the Minsk Voivodeship, in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. It was part of a region annexed by the Russian Empire in 1793, as a consequence of the Second Partition of Poland. From 1919 to 1991, after the Russian Revolution, Minsk was the capital of the Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic, in the Soviet Union. Minsk will host the 2019 European Games.
Contents
1 Etymology and historical names
2 History
2.1 Early history
2.2 Late Middle Ages
2.3 Russian rule
2.4 20th century
2.5 Recent developments
3 Geography
3.1 Climate
3.2 Ecological situation
4 Demographics
4.1 Population growth
4.2 Ethnic groups
4.3 Languages
4.4 Religion
4.5 Crime
5 Economy
5.1 Industry
5.2 Unemployment
6 Government and administrative divisions
7 Culture
7.1 Churches
7.2 Cemeteries
7.3 Theatres
7.4 Museums
7.5 Recreation areas
7.6 Cinemas
8 Tourism
9 Sports
9.1 Football
9.2 Ice hockey
9.3 Handball
9.4 Basketball
9.5 International sporting events
10 Transport
10.1 Local transport
10.2 Rapid transit
10.3 Railway and intercity bus
10.4 Airports
11 Education
11.1 Major higher educational institutions
12 Honors
13 Notable residents
14 International relations
14.1 Twin towns and sister cities
15 See also
16 References
17 Bibliography
18 Further reading
19 External links
Etymology and historical names

Independence Square in the centre of Minsk.
The Old East Slavic name of the town was Мѣньскъ (i.e. Měnsk < Early Proto-Slavic or Late Indo-European Mēnĭskŭ), derived from a river name Měn (< Mēnŭ). The direct continuation of this name in Belarusian is Miensk (pronounced [mʲɛnsk]).
The resulting form of the name, Minsk (spelled either Минскъ or Мѣнскъ), was taken over both in Russian (modern spelling: Минск) and Polish (Mińsk), and under the influence especially of Russian it also became official in Belarusian. However, some Belarusian-speakers continue to use Miensk (spelled Менск) as their preferred name for the city.
When Belarus was under Polish rule, the names Mińsk Litewski 'Minsk of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania' and Mińsk Białoruski 'Minsk in Belarus' were used to differentiate this place name from Mińsk Mazowiecki 'Minsk in Masovia'. In modern Polish, Mińsk without an attribute usually refers to the city in Belarus, which is about 50 times bigger than Mińsk Mazowiecki; (cf. Brest-Litovsk and Brześć Kujawski for a similar case).
History
Early history

The Saviour Church, built under the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth in 1577, is part of an archaeological preservation in Zaslavl, 23 km (14 mi) northwest of Minsk.
The area of today's Minsk was settled by the Early East Slavs by the 9th century AD. The Svislach River valley was the settlement boundary between two Early East Slav tribes – the Krivichs and Dregovichs. By 980, the area was incorporated into the early medieval Principality of Polotsk, one of the earliest East Slav principalities of Old Rus' state. Minsk was first mentioned in the name form Měneskъ (Мѣнескъ) in the Primary Chronicle for the year 1067 in association with the Battle on the River Nemiga.[5] 1067 is now widely accepted as the founding year of Minsk. City authorities consider the date of 3 March 1067, to be the exact founding date of the city,[6] though the town (by then fortified by wooden walls) had certainly existed for some time by then. The origin of the name is unknown but there are several theories.
In the early 12th century, the Principality of Polotsk disintegrated into smaller fiefs. The Principality of Minsk was established by one of the Polotsk dynasty princes. In 1129, the Principality of Minsk was annexed by Kiev, the dominant principality of Kievan Rus; however in 1146 the Polotsk dynasty regained control of the principality. By 1150, Minsk rivaled Polotsk as the major city in the former Principality of Polotsk. The princes of Minsk and Polotsk were engaged in years of struggle trying to unite all lands previously under the rule of Polotsk.
Late Middle Ages

Trayetskaye Pradmestsye contains the remains of pre-WWII Minsk on the Svislach bank.
Minsk escaped the Mongol invasion of Rus in 1237–1239. In 1242, Minsk became a part of the expanding Grand Duchy of Lithuania. It joined peacefully and local elites enjoyed high rank in the society of the Grand Duchy. In 1413, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and Kingdom of Poland entered into a union. Minsk became the centre of Minsk Voivodship (province). In 1441, the Polish-Lithuanian prince and future king Casimir IV included Minsk in a list of cities enjoying certain privileges, and in 1499, during the reign of his son, Alexander I Jagiellon, Minsk received town privileges under Magdeburg law. In 1569, after the Union of Lublin, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and the Kingdom of Poland merged into a single state, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. Afterwards, a Polish community including government clerks, officers and craftsmen settled in Minsk.[citation needed]
By the middle of the 16th century, Minsk was an important economic and cultural centre in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. It was also an important centre for the Eastern Orthodox Church. Following the Union of Brest, both the Uniate church and the Roman Catholic Church increased in influence.[citation needed]
In 1655, Minsk was conquered by troops of Tsar Alexei of Russia.[7] Russians governed the city until 1660 when it was regained by John II Casimir, King of Poland. By the end of the Polish-Russian War, Minsk had only about 2,000 residents and just 300 houses. The second wave of devastation occurred during the Great Northern War, when Minsk was occupied in 1708 and 1709 by the army of Charles XII of Sweden and then by the army of Peter the Great.[citation needed] The last decades of the Polish rule involved decline or very slow development, since Minsk had become a small provincial town of little economic or military significance.
Russian rule

Russian Orthodox church of St. Mary Magdalene (built in 1847)

A street in central Minsk
Minsk was annexed by Russia in 1793 as a consequence of the Second Partition of Poland.[8] In 1796, it became the centre of the Minsk Governorate. All of the initial street names were replaced by Russian names, though the spelling of the city's name remained unchanged. It was briefly occupied by the Grande Armée during French invasion of Russia in 1812.
Throughout the 19th century, the city continued to grow and significantly improve. In the 1830s, major streets and squares of Minsk were cobbled and paved. A first public library was opened in 1836, and a fire brigade was put into operation in 1837. In 1838, the first local newspaper, Minskiye gubernskiye vedomosti (“Minsk province news”) went into circulation. The first theatre was established in 1844. By 1860, Minsk was an important trading city with a population of 27,000. There was a construction boom that led to the building of 2 and 3-story brick and stone houses in Upper Town.
Minsk's development was boosted by improvements in transportation. In 1846, the Moscow-Warsaw road was laid through Minsk. In 1871, a railway link between Moscow and Warsaw ran via Minsk, and in 1873, a new railway from Romny in Ukraine to the Baltic Sea port of Libava (Liepāja) was also constructed. Thus Minsk became an important rail junction and a manufacturing hub. A municipal water supply was introduced in 1872, the telephone in 1890, the horse tram in 1892, and the first power generator in 1894. By 1900, Minsk had 58 factories employing 3,000 workers. The city also boasted theatres, cinemas, newspapers, schools and colleges, as well as numerous monasteries, churches, synagogues, and a mosque. According to the 1897 Russian census, the city had 91,494 inhabitants, with some 47,561 Jews constituting more than half of the city population.
20th century

The Jesuit Collegium in 1912.

Railway Station Square, an example of Stalinist Minsk.

Children during the German bombing of Minsk
24 June 1941

War memorial in Victory Square, Minsk.
In the early years of the 20th century, Minsk was a major centre for the worker's movement in Belarus. The 1st Congress of the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party, the forerunner to the Bolsheviks and eventually the CPSU, was held there in 1898. It was also one of the major centres of the Belarusian national revival, alongside Vilnia. However, the First World War affected the development of Minsk tremendously. By 1915, Minsk was a battle-front city. Some factories were closed down, and residents began evacuating to the east. Minsk became the headquarters of the Western Front of the Russian army and also housed military hospitals and military supply bases.[citation needed]
The Russian Revolution had an immediate effect in Minsk. A Workers' Soviet was established in Minsk in October 1917, drawing much of its support from disaffected soldiers and workers. After the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk, German forces occupied Minsk on 21 February 1918.[9] On 25 March 1918, Minsk was proclaimed the capital of the Belarusian People's Republic. The republic was short-lived; in December 1918, Minsk was taken over by the Red Army. In January 1919 Minsk was proclaimed the capital of the Belorussian SSR, though later in 1919 (see Operation Minsk) and again in 1920, the city was controlled by the Second Polish Republic during the course of the Polish-Bolshevik War between 8 August 1919 and 11 July 1920 and again between 14 October 1920 and 19 March 1921. Under the terms of the Peace of Riga, Minsk was handed back to the Russian SFSR and became the capital of the Belorussian SSR, one of the founding republics of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics.

German troops marching through Minsk.
A programme of reconstruction and development was begun in 1922. By 1924, there were 29 factories in operation; schools, museums, theatres and libraries were also established. Throughout the 1920s and the 1930s, Minsk saw rapid development with dozens of new factories being built and new schools, colleges, higher education establishments, hospitals, theatres and cinemas being opened. During this period, Minsk was also a centre for the development of Belarusian language and culture.
Before the Second World War, Minsk had a population of 300,000 people. After Germany invaded the Soviet Union on 22 June 1941, as part of Operation Barbarossa, Minsk immediately came under attack. The city was bombed on the first day of the invasion and came under Wehrmacht control four days later. However, some factories, museums and tens of thousands of civilians had been evacuated to the east. The Germans designated Minsk the administrative centre of Reichskomissariat Ostland. Communists and sympathisers were killed or imprisoned, both locally and after being transported to Germany. Homes were requisitioned to house invading German forces. Thousands starved as food was seized by the German Army and paid work was scarce. Minsk was the site of one of the largest Nazi-run ghettos in the Second World War, temporarily housing over 100,000 Jews (see Minsk Ghetto). Some anti-Soviet residents of Minsk, who hoped that Belarus could regain independence, did support the Germans, especially at the beginning of the occupation, but by 1942, Minsk had become a major centre of the Soviet partisan resistance movement against the invasion, in what is known as the German-Soviet War. For this role, Minsk was awarded the title Hero City in 1974.
Minsk was recaptured by Soviet troops on 3 July 1944, during Operation Bagration. The city was the centre of German resistance to the Soviet advance and saw heavy fighting during the first half of 1944. Factories, municipal buildings, power stations, bridges, most roads and 80% of the houses were reduced to rubble. In 1944, Minsk's population was reduced to a mere 50,000.

Coat of Arms of Minsk during the Soviet era
After the Second World War, Minsk was rebuilt, but not reconstructed. The historical centre was replaced in the 1940s and 1950s by Stalinist architecture, which favoured grand buildings, broad avenues and wide squares. Subsequently, the city grew rapidly as a result of massive industrialisation. Since the 1960s Minsk's population has also grown apace, reaching 1 million in 1972 and 1.5 million in 1986.
Construction of Minsk Metro began on 16 June 1977, and the system was opened to the public on 30 June 1984, becoming the ninth metro system in the Soviet Union.
The rapid population growth was primarily driven by mass migration of young, unskilled workers from rural areas of Belarus, as well as by migration of skilled workers from other parts of the Soviet Union.[citation needed][10] To house the expanding population, Minsk spread beyond its historical boundaries. Its surrounding villages were absorbed and rebuilt as mikroraions, districts of high-density apartment housing.
Recent developments

Independence Avenue (Initial part of avenue candidates for inclusion in World Heritage Site)

Another view of Independence Avenue
Throughout the 1990s, after the fall of Communism, the city continued to change. As the capital of a newly independent country, Minsk quickly acquired the attributes of a major city. Embassies were opened, and a number of Soviet administrative buildings became government centres. During the early and mid-1990s, Minsk was hit by an economic crisis and many development projects were halted, resulting in high unemployment and underemployment. Since the late 1990s, there have been improvements in transport and infrastructure, and a housing boom has been underway since 2002. On the outskirts of Minsk, new mikroraions of residential development have been built. Metro lines have been extended, and the road system (including the Minsk BeltWay) has been improved. In the recent years Minsk has been continuously decentralizing,[11] and with a third line of Minsk Metro set to open in 2020, the city is expected to change even further.[12] More development is planned for several areas outside the city centre, while the future of the older neighborhoods is still unclear.[13]
Geography
Minsk is located on the southeastern slope of the Minsk Hills, a region of rolling hills running from the southwest (upper reaches of the river Nioman) to the northeast – that is, to Lukomskaye Lake in northwestern Belarus. The average altitude above sea level is 220 metres (720 ft). The physical geography of Minsk was shaped over the two most recent ice ages. The Svislach River, which flows across the city from the northwest to the southeast, is in the urstromtal, an ancient river valley formed by water flowing from melting ice sheets at the end of the last Ice Age. There are six smaller rivers within the city limits, all part of the Black Sea basin.
Minsk is in the area of mixed forests typical of most of Belarus. Pinewood and mixed forests border the edge of the city, especially in the north and east. Some of the forests were preserved as parks (for instance, the Chelyuskinites Park) as the city grew.
The city was initially built on the hills, which allowed for defensive fortifications, and the western parts of the city are the most hilly.
Climate
Minsk has a warm summer humid continental climate (Köppen Dfb), owing to its location between the strong influence of the moist air of the Atlantic Ocean and the dry air of the Eurasian landmass. Its weather is unstable and tends to change relatively often. The average January temperature is −4.5 °C (23.9 °F), while the average July temperature is 18.5 °C (65.3 °F). The lowest temperature was recorded on 17 January 1940, at −40 °C (−40 °F) and the warmest on 29 July 1936 at 35 °C (95 °F), and on 3 August 2014 at 35 °C (95 °F). There are frequent fogs, common in the autumn and spring. Minsk receives annual precipitation of 690 millimetres (27 in), of which one third falls during the cold period (as snow and rain) and two thirds in the warm period. Throughout the year, most winds are westerly and northwesterly, bringing cool and moist air from the Atlantic. Similar climatic regimes are found in Stockholm, Sweden and in Halifax, Canada.
| Climate data for Minsk (1981–2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 10.3 (50.5) | 13.6 (56.5) | 18.9 (66.0) | 28.8 (83.8) | 30.9 (87.6) | 32.5 (90.5) | 35.0 (95.0) | 35.6 (96.1) | 30.3 (86.5) | 24.7 (76.5) | 16.0 (60.8) | 10.3 (50.5) | 35.6 (96.1) |
| Average high °C (°F) | −2.1 (28.2) | −1.4 (29.5) | 3.8 (38.8) | 12.2 (54.0) | 18.7 (65.7) | 21.5 (70.7) | 23.6 (74.5) | 22.8 (73.0) | 16.7 (62.1) | 10.2 (50.4) | 2.9 (37.2) | −1.2 (29.8) | 10.6 (51.1) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −4.5 (23.9) | −4.4 (24.1) | 0.0 (32.0) | 7.2 (45.0) | 13.3 (55.9) | 16.4 (61.5) | 18.5 (65.3) | 17.5 (63.5) | 12.1 (53.8) | 6.6 (43.9) | 0.6 (33.1) | −3.4 (25.9) | 6.7 (44.1) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −6.7 (19.9) | −7 (19) | −3.3 (26.1) | 2.6 (36.7) | 8.1 (46.6) | 11.7 (53.1) | 13.8 (56.8) | 12.8 (55.0) | 8.2 (46.8) | 3.6 (38.5) | −1.3 (29.7) | −5.5 (22.1) | 3.1 (37.6) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −39.1 (−38.4) | −35.1 (−31.2) | −30.5 (−22.9) | −18.4 (−1.1) | −5 (23) | 0.0 (32.0) | 3.8 (38.8) | 1.7 (35.1) | −4.7 (23.5) | −12.9 (8.8) | −20.4 (−4.7) | −30.6 (−23.1) | −39.1 (−38.4) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 45 (1.8) | 39 (1.5) | 44 (1.7) | 42 (1.7) | 65 (2.6) | 89 (3.5) | 89 (3.5) | 68 (2.7) | 60 (2.4) | 52 (2.0) | 48 (1.9) | 49 (1.9) | 690 (27.2) |
| Average rainy days | 11 | 9 | 11 | 13 | 18 | 19 | 18 | 15 | 18 | 18 | 17 | 13 | 180 |
| Average snowy days | 24 | 21 | 15 | 4 | 0.3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.04 | 3 | 13 | 22 | 102 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 86 | 83 | 77 | 67 | 66 | 70 | 71 | 72 | 79 | 82 | 88 | 88 | 77 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 44 | 66 | 134 | 181 | 257 | 273 | 269 | 242 | 165 | 97 | 36 | 27 | 1,790 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 18 | 24 | 37 | 43 | 52 | 54 | 53 | 53 | 43 | 30 | 14 | 12 | 40 |
| Source #1: Pogoda.ru.net[14] | |||||||||||||
| Source #2: Belarus Department of Hydrometeorology (sun data from 1938, 1940, and 1945–2000)[15] | |||||||||||||
Ecological situation
The ecological situation is monitored by Republican Centre of Radioactive and Environmental Control.[16]

Minsk. A view of the Svislach river and Troitskoye Predmestye (Trinity Suburb)
During 2003–2008 the overall weight of contaminants increased from 186,000 to 247,400 tons.[16] The change from gas as industrial fuel to mazut for financial reasons has worsened the ecological situation.[16] However, the majority of overall air pollution is produced by cars.[16] Belarusian traffic police DAI every year hold operation "Clean Air" to prevent the use of cars with extremely polluting engines.[17] Sometimes the maximum normative concentration of formaldehyde and ammonia in air is exceeded in Zavodski District.[16] Other major contaminants are Chromium-VI and nitrogen dioxide.[16] Zavodski, Partyzanski and Leninski districts, which are situated in the southeastern part of Minsk, are the most polluted areas in the city.[18]
Demographics

Apartment buildings in Minsk.
Population growth
|
|
|
|
* Census
Ethnic groups
During its first centuries, Minsk was a city with a predominantly Early East Slavic population (the forefathers of modern-day Belarusians). After the 1569 Polish–Lithuanian union, the city became a destination for migrating Poles (who worked as administrators, clergy, teachers and soldiers) and Jews (Ashkenazim, who worked in the retail trade and as craftsmen, as other opportunities were prohibited by discrimination laws). During the last centuries of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, many Minsk residents became polonised, adopting the language of the dominant Poles and assimilating to its culture.
After the second partition of Poland-Lithuania in 1793, Minsk and its larger region became part of the Russian Empire. The Russians dominated the city's culture as had the Poles in earlier centuries. By the end of the 19th century, residents in Minsk accepted increasing Russification.
At the time of the 1897 census under the Russian Empire, Jews were the largest ethnic group in Minsk, at 52% of the population, with 47,500 of the 91,000 residents.[19] Other substantial ethnic groups were Russians (25.5%), Poles (11.4%) and Belarusians (9%). The latter figure may be not accurate as some local Belarusians were likely counted as Russians. A small traditional community of Lipka Tatars had been living in Minsk for centuries.
Between the 1880s and 1930s many Jews, as well as peasants from other backgrounds, emigrated from the city to the United States as part of a Belarusian diaspora.

Jewish Holocaust memorial

Former Jewish hospital in the Minsk Ghetto

Zaslayavska memorial to Jews murdered in Minsk
The high mortality of the First World War and the Second World War affected the demographics of the city, particularly the destruction of Jews under the Nazi occupation of the Second World War. Working through local populations, Germans instituted deportation of Jewish citizens to concentration camps, murdering most of them there. The Jewish community of Minsk suffered catastrophic losses in the Holocaust. From more than half the population of the city, the percentage of Jews dropped to less than 10% more than ten years after the war. After its limited population peaked in the 1970s, continuing anti-Semitism under the Soviet Union and increasing nationalism in Belarus caused most Jews to emigrate to Israel and western countries in the 1980s; by 1999, less than 1% of the population of Minsk was Jewish.
In the first three decades of the post-war years, the most numerous new residents in Minsk were rural migrants from other parts of Belarus; the proportion of ethnic Belarusians increased markedly. Numerous skilled Russians and other migrants from other parts of the Soviet Union migrated for jobs in the growing manufacturing sector.[20] In 1959 Belarusians made up 63.3% of the city's residents. Other ethnic groups included Russians (22.8%), Jews (7.8%), Ukrainians (3.6%), Poles (1.1%) and Tatars (0.4%). Continued migration from rural Belarus in the 1960s and 1970s changed the ethnic composition further. By 1979 Belarusians made up 68.4% of the city's residents. Other ethnic groups included Russians (22.2%), Jews (3.4%), Ukrainians (3.4%), Poles (1.2%) and Tatars (0.2%).[20]
According to the 1989 census, 82% percent of Minsk residents have been born in Belarus. Of those, 43% have been born in Minsk and 39% – in other parts of Belarus. 6.2% of Minsk residents came from regions of western Belarus (Grodno and Brest Regions) and 13% – from eastern Belarus (Mogilev, Vitebsk and Gomel Regions). 21.4% of residents came from central Belarus (Minsk Region).
According to the 1999 census, Belarusians make up 79.3% of the city's residents. Other ethnic groups include Russians (15.7%), Ukrainians (2.4%), Poles (1.1%) and Jews (0.6%). The Russian and Ukrainian populations of Minsk peaked in the late 1980s (at 325,000 and 55,000 respectively). After the break-up of the Soviet Union and increased nationalism in Belarus creating hostility to ethnic Russians and Ukrainians, many of them chose to move to their respective mother countries, although some families had been in Minsk for generations. Another factor in the shifting demographics of the city was the changing self-identification of Minsk residents of mixed ancestry in independent Belarus they identify as Belarusians.
The Jewish population of Minsk peaked in the early 1970s at 50,000 according to official figures; independent estimates put the figure at between 100,000 and 120,000. Beginning in the 1980s, there has been mass-scale emigration to Israel, the US, and Germany. Today only about 10,000 Jews live in Minsk. The traditional minorities of Poles and Tatars have remained at much the same size (17,000 and 3,000 respectively). Rural Poles have migrated from the western part of Belarus to Minsk, and many Tatars have moved to Minsk from Tatarstan.
Some more recent ethnic minority communities have developed as a result of immigration. The most prominent are immigrants from the Caucasus countries – Armenians, Azerbaijanis and Georgians each numbering about 2,000 to 5,000. They began migrating to Minsk in the 1970s, and more immigrants have joined them since. Many work in the retail trade in open-air markets. A small but prominent Arab community has developed in Minsk, primarily represented by recent economic immigrants from Syria, Lebanon, Egypt, Algeria, etc. (In many cases, they are graduates of Minsk universities who decide to settle in Belarus and bring over their families). A small community of Romani, numbering about 2,000, are settled in suburbs of north-western and southern Minsk.
Languages
Throughout its history Minsk has been a city of many languages. Initially most of its residents spoke Ruthenian (which later developed into modern Belarusian). However, after 1569 the official language was Polish.[21] In the 19th-century Russian became the official language and by the end of that century it had become the language of administration, schools and newspapers. The Belarusian national revival increased interest in the Belarusian language – its use has grown since the 1890s, especially among the intelligentsia. In the 1920s and early 1930s Belarusian was the major language of Minsk, including use for administration and education (both secondary and tertiary). However, since the late 1930s Russian again began gaining dominance.[citation needed]
A short period of Belarusian national revival in the early 1990s saw a rise in the numbers of Belarusian speakers. However, in 1994 the newly elected president Alexander Lukashenko slowly reversed this trend. Most residents of Minsk now use Russian exclusively in their everyday lives at home and at work, although Belarusian is understood as well. Substantial numbers of recent migrants from the rural areas use Trasyanka (a Russo-Belarusian mixed language) in their everyday lives.[citation needed]
The most commonly used and understood foreign language in Minsk, especially among the younger generation, is English.[22]

Chinese signage, Minsk railway station (2018)
Religion
There are no reliable statistics on the religious affiliations of those living in Minsk, or among the population of Belarus generally. The majority of Christians belong to the Belarusian Orthodox Church, which is the exarchate of the Russian Orthodox Church in Belarus. There is a significant minority of Roman Catholics.
As of 2006, there are approximately 30 religious communities of various denominations in Minsk.[23][24]
Crime
Minsk has the highest crime rate in Belarus – 193.5 crimes per 10,000 citizens.[25][26] 20–25% of all serious crimes in Belarus, 55% of bribes and 67% of mobile phone thefts are committed in Minsk.[25][27] However, attorney general Grigory Vasilevich stated that homicide rate in Minsk in 2008 was "relatively fine".[28]
Crime rate grew significantly in 2009 and 2010:[25] for example, number of corruption crimes grew by 36% in 2009 alone.[29] Crime detection level varies from 13% in burglary[30] to 92% in homicide[31] with an average 40.1%.[32] Many dwellers are concerned for their safety at night and the strongest concern was expressed by residents of Chizhovka and Shabany microdistricts (both in Zavodski District).[31]
The SIZO-1 detention center, IK-1 general prison, and the KGB special jail called "Amerikanka" are all located in Minsk. Alexander Lukashenko's rivals in the 2010 presidential election were imprisoned in the KGB jail[33] along with other prominent politicians and civil activists. Ales Michalevic, who was kept in this jail, accused the KGB of using torture.[34][35]
Economy
Minsk is the economic capital of Belarus. It has developed industrial and services sectors which serve the needs not only of the city, but of the entire nation. Minsk's contributions form nearly 46% of Belarusian budget.[36] According to 2010 results, Minsk paid 15 trillion BYR to state budget while the whole income from all other regions was 19.9 trillion BYR.[37] In the period January 2013 to October 2013, 70.6% of taxes in the budget of Minsk were paid by non-state enterprises, 26.3% by state enterprises, and 1.8% by individual entrepreneurs. Among the top 10 taxpayers were five oil and gas companies (including two Gazprom's and one Lukoil's subsidiaries), two mobile network operators (MTS and Velcom), two companies producing alcoholic beverages (Minsk-Kristall and Minsk grape wines factory) and one producer of tobacco goods.[38]
In 2012, Gross Regional Product of Minsk was formed mainly by industry (26.4%), wholesale (19.9%), transportation and communications (12.3%), retail (8.6%) and construction (5.8%). GRP of Minsk measured in rubles was nearly 120×1012 (trillions or millions of millions; BYR 120 trillion ≈ USD 12.76 billion), or 23.7% of Gross domestic product of Belarus.[39]
Industry

View toward power plant from Turist Hotel
Minsk is the major industrial centre of Belarus. According to 2012 statistics, Minsk-based companies produced 21.5% of electricity, 76% of trucks, 15.9% of footwear, 89.3% of television sets, 99.3% of washing machines, 30% of chocolate, 27.7% of distilled alcoholic beverages and 19.7% of tobacco goods in Belarus.[40]
Today the city has over 250 factories and plants. Its industrial development started in the 1860s and was facilitated by the railways built in the 1870s. However, much of the industrial infrastructure was destroyed during World War I and especially during World War II. After the last war the development of the city was linked to the development of industry, especially of R&D-intensive sectors (heavy emphasis of R&D intensive industries in urban development in the USSR is known in Western geography as 'Minsk phenomenon').[citation needed] Minsk was turned into a major production site for trucks, tractors, gears, optical equipment, refrigerators, television sets and radios, bicycles, motorcycles, watches, and metal-processing equipment. Outside machine-building and electronics, Minsk also had textiles, construction materials, food processing, and printing industries. During the Soviet period, development of the industries was linked to suppliers and markets within the USSR, and the break-up of the union in 1991 led to a serious economic meltdown in 1991–1994.[citation needed]
However, since the adoption of the neo-Keynesean policies under Alexander Lukashenko's government in 1995, much of the gross industrial production was regained.[citation needed] Unlike many other cities in the CIS and Eastern Europe Minsk was not heavily de-industrialised in the 1990s. About 40% of the work force is still employed in the manufacturing sector. Over 70% of produced goods are exported from Belarus, especially to Russia and other members of the Commonwealth of Independent States.[citation needed] However, the recent industrial revival did not lead to updating technologies and equipment (as FDI was discouraged), therefore much of the local industry is not highly competitive by international standards.[citation needed]
Major industrial employers include:
Minsk Tractor Plant – specialised in manufacturing tractors. Established in 1946 in eastern Minsk, is among major manufacturers of wheeled tractors in the CIS. Employs about 30,000 staff.
Minsk Automobile Plant – specialising in producing trucks, buses and mini-vans. Established in 1944 in south-eastern Minsk, is among major vehicle manufacturers in the CIS.
Minsk Refrigerator Plant (also known as Atlant) – specialised in manufacturing household goods, such as refrigerators, freezers, and recently also of washing machines. Established in 1959 in north-west of the city.- Horizont – specialised in producing TV-sets, audio and video electronics. Established in 1950 in north-central Minsk.
Unemployment
In 2011 official statistics quote unemployment in Minsk at 0.3%.[41] During 2009 census 5.6% of Minsk residents of employable age called themselves unemployed.[41]
The government discourages official unemployment registration with tiny unemployment benefits (70 000 BYR ≈ $7 per month) and obligatory public works.
Government and administrative divisions

House of Representatives of Belarus

Victory Square
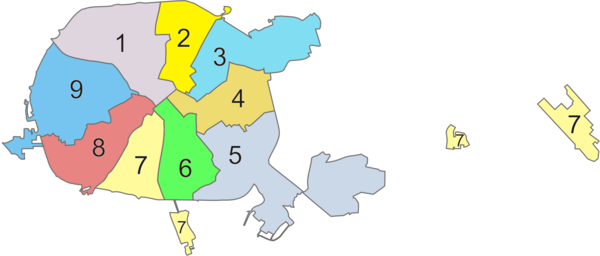
Currently Minsk is subdivided into 9 raions (districts):
Tsentralny (Belarusian: Цэнтральны, Russian: Центральный), or "Central District"
Savetski (Belarusian: Савецкі, Russian: Советский, Sovetsky), or "Soviet District"
Pershamayski (Belarusian: Першамайскі, Russian: Первомайский, Pervomaysky), named after 1 May
Partyzanski (Belarusian: Партызанскі, Russian: Партизанский, Partizansky), named after the Soviet partisans
Zavodski (Belarusian: Заводскі, Russian: Заводской, Zavodskoy), or "Factory district" (initially it included major plants, Minsk Tractor Works (MTZ) and Minsk Automobile Plant (MAZ), later the Partyzanski District with MTZ was split off it)
Leninski (Belarusian: Ленінскі, Russian: Ленинский, Leninsky), named after Lenin
Kastrychnitski (Belarusian: Кастрычніцкі, Russian: Октябрьский, Oktyabrsky), named after the October Revolution
Maskouski (Belarusian: Маскоўскі, Russian: Московский, Moskovsky), named after Moscow
Frunzenski (Belarusian: Фрунзенскі, Russian: Фрунзенский, Frunzensky), named after Mikhail Frunze
In addition, a number of residential neighbourhoods are recognised in Minsk, called microdistricts, with no separate administration.
Culture
Minsk is the major cultural centre of Belarus. Its first theatres and libraries were established in the middle of the 19th century. Now it has 11 theatres and 16 museums. There are 20 cinemas and 139 libraries.
Churches
- The Orthodox Cathedral of the Holy Spirit is actually the former church of the Bernardine convent. It was built in the simplified Baroque style in 1642–87 and went through renovations in 1741–46 and 1869.
- The Cathedral of Saint Mary was built by the Jesuits as their principal church in 1700–10, restored in 1951 and 1997; it overlooks the recently restored 18th-century city hall, located on the other side of the Liberty Square;
- Two other historic churches are the cathedral of Saint Joseph, formerly affiliated with the Bernardine monastery, built in 1644–52 and repaired in 1983, and the fortified church of Sts. Peter and Paul, originally built in the 1620s and recently restored, complete with its flanking twin towers.
- The impressive Neo-Romanesque Roman Catholic Red Church (Cathedral of Sts. Simeon and Helene) was built in 1906–10 immediately after religious freedoms were proclaimed in Imperial Russia and the tsar allowed dissidents to build their churches;
- The largest church built in the Russian imperial period of the town's history is dedicated to St. Mary Magdalene;
- Many Orthodox churches were built after the dissolution of the USSR in a variety of styles, although most remain true to the Neo-Russian idiom. A good example is St. Elisabeth's Convent, founded in 1999.
Cathedral of the Holy Spirit (Russian Orthodox).

Cathedral of Saint Virgin Mary (Roman Catholic).

Church of St.Joseph (formerly Uniate, currently used as an archive).

Church of Sts. Peter and Paul (Russian Orthodox).

The Red Church (Roman Catholic).

Church of St. Mary Magdalene (Russian Orthodox).

Church of Exaltation of the Holy Cross (Roman Catholic).

Church of Holy Trinity (Saint Rochus) (Roman Catholic).

Church of All Saints (Russian Orthodox).

Church of St.Yevfrosinya of Polotsk (Russian Orthodox).

Church of St. Elizabeth Convent (Russian Orthodox)
Cemeteries
Kalvaryja (Calvary Cemetery) is the oldest surviving cemetery in the city. Many famous people of Belarus are buried here. The cemetery was closed to new burials in the 1960s.- Military Cemetery
- Eastern Cemetery
- Čyžoŭskija Cemetery
- Northern Cemetery
Theatres
Major theatres are:
National Academic Grand Opera and Ballet Theatre of the Republic of Belarus
National Academic Grand Opera and Ballet Theatre of the Republic of Belarus
- Belarusian State Musical Theatre (performances in Russian)
Maxim Gorky National Drama Theatre (performances in Russian)
Yanka Kupala National Drama Theatre (performances in Belarusian)
Museums

The city hall (rebuilt in 2003) overlooks the Cathedral of Saint Virgin Mary.

Great Patriotic War Museum.
Major museums include:
- Belarusian National Arts Museum
- Belarusian Great Patriotic War Museum
- Belarusian National History and Culture Museum
- Belarusian Nature and Environment Museum
- Maksim Bahdanovič Literary Museum
- Old Belarusian History Museum
- Yanka Kupala Literary Museum
Art galleries include:
- Ў gallery
Recreation areas
- Chelyuskinites Park
- Children's Railroad
- Gorky Park (Minsk)
- Yanka Kupala Park
Cinemas
List of cinemas in Minsk:
Silver Screen Cinemas
- In Galileo shopping center
- In ARENAcity shopping center
- In Dana Mall ( Uschod Metro stop ) - Velcom 3rd Floor
- Центральный (3D) (English: Central)
- 3D cinema in shopping center «Замок» / Zamok
- Аврора / Avrora (3D)
- Автокинотеатр / Avtokinoteatr
- Беларусь / Belarus
- Берестье / Bierascie (3D)
- Дворец Республики / Palac Respubliki (3D)
- Дом Кино / Dom kino
- Киев / Kiev (3D)
- Комсомолец / Kamsamoliec
- Мир / Mir (3D)
- Москва / Maskva
- Музей кино / Muzej kino
- Октябрь / Oktyabr'
- Пионер / Pianier
- Победа / Pieramoha
- Ракета / Raketa
- Салют / Saliut (3D)
Tourism
There are more than 400 travel agencies in Minsk, about a quarter of them provide agent activity, and most of them are tour operators.[42][43]
Sports
Football
- FC Dinamo Minsk
- FC Minsk
- FC Torpedo Minsk
Ice hockey
- HC Dinamo Minsk
- HC Yunost Minsk
Handball
- SKA Minsk
Basketball
- BC Tsmoki-Minsk
International sporting events
Minsk hosted the 2014 IIHF World Championship at the Botvinik Arena.
In January 2016, the 2016 European Speed Skating Championships were held in the Minsk Arena. Minsk Arena is the only indoor speed skating rink in Belarus.
On 21 October 2016, it was confirmed by the European Olympic Committee that Minsk will host the 2019 European Games.
The 2019 European Figure Skating Championships were held in the Minsk Arena from the 21st to the 27th of January.
Transport
Local transport
Minsk has an extensive public transport system.[44] Passengers are served by 8 tramway lines, over 70 trolleybus lines, 2 subway lines and over 100 bus lines. Trams were the first public transport used in Minsk (since 1892 – the horse-tram, and since 1929 – the electric tram). Public buses have been used in Minsk since 1924, and trolleybuses since 1952.
All public transport is operated by Minsktrans, a government-owned and -funded transport not-for-profit company. As of January 2008, Minsktrans used 1,420 buses, 1,010 trolleybuses and 153 tramway cars in Minsk.
The Minsk city government in 2003 decreed that local transport provision should be set at a minimum level of 1 vehicle (bus, trolleybus or tram) per 1,500 residents. Currently the number of vehicles in use by Minsktrans is 2.2 times higher than the minimum level.[citation needed]
Public transport fares are controlled by city's executive committee (city council). Single trip ticket for bus, trolleybus or tramway costs 0.6 BYN (≈ USD 0.3),[45] 0.65 BYN for metro and 0.75 BYN for express buses.[45] Monthly ticket for one kind of transport costs 27 BYN and 49 BYN for all four.[45] Commercial marshrutka's prices varies from 1.5 to 2 BYN.
Rapid transit

Partyzanskaja station in the Minsk Metro.
Minsk is the only city in Belarus with an underground metro system. Construction of the metro began in 1977, soon after the city reached over a million people, and the first line with 8 stations was opened in 1984. Since then it has expanded into two lines: Maskoŭskaja and Aŭtazavodskaja, which are 18.1 and 17.3 km (11.2 and 10.7 mi) long with 14 and 14 stations, respectively. On 7 November 2012, three new stations on the Moskovskaya Line were opened; work continues on a 1.8 km (1.1 mi) extension, with one more station slated to open in 2014.
There are plans for a network with three lines totalling (based on present expansion plans) 58.3 km (36.2 mi) of track with 45 stations and three train depots. For this to happen the third line should cut the city on a north–south axis crossing the existing two and thus forming a typical Soviet triangle layout; construction of the third line is expected to begin in 2011 and for the first stage to be delivered in the late 2010s. Some layout plans speculate on a possible fourth line running from Vyasnyanka to Serabranka micro-rayons.
As of 2013[update] Minsk metro had 28 stations and 35.5 kilometres (22 miles) of tracks. Trains use 243 standard Russian metro-cars. On a typical day Minsk metro is used by 800,000 passengers. In 2007 ridership of Minsk metro was 262.1 million passengers,[46] in 2017 ridership of Minsk metro was 284,1 million passengers,[47]
making it the 5th busiest metro network in the former USSR (behind Moscow, St. Petersburg, Kiev and Kharkiv). During peak hours trains run each 2–2.5 minutes. The metro network employs 3,200 staff.
Currently most of the urban transport is being actively renovated and upgraded to modern standards. For instance, all metro stations built since 2001 have passenger lifts from platform to street level, thus enabling the use of the newer stations by disabled passengers.
Railway and intercity bus

Minsk Central Bus Station
Minsk is the largest transport hub in Belarus. Minsk is located at the junction of the Warsaw-Moscow railway (built in 1871) running from the southwest to the northeast of the city and the Liepaja-Romny railway (built in 1873) running from the northwest to the south. The first railway connects Russia with Poland and Germany; the second connects Ukraine with Lithuania and Latvia. They cross at the Minsk-Pasažyrski railway station, the main railway station of Minsk. The station was built in 1873 as Vilenski vakzal. The initial wooden building was demolished in 1890 and rebuilt in stone. During World War II the Minsk railway station was completely destroyed. It was rebuilt in 1945 and 1946 and served until 1991. The new building of the Minsk-Pasažyrski railway station was built during 1991–2002. Its construction was delayed due to financial difficulties; now, however, Minsk boasts one of the most modern and up-to-date railway stations in the CIS. There are plans to move all suburban rail traffic from Minsk-Pasažyrski to the smaller stations, Minsk-
Uschodni (East), Minsk-Paŭdniovy (South) and Minsk-Paŭnočny (North), by 2020.
There are three intercity bus stations that link Minsk with the suburbs and other cities in Belarus and the neighbouring countries. Frequent schedules of bus routes connect Minsk to Moscow, Smolensk, Vilnius, Riga, Kiev and Warsaw.
Airports
Minsk National Airport is located 42 km (26 mi) to the east of the city. It opened in 1982 and the current railway station opened in 1987. It is an international airport with flights to Europe and the Middle East.
Minsk-1 opened in 1933 a few kilometres to the south of the historical centre. In 1955 it became an international airport and by 1970 served over 1 million passengers a year.
From 1982 it mainly served domestic routes in Belarus and short-haul routes to Moscow, Kiev and Kaliningrad. Minsk-1 was expected to be closed in 2008 because of the noise pollution in the surrounding residential areas, but in the mid-2010 it is still functioning. The land of the airport is planned to be redeveloped for residential and commercial real estate, currently branded as Minsk-City.
Minsk Borovaya Airfield (UMMB) is situated in a suburb north-east of the city, next to Zaliony Luh Forest Park, housing Aero Club Minsk and Minsk Aviation Museum.[48]
Education
It has about 451 kindergartens, 241 schools, 22 further education colleges,[49] and 29 higher education institutions,[50] including 12 major national universities.[citation needed]
Major higher educational institutions
Academy of Public Administration under the aegis of the President of the Republic of Belarus. The Academy was established in 1991 and it acquired the status of a presidential institution in 1995. In structure of Academy 3 institutes: Institute of Administrative Personnel has 3 departments, Institute of Civil Service has also 3 departments and Research Institute of the Theory and Practice of Public Administration.
Belarusian State University. Major Belarusian universal university, founded in 1921. In 2006 had 15 major departments (Applied Mathematics and Informatics; Biology; Chemistry; Geography; Economics; International Relations; Journalism; History; Humanitarian Sciences; Law; Mechanics and Mathematics; Philology; Philosophy and Social Sciences; Physics; Radiophysics and Electronics). It also included 5 R&D institutes, 24 Research Centres, 114 R&D laboratories. The University employs over 2,400 lecturers and 1,000 research fellows; 1,900 of these hold PhD or Dr. Sc. degrees. There are 16,000 undergraduate students at the university, as well as over 700 PhD students. In 2018 Olga Chupris was the first female Vice-Rector appointed to the institution (Academic Work and Educational Innovations).
Belarusian State University of Agricultural Technology. Specialised in agricultural technology and agricultural machinery.
Belarusian National Technical University. Specialised in technical disciplines.
Belarusian State Medical University. Specialised in Medicine and Dentistry. Since 1921 – Medicine Department of the Belarusian State University. In 1930 becomes separate as Belarusian Medical Institute. In 2000 upgraded to university level. Currently has 6 departments.
Belarusian State Economic University. Specialised in Finance and Economics. Founded in 1933 as Belarusian Institute for National Economy. Upgraded to university level in 1992.
Maxim Tank Belarusian State Pedagogical University. Specialised in teacher training for secondary schools.
Belarusian State University of Informatics and Radioelectronics. Specialised in IT and radioelectronic technologies. Established in 1964 as Minsk Institute for Radioelectronics.
Belarusian State University of Physical Training. Specialised in sports, coaches and PT teachers training.
Belarusian State Technological University. Specialised in chemical and pharmaceutical technology, in printing and forestry. Founded in 1930 as Forestry Institute in Homel. In 1941 evacuated to Sverdlovsk, now Yekaterinburg. Returned to Gomel in 1944, but in 1946 relocated to Minsk as Belarusian Institute of Technology. Upgraded to university level in 1993. Currently has 9 departments.
Minsk State Linguistic University. Specialised in foreign languages. Founded in 1948 as Minsk Institute for Foreign Languages. In 2006 had 8 departments. Major focus on English, French, German and Spanish.
Belarusian State University of Culture and Arts. Specializes in cultural studies, visual and Performing Arts. Founded in 1975 as Minsk Institute of Culture. Reorganized in 1993.
International Sakharov Environmental Institute. Specialised in environmental sciences. Established in 1992 with the support from the United Nations. Focus on study and research of radio-ecological consequences of the Chernobyl nuclear power station disaster in 1986, which heavily affected Belarus.
International Institute of Labour and Social Relations. Specializes in International Economic Relations, International Law, Marketing, Finance and Management. It is established by Federations of Trade Unions of Belarus.
Minsk Institute of Management. The largest private higher educational institution in Belarus. Established in 1991. Specializes in Economics, Management, Marketing, Finance, Psychology and Information technology.

Faculty of Biology, Belarusian State University.

University of Informatics and Radioelectronics

Pedagogical University.
Honors
A minor planet 3012 Minsk discovered by Soviet astronomer Nikolai Chernykh in 1979 is named after the city.[51]
Notable residents
Andrei Arlovski, grew up and lived in Minsk before moving to the US to fight in the Ultimate Fighting Championship
Victoria Azarenka, former World No. 1 tennis player and 2012 and 2013 Australian Open winner, born in Minsk moving to Arizona at 16
Yuri Bessmertny, kickboxer
Svetlana Boginskaya, gold medal winning gymnast at the 1988 and 1992 Olympics, birthplace
Isaac Boleslavsky, chess grandmaster
Masha Bruskina, World War II partisan
Olga Chupris, first female Vice Rector of the Belarusian State University.
Darya Domracheva, gold (4 times) and bronze medal winning biathlete at the 2010 and 2014 Winter Olympics
Dimitry Elyashkevich, producer and camera operator, birthplace
Avraham Even-Shoshan (1906–84), Israeli linguist and lexicographer
Sophie Fedorovitch, ballet, opera and theatre designer, birthplace
Boris Gelfand, chess Grandmaster
Max Geller (born 1971), Israeli Olympic wrestler
Ella German (born 1937), girlfriend of Lee Harvey Oswald
Moisei Ginzburg, constructivist architect
Marina Gordon, soprano, birthplace
Oleg Karavayev, wrestler and Olympic champion
Boris Khaykin, conductor
Maryna Linchuk, fashion model
Ivan Lubennikov, Russian painter, birthplace
Louis Burt Mayer, American film producer, one of the founders of Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer
Isaak Mazel, chess master
Max Mirnyi, tennis player
Bronislava Nijinska, ballerina and choreographer of the Ballets Russes, birthplace
Lee Harvey Oswald, assassin of US President John F Kennedy, resided in Minsk from January 1960 to June 1962.
Yulia Raskina, individual rhythmic gymnast, won the All-Around Silver at the 2000 Sydney Olympics
Alexander Rybak, winner of the Eurovision Song Contest 2009 for Norway, birthplace
Yuri Shulman, chess grandmaster
Vanda Skuratovich, Roman Catholic activist
Mark Slavin, Israeli Olympic Greco-Roman wrestler and victim of the Munich massacre at the 1972 Summer Olympics
Anna Smashnova (born 1976), Belarus-born Israeli tennis player
Rachel Wischnitzer, architect and art historian
Simcha Zorin, World War II partisan
International relations
Twin towns and sister cities
Minsk is twinned with:[52]
|
|
|
See also
- List of Squares in Minsk
References
^ ab "Численность населения на 1 января 2018 г. и среднегодовая численность населения за 2017 год по Республике Беларусь в разрезе областей, районов, городов и поселков городского типа" (in Russian). National Statistical Committee of the Republic of Belarus. 29 March 2018..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ "Minsk City Executive Committee". 18 January 2019. Official portal minsk.gov.by
^ "Eternal Daylight Saving Time (DST) in Belarus". timeanddate.com. 19 September 2011. Retrieved 30 October 2014.
^ https://hdi.globaldatalab.org/areadata/shdi/
^ "Въ лЂто 6563 [1055] – [6579 1071]. Іпатіївський літопис". Litopys.org.ua. Retrieved 5 May 2009.
^ "The Celebration of the 940th anniversary of Minsk will start with ringing of bells – Minsk City Executive Committee". Minsk.gov.by. Archived from the original on 15 June 2008. Retrieved 5 May 2009.
^ Robert I. Frost. After the Deluge: Poland-Lithuania and the Second Northern War, 1655–1660. Cambridge University Press. 2004. p. 48.
^ Инфоцентр «Минск»|History of Minsk
^ "History". Belarusian Tour operator. 29 October 2013. Archived from the original on 3 November 2013. Retrieved 29 October 2013.
^ Marples, David R. (1 November 2016). "The "Minsk Phenomenon:" demographic development in the Republic of Belarus". Nationalities Papers. 44 (6): 919–931. doi:10.1080/00905992.2016.1218451. ISSN 0090-5992.
^ "Минск-2030: где будут новые жилые центры города". Retrieved 11 November 2017.
^ "Третья ветка минского метро заработает только в 2020 году Читать дальше: https://sputnik.by/society/20180209/1033553977/tretya-vetka-minskogo-metro-zarabotaet-tolko-v-2020-godu.html". Retrieved 9 February 2018. External link in|title=(help)
^ "Минск-2030: где будут новые жилые центры города". Retrieved 11 November 2017.
^ "Weather and Climate- The Climate of Minsk" (in Russian). Weather and Climate (Погода и климат). Retrieved 28 November 2015.
^ "Солнечное сияние. Обобщения II часть: Таблица 2.1. Характеристики продолжительности и суточный ход (доли часа) солнечного сияния. Продолжение" (in Russian). Department of Hydrometeorology. Archived from the original on 26 April 2017. Retrieved 25 April 2017.
^ abcdef Не сосновый бор, но дышать можно смело (in Russian). naviny.by. 18 September 2009.
^ Минская ГАИ проводит акцию "Чистый воздух" (in Russian). naviny.by. 9 June 2007.
^ "Самый загрязненный воздух в Минске — на улице Тимирязева" [The most polluted air in Minsk is on Timiryazev Street] (in Russian). naviny.by. 3 June 2009.
^ Joshua D. Zimmerman, Poles, Jews and the Politics of Nationality, Univ of Wisconsin Press, 2004,
ISBN 0-299-19464-7, Google Print, p.16
^ ab Zimmerman (2004), Poles, Jews, and Politics
^ Między Wschodem i Zachodem: international conference, Lublin, 18–21 June 1991
^ Östlund, Anders (13 July 2013). "LANGUAGES". Archived from the original on 3 November 2013. Retrieved 29 October 2013.
^ local-life.com: minsk
^ gov.by
^ abc Лукашенко недоволен минскими властями (in Russian). TUT.BY. 29 June 2010.
^ "Уровень преступности в Минской области – один из самых высоких в стране" (in Russian). TUT.BY. 25 January 2011.
^ Кражи составляют в Минске около 70% преступлений (in Russian). TUT.BY. 18 April 2011.
^ Генпрокуратура анализирует состояние с преступностью в Беларуси по коэффициенту преступности (in Russian). interfax.by. 2 October 2008. Archived from the original on 26 August 2011.
^ "В Минске увеличивается число выявленных коррупционных преступлений – Генпрокуратура" (in Russian). interfax.by. 10 March 2010. Archived from the original on 26 August 2011.
^ Я из ЖЭСа. Разрешите вас обокрасть! (in Russian). interfax.by. 2 January 2009.
^ ab Рейтинг всех служб и подразделений ГУВД Мингорисполкома вырос, National Law Portal of Belarus (10 February 2006). Archived 23 July 2011 at the Wayback Machine
^ "В Минске снижается число хищений сотовых телефонов – Генпрокуратура" (in Russian). interfax.by. 27 October 2009. Archived from the original on 2013-11-02.
^ Lukashenka`s presidential rivals held in KGB jail Archived 18 May 2013 at the Wayback Machine, Belarus News (21 December 2010)
^ Mikhalevich to complain to UN Committee Against Torture about his detention conditions in KGB jail Archived 18 May 2013 at the Wayback Machine, Belarus News (28 February 2011)
^ Belarus 'tortured protesters in jail', BBC News (1 March 2011)
^ "Четвертую часть поступлений в бюджет Минска обеспечили 5 плательщиков" [The fourth part of receipts in the budget of Minsk was provided by 5 payers]. afn.by (in Russian).
^ Минск – основной плательщик НДС (in Russian)
^ "73,7 % поступлений в консолидированный бюджет города Минска за 10 месяцев 2013 года обеспечено негосударственным сектором экономики. – Новости инспекции – Министерство по налогам и сборам Республики Беларусь". nalog.gov.by.
^ Социально-экономическое положение Республики Беларусь в январе-октябре 2013 г. (in Russian) Archived 3 December 2013 at the Wayback Machine
^ Shares of region and Minsk City in the national output of selected industrial products in 2012 Archived 10 December 2013 at the Wayback Machine
^ Ministry of Sports and Tourism of the Republic of Belarus. (2011). "Number of organizations engaged in tourist activities in 2010 in Belarus". Land of Ancestors. National Statistical Committee of the Republic of Belarus. Retrieved 9 October 2013.
^ Ministry of Sports and Tourism of the Republic of Belarus. (2011). "Number of organisations engaged in tourist activities in Belarus by region". Land of Ancestors. National Statistical Committee of the Republic of Belarus. Retrieved 9 October 2013.
^ "Public transport in Minsk". D-Minsk. 4 October 2012. Retrieved 4 October 2012.
^ abc Тарифы / Минсктранс (in Russian)
^ "CIS Metro Statistics". Mrl.ucsb.edu. 21 June 2010. Retrieved 4 July 2010.
^ "Метро сегодня". metropoliten.b. 2018.
^ https://www.world-airport-codes.com/belarus/borovaya-airfield-82793.html
^ "комитет по образованию Мингорисполкома" [Committee of Education (Minsk City Executive Committee)] (in Russian). Retrieved 23 July 2018.
^ "Управление высшего образования" [the management of higher education] (in Russian). Ministry of education of the Republic of Belarus. Retrieved 23 July 2018.
^ Dictionary of Minor Planet Names – p.248. Books.google.com. Retrieved 4 July 2010.
^ abcdefghijklmnopqrs "Twin towns of Minsk". Minsk City Executive Committee. Retrieved 21 July 2013.
^ "European networks and city partnerships". Nottingham City Council. 22 June 2012. Archived from the original on 25 June 2012.
^ "Partner Cities of Lyon and Greater Lyon". 2008 Mairie de Lyon. Archived from the original on 19 July 2009. Retrieved 17 July 2009.
^ "Mayor's International Council Sister Cities Program". Belo Horizonte, Minas Gerais. Archived from the original on 23 December 2007. Retrieved 18 August 2008.
^ "Miasta partnerskie – Urząd Miasta Łodzi [via WaybackMachine.com]". City of Łódź (in Polish). Archived from the original on 24 June 2013. Retrieved 21 July 2013.
^ "City Twinnings and Project Partnerships". Bonn.de. 23 June 2008. Archived from the original on 10 April 2013. Retrieved 13 August 2010.
^ "Regions: Dushanbe & Surroundings". Official Website of the Tourism Authority of Tajikistan. Committee of Youth Affairs, Sports and Tourism. Archived from the original on 22 November 2012. Retrieved 10 May 2013.
^ "Oraşe înfrăţite (Twin cities of Minsk) [via WaybackMachine.com]" (in Romanian). Primăria Municipiului Chişinău. Archived from the original on 3 September 2012. Retrieved 21 July 2013.
^ "Kardeş Kentleri Listesi ve 5 Mayıs Avrupa Günü Kutlaması [via WaybackMachine.com]" (in Turkish). Ankara Büyükşehir Belediyesi – Tüm Hakları Saklıdır. Archived from the original on 14 January 2009. Retrieved 21 July 2013.
^ "CÁC ĐỊA PHƯƠNG NƯỚC NGOÀI ĐÃ THIẾT LẬP QUAN HỆ HỮU NGHỊ HỢP TÁC VỚI TPHCM". www.mofahcm.gov.vn. 9 October 2010. Retrieved 8 January 2011.
Bibliography
Thomas M. Bohn: Minsk – Musterstadt des Sozialismus. Stadtplanung und Urbanisierung in der Sowjetunion nach 1945. Böhlau, Köln 2008, ISBN 978-3-412-20071-8
Бон, Т.М. «Минский феномен». Городское планирование и урбанизация в Советском Союзе после Второй мировой войны / Томас М. Бон ; [пер. Е. Слепович]. — Москва : РОССПЭН, 2013. — 416 с.
Бон, Т.М. «Мінскі феномен». Гарадское планаванне і ўрбанізацыя ў Савецкім Саюзе пасля 1945 г. / Томас М. Бон ; пер. з ням. мовы М. Рытаровіч ; навук. рэд. Г. Сагановіч. — Мінск : Зміцер Колас, 2016. — 436 с.
Further reading
.mw-parser-output .refbegin{font-size:90%;margin-bottom:0.5em}.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>ul{list-style-type:none;margin-left:0}.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>ul>li,.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>dl>dd{margin-left:0;padding-left:3.2em;text-indent:-3.2em;list-style:none}.mw-parser-output .refbegin-100{font-size:100%}
Nechepurenko, Ivan (October 5, 2017). "How Europes Last Dictatorship Became a Tech Hub". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Minsk. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Minsk. |
34mag city guide a city guide for Minsk
Minsk city on the official website of Belarus- Why Minsk Is Not Like Other Capitals.
- Lost In Translation In Minsk – The "Real Belarus" Travel Tips.
- The Minsk Herald online magazine in English
Minsk, Belarus at JewishGen


















Comments
Post a Comment