Exponential distribution
Probability density function  | |
Cumulative distribution function  | |
| Parameters | λ > 0 rate, or inverse scale |
|---|---|
| Support | x ∈ [0, ∞) |
| λ e−λx | |
| CDF | 1 − e−λx |
| Quantile | −ln(1 − F) / λ |
| Mean | λ−1 (= β) |
| Median | λ−1ln(2) |
| Mode | 0 |
| Variance | λ−2 (= β2) |
| Skewness | 2 |
| Ex. kurtosis | 6 |
| Entropy | 1 − ln(λ) |
| MGF | λλ−t, for t<λ{displaystyle {frac {lambda }{lambda -t}},{text{ for }}t<lambda } |
| CF | λλ−it{displaystyle {frac {lambda }{lambda -it}}} |
| Fisher information | λ−2{displaystyle lambda ^{-2}} |
In probability theory and statistics, the exponential distribution (also known as the negative exponential distribution) is the probability distribution that describes the time between events in a Poisson point process, i.e., a process in which events occur continuously and independently at a constant average rate. It is a particular case of the gamma distribution. It is the continuous analogue of the geometric distribution, and it has the key property of being memoryless. In addition to being used for the analysis of Poisson point processes it is found in various other contexts.
The exponential distribution is not the same as the class of exponential families of distributions, which is a large class of probability distributions that includes the exponential distribution as one of its members, but also includes the normal distribution, binomial distribution, gamma distribution, Poisson, and many others.
Contents
1 Characterization
1.1 Probability density function
1.2 Cumulative distribution function
1.3 Alternative parameterization
2 Properties
2.1 Mean, variance, moments and median
2.2 Memorylessness
2.3 Quantiles
2.4 Kullback–Leibler divergence
2.5 Maximum entropy distribution
2.6 Distribution of the minimum of exponential random variables
2.7 Joint moments of i.i.d. exponential order statistics
2.8 Sum of two independent exponential random variables
3 Parameter estimation
3.1 Maximum likelihood
3.2 Approximate minimizer of expected squared error
3.3 Fisher Information
3.4 Confidence intervals
3.5 Bayesian inference
4 Generating exponential variates
5 Related distributions
6 Applications of exponential distribution
6.1 Occurrence of events
6.2 Prediction
7 See also
8 References
9 External links
Characterization
Probability density function
The probability density function (pdf) of an exponential distribution is
- f(x;λ)={λe−λxx≥0,0x<0.{displaystyle f(x;lambda )={begin{cases}lambda e^{-lambda x}&xgeq 0,\0&x<0.end{cases}}}
Alternatively, this can be defined using the right-continuous Heaviside step function, H(x) where H(0) = 1:
- f(x;λ)=λe−λxH(x){displaystyle f(x;lambda )=lambda e^{-lambda x}H(x)}
Here λ > 0 is the parameter of the distribution, often called the rate parameter. The distribution is supported on the interval [0, ∞). If a random variable X has this distribution, we write X ~ Exp(λ).
The exponential distribution exhibits infinite divisibility.
Cumulative distribution function
The cumulative distribution function is given by
- F(x;λ)={1−e−λxx≥0,0x<0.{displaystyle F(x;lambda )={begin{cases}1-e^{-lambda x}&xgeq 0,\0&x<0.end{cases}}}
Alternatively, this can be defined using the Heaviside step function, H(x).
- F(x;λ)=(1−e−λx)H(x){displaystyle F(x;lambda )=mathrm {(} 1-e^{-lambda x})H(x)}
Alternative parameterization
A commonly used alternative parametrization is to define the probability density function (pdf) of an exponential distribution as
- f(x;β)={1βe−xβx≥0,0x<0.{displaystyle f(x;beta )={begin{cases}{frac {1}{beta }}e^{-{frac {x}{beta }}}&xgeq 0,\0&x<0.end{cases}}}
where β > 0 is mean, standard deviation, and scale parameter of the distribution, the reciprocal of the rate parameter, λ, defined above. In this specification, β is a survival parameter in the sense that if a random variable X is the duration of time that a given biological or mechanical system manages to survive and X ~ Exp(β) then E[X] = β. That is to say, the expected duration of survival of the system is β units of time. The parametrization involving the "rate" parameter arises in the context of events arriving at a rate λ, when the time between events (which might be modeled using an exponential distribution) has a mean of β = λ−1.
The alternative specification is sometimes more convenient than the one given above, and some authors will use it as a standard definition. This alternative specification is not used here. Unfortunately this gives rise to a notational ambiguity. In general, the reader must check which of these two specifications is being used if an author writes "X ~ Exp(λ)", since either the notation in the previous (using λ) or the notation in this section (here, using β to avoid confusion) could be intended. An example of this notational switch: reference[1] uses λ for β.
Properties
Mean, variance, moments and median
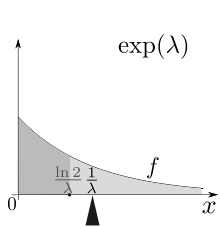
The mean is the probability mass centre, that is the first moment.
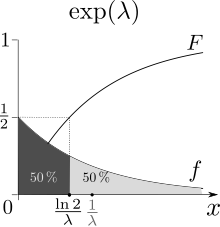
The median is the preimage F−1(1/2).
The mean or expected value of an exponentially distributed random variable X with rate parameter λ is given by
E[X]=1λ=β,{displaystyle operatorname {E} [X]={frac {1}{lambda }}=beta ,}see above.
In light of the examples given above, this makes sense: if you receive phone calls at an average rate of 2 per hour, then you can expect to wait half an hour for every call.
The variance of X is given by
- Var[X]=1λ2=β2,{displaystyle operatorname {Var} [X]={frac {1}{lambda ^{2}}}=beta ^{2},}
so the standard deviation is equal to the mean.
The moments of X, for n∈N{displaystyle nin mathbb {N} }
- E[Xn]=n!λn.{displaystyle operatorname {E} left[X^{n}right]={frac {n!}{lambda ^{n}}}.}
The central moments of X, for n∈N{displaystyle nin mathbb {N} }
- μn=!nλn=n!λn∑k=0n(−1)kk!.{displaystyle mu _{n}={frac {!n}{lambda ^{n}}}={frac {n!}{lambda ^{n}}}sum _{k=0}^{n}{frac {(-1)^{k}}{k!}}.}
where !n is the subfactorial of n
The median of X is given by
- m[X]=ln(2)λ<E[X],{displaystyle operatorname {m} [X]={frac {ln(2)}{lambda }}<operatorname {E} [X],}
where ln refers to the natural logarithm. Thus the absolute difference between the mean and median is
- |E[X]−m[X]|=1−ln(2)λ<1λ=standard deviation,{displaystyle |operatorname {E} [X]-operatorname {m} [X]|={frac {1-ln(2)}{lambda }}<{frac {1}{lambda }}={text{standard deviation}},}
in accordance with the median-mean inequality.
Memorylessness
An exponentially distributed random variable T obeys the relation
- Pr(T>s+t∣T>s)=Pr(T>t),∀s,t≥0.{displaystyle Pr left(T>s+tmid T>sright)=Pr(T>t),qquad forall s,tgeq 0.}
This can be seen by considering the complementary cumulative distribution function:
- Pr(T>s+t∣T>s)=Pr(T>s+t∩T>s)Pr(T>s)=Pr(T>s+t)Pr(T>s)=e−λ(s+t)e−λs=e−λt=Pr(T>t).{displaystyle {begin{aligned}Pr left(T>s+tmid T>sright)&={frac {Pr left(T>s+tcap T>sright)}{Pr left(T>sright)}}\[4pt]&={frac {Pr left(T>s+tright)}{Pr left(T>sright)}}\[4pt]&={frac {e^{-lambda (s+t)}}{e^{-lambda s}}}\[4pt]&=e^{-lambda t}\[4pt]&=Pr(T>t).end{aligned}}}
When T is interpreted as the waiting time for an event to occur relative to some initial time, this relation implies that, if T is conditioned on a failure to observe the event over some initial period of time s, the distribution of the remaining waiting time is the same as the original unconditional distribution. For example, if an event has not occurred after 30 seconds, the conditional probability that occurrence will take at least 10 more seconds is equal to the unconditional probability of observing the event more than 10 seconds after the initial time.
The exponential distribution and the geometric distribution are the only memoryless probability distributions.
The exponential distribution is consequently also necessarily the only continuous probability distribution that has a constant failure rate.
Quantiles

Tukey criteria for anomalies.[citation needed]
The quantile function (inverse cumulative distribution function) for Exp(λ) is
- F−1(p;λ)=−ln(1−p)λ,0≤p<1{displaystyle F^{-1}(p;lambda )={frac {-ln(1-p)}{lambda }},qquad 0leq p<1}
The quartiles are therefore:
- first quartile: ln(4/3)/λ
median: ln(2)/λ
- third quartile: ln(4)/λ
And as a consequence the interquartile range is ln(3)/λ.
Kullback–Leibler divergence
The directed Kullback–Leibler divergence of eλ{displaystyle e^{lambda }}

- Δ(λ0||λ)=Eλ0(logpλ0(x)pλ(x))=Eλ0(logλ0e−λ0xλe−λx)=log(λ0)−log(λ)−(λ0−λ)Eλ0(x)=log(λ0)−log(λ)+λλ0−1.{displaystyle {begin{aligned}Delta (lambda _{0}||lambda )&=mathbb {E} _{lambda _{0}}left(log {frac {p_{lambda _{0}}(x)}{p_{lambda }(x)}}right)\&=mathbb {E} _{lambda _{0}}left(log {frac {lambda _{0}e^{-lambda _{0}x}}{lambda e^{-lambda x}}}right)\&=log(lambda _{0})-log(lambda )-(lambda _{0}-lambda )E_{lambda _{0}}(x)\&=log(lambda _{0})-log(lambda )+{frac {lambda }{lambda _{0}}}-1.end{aligned}}}
Maximum entropy distribution
Among all continuous probability distributions with support [0, ∞) and mean μ, the exponential distribution with λ = 1/μ has the largest differential entropy. In other words, it is the maximum entropy probability distribution for a random variate X which is greater than or equal to zero and for which E[X] is fixed.[2]
Distribution of the minimum of exponential random variables
Let X1, ..., Xn be independent exponentially distributed random variables with rate parameters λ1, ..., λn. Then
- min{X1,…,Xn}{displaystyle min left{X_{1},dotsc ,X_{n}right}}
is also exponentially distributed, with parameter
- λ=λ1+⋯+λn.{displaystyle lambda =lambda _{1}+dotsb +lambda _{n}.}
This can be seen by considering the complementary cumulative distribution function:
- Pr(min{X1,…,Xn}>x)=Pr(X1>x,…,Xn>x)=∏i=1nPr(Xi>x)=∏i=1nexp(−xλi)=exp(−x∑i=1nλi).{displaystyle {begin{aligned}Pr left(min{X_{1},dotsc ,X_{n}}>xright)&=Pr left(X_{1}>x,dotsc ,X_{n}>xright)\&=prod _{i=1}^{n}Pr(X_{i}>x)\&=prod _{i=1}^{n}exp(-xlambda _{i})=exp left(-xsum _{i=1}^{n}lambda _{i}right).end{aligned}}}
The index of the variable which achieves the minimum is distributed according to the law
- Pr(k∣Xk=min{X1,…,Xn})=λkλ1+⋯+λn.{displaystyle Pr left(kmid X_{k}=min{X_{1},dotsc ,X_{n}}right)={frac {lambda _{k}}{lambda _{1}+dotsb +lambda _{n}}}.}
Note that
- max{X1,…,Xn}{displaystyle max{X_{1},dotsc ,X_{n}}}
is not exponentially distributed.[3]
Joint moments of i.i.d. exponential order statistics
Let X1,…,Xn{displaystyle X_{1},dotsc ,X_{n}}

Let X(1),…,X(n){displaystyle X_{(1)},dotsc ,X_{(n)}}
For i<j{displaystyle i<j}
![{displaystyle E[X_{(i)}X_{(j)}]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/5cd545ace06eeb590c70df7b9ca047360ab9c5c3)


- E[X(i)X(j)]=1(n−j+1)λE[X(i)]+E[X(i)2]=1(n−j+1)λ1(n−i+1)λ+2((n−i+1)λ)2.{displaystyle E[X_{(i)}X_{(j)}]={frac {1}{(n-j+1)lambda }}E[X_{(i)}]+E[X_{(i)}^{2}]={frac {1}{(n-j+1)lambda }}{frac {1}{(n-i+1)lambda }}+{frac {2}{((n-i+1)lambda )^{2}}}.}
This can be seen by invoking the law of total expectation and the memoryless property:
- E[X(i)X(j)]=∫0∞E[X(i)X(j)∣X(i)=x]fX(i)(x)dx=∫x=0∞xE[X(j)∣X(j)≥x]fX(i)(x)dx(since X(i)=x⟹X(j)≥x)=∫x=0∞x[1(n−j+1)λ+x]fX(i)(x)dx(by the memoryless property)=1(n−j+1)λE[X(i)]+E[X(i)2].{displaystyle {begin{aligned}operatorname {E} [X_{(i)}X_{(j)}]&=int _{0}^{infty }operatorname {E} [X_{(i)}X_{(j)}mid X_{(i)}=x]f_{X_{(i)}}(x),dx\&=int _{x=0}^{infty }xoperatorname {E} [X_{(j)}mid X_{(j)}geq x]f_{X_{(i)}}(x),dxqquad ({textrm {since}}~X_{(i)}=ximplies X_{(j)}geq x)\&=int _{x=0}^{infty }xleft[{frac {1}{(n-j+1)lambda }}+xright]f_{X_{(i)}}(x),dxqquad ({text{by the memoryless property}})\&={frac {1}{(n-j+1)lambda }}operatorname {E} [X_{(i)}]+operatorname {E} [X_{(i)}^{2}].end{aligned}}}
The first equation follows from the law of total expectation.
The second equation exploits the fact that once we condition on X(i)=x{displaystyle X_{(i)}=x}

The third equation relies on the memoryless property to replace E[X(j)∣X(j)≥x]{displaystyle operatorname {E} [X_{(j)}mid X_{(j)}geq x]}![{displaystyle operatorname {E} [X_{(j)}mid X_{(j)}geq x]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/77cf099e937427dc1d419a1cbcab748cb9cb6311)
![{displaystyle operatorname {E} [X_{(j)}]+x}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/e7751a455373c180c8f9c08d9e124271da118abf)
Sum of two independent exponential random variables
The sum of two independent variables corresponds to the convolution of probability distributions.
If X1{displaystyle X_{1}}




- fZ(z)=∫0zfX1(x1)fX2(z−x1)dx1=λ1λ2exp[−λ2z]∫0zexp[(λ2−λ1)x1]dx1=λ1λ2λ2−λ1(exp[−λ1z]−exp[−λ2z]){displaystyle {begin{aligned}f_{Z}(z)=&int _{0}^{z}f_{X_{1}}(x_{1})f_{X_{2}}(z-x_{1}),dx_{1}\=&lambda _{1}lambda _{2}exp[-lambda _{2}z]int _{0}^{z}exp[(lambda _{2}-lambda _{1})x_{1}],dx_{1}\=&{frac {lambda _{1}lambda _{2}}{lambda _{2}-lambda _{1}}}left(exp[-lambda _{1}z]-exp[-lambda _{2}z]right)end{aligned}}}
The mean and variance of Z=X1+X2{displaystyle Z=X_{1}+X_{2}}
- E[Z]=∫zdfZ(z)=λ1−1+λ2−1var(Z)=E[Z2]−E[Z]2=∫z2dfZ(z)−(λ1−1+λ2−1)2=λ1−2+λ2−2{displaystyle {begin{aligned}operatorname {E} [Z]=&int z,df_{Z}(z)\[4pt]=&lambda _{1}^{-1}+lambda _{2}^{-1}\[4pt]operatorname {var} (Z)=&operatorname {E} [Z^{2}]-operatorname {E} [Z]^{2}\[4pt]=&int z^{2},df_{Z}(z)-(lambda _{1}^{-1}+lambda _{2}^{-1})^{2}\[4pt]=&lambda _{1}^{-2}+lambda _{2}^{-2}end{aligned}}}
The cumulative density function of the sum of two independent exponential random variables then follows as,
- FZ(z)=Pr(Z≤z)=∫0zfZ(t)dt=1+λ1λ2−λ1exp[−λ2z]−λ2λ2−λ1exp[−λ1z]{displaystyle {begin{aligned}F_{Z}(z)=Pr(Zleq z)=&int _{0}^{z}f_{Z}(t),dt\[4pt]=&1+{frac {lambda _{1}}{lambda _{2}-lambda _{1}}}exp[-lambda _{2}z]-{frac {lambda _{2}}{lambda _{2}-lambda _{1}}}exp[-lambda _{1}z]end{aligned}}}
Parameter estimation
Below, suppose random variable X is exponentially distributed with rate parameter λ, and x1,…,xn{displaystyle x_{1},dotsc ,x_{n}}

Maximum likelihood
The likelihood function for λ, given an independent and identically distributed sample x = (x1, ..., xn) drawn from the variable, is:
- L(λ)=∏i=1nλexp(−λxi)=λnexp(−λ∑i=1nxi)=λnexp(−λnx¯),{displaystyle L(lambda )=prod _{i=1}^{n}lambda exp(-lambda x_{i})=lambda ^{n}exp left(-lambda sum _{i=1}^{n}x_{i}right)=lambda ^{n}exp left(-lambda n{overline {x}}right),}
where:
- x¯=1n∑i=1nxi{displaystyle {overline {x}}={1 over n}sum _{i=1}^{n}x_{i}}
is the sample mean.
The derivative of the likelihood function's logarithm is:
- ddλln(L(λ))=ddλ(nln(λ)−λnx¯)=nλ−nx¯ {>0,0<λ<1x¯,=0,λ=1x¯,<0,λ>1x¯.{displaystyle {frac {mathrm {d} }{mathrm {d} lambda }}ln(L(lambda ))={frac {mathrm {d} }{mathrm {d} lambda }}left(nln(lambda )-lambda n{overline {x}}right)={frac {n}{lambda }}-n{overline {x}} {begin{cases}>0,&0<lambda <{frac {1}{overline {x}}},\[8pt]=0,&lambda ={frac {1}{overline {x}}},\[8pt]<0,&lambda >{frac {1}{overline {x}}}.end{cases}}}
Consequently, the maximum likelihood estimate for the rate parameter is:
- λ^=1x¯=n∑ixi{displaystyle {widehat {lambda }}={frac {1}{overline {x}}}={frac {n}{sum _{i}x_{i}}}}
Although this is not an unbiased estimator of λ{displaystyle lambda }



Approximate minimizer of expected squared error
Assume you have at least three samples. If we seek a minimizer of expected mean squared error (see also: Bias–variance tradeoff) that is similar to the maximum likelihood estimate (i.e. a multiplicative correction to the likelihood estimate) we have:
- λ^=(n−2n)(1x¯)=n−2∑ixi{displaystyle {widehat {lambda }}=left({frac {n-2}{n}}right)left({frac {1}{bar {x}}}right)={frac {n-2}{sum _{i}x_{i}}}}
This is derived from the mean and variance of the Inverse-gamma distribution: Inv-Gamma(n,λ){textstyle {mbox{Inv-Gamma}}(n,lambda )}
Fisher Information
The Fisher information, denoted I(λ){displaystyle {mathcal {I}}(lambda )}

- I(λ)=E[(∂∂λlogf(x;λ))2|λ]=∫(∂∂λlogf(x;λ))2f(x;λ)dx{displaystyle {mathcal {I}}(lambda )=operatorname {E} left[left.left({frac {partial }{partial lambda }}log f(x;lambda )right)^{2}right|lambda right]=int left({frac {partial }{partial lambda }}log f(x;lambda )right)^{2}f(x;lambda ),dx}
Plugging in the distribution and solving gives:
- I(λ)=∫0∞(∂∂λlogλe−λx)2λe−λxdx=∫0∞(1λ−x)2λe−λxdx=λ−2.{displaystyle {mathcal {I}}(lambda )=int _{0}^{infty }left({frac {partial }{partial lambda }}log lambda e^{-lambda x}right)^{2}lambda e^{-lambda x},dx=int _{0}^{infty }left({frac {1}{lambda }}-xright)^{2}lambda e^{-lambda x},dx=lambda ^{-2}.}
This determines the amount of information each independent sample of an exponential distribution carries about the unknown rate parameter λ{displaystyle lambda }
Confidence intervals
The 100(1 − α)% confidence interval for the rate parameter of an exponential distribution is given by:[7]
- 2nλ^χα2,2n2<1λ<2nλ^χ1−α2,2n2{displaystyle {frac {2n}{{widehat {lambda }}chi _{{frac {alpha }{2}},2n}^{2}}}<{frac {1}{lambda }}<{frac {2n}{{widehat {lambda }}chi _{1-{frac {alpha }{2}},2n}^{2}}}}
which is also equal to:
- 2nx¯χα2,2n2<1λ<2nx¯χ1−α2,2n2{displaystyle {frac {2n{overline {x}}}{chi _{{frac {alpha }{2}},2n}^{2}}}<{frac {1}{lambda }}<{frac {2n{overline {x}}}{chi _{1-{frac {alpha }{2}},2n}^{2}}}}
where χ2
p,v is the 100(p) percentile of the chi squared distribution with v degrees of freedom, n is the number of observations of inter-arrival times in the sample, and x-bar is the sample average. A simple approximation to the exact interval endpoints can be derived using a normal approximation to the χ2
p,v distribution. This approximation gives the following values for a 95% confidence interval:
- λlower=λ^(1−1.96n){displaystyle lambda _{text{lower}}={widehat {lambda }}left(1-{frac {1.96}{sqrt {n}}}right)}
- λupper=λ^(1+1.96n){displaystyle lambda _{text{upper}}={widehat {lambda }}left(1+{frac {1.96}{sqrt {n}}}right)}
This approximation may be acceptable for samples containing at least 15 to 20 elements.[8]
Bayesian inference
The conjugate prior for the exponential distribution is the gamma distribution (of which the exponential distribution is a special case). The following parameterization of the gamma probability density function is useful:
- Gamma(λ;α,β)=βαΓ(α)λα−1exp(−λβ).{displaystyle operatorname {Gamma} (lambda ;alpha ,beta )={frac {beta ^{alpha }}{Gamma (alpha )}}lambda ^{alpha -1}exp(-lambda beta ).}
The posterior distribution p can then be expressed in terms of the likelihood function defined above and a gamma prior:
- p(λ)∝L(λ)×Gamma(λ;α,β)=λnexp(−λnx¯)×βαΓ(α)λα−1exp(−λβ)∝λ(α+n)−1exp(−λ(β+nx¯)).{displaystyle {begin{aligned}p(lambda )&propto L(lambda )times mathrm {Gamma} (lambda ;alpha ,beta )\&=lambda ^{n}exp left(-lambda n{overline {x}}right)times {frac {beta ^{alpha }}{Gamma (alpha )}}lambda ^{alpha -1}exp(-lambda beta )\&propto lambda ^{(alpha +n)-1}exp(-lambda left(beta +n{overline {x}}right)).end{aligned}}}
Now the posterior density p has been specified up to a missing normalizing constant. Since it has the form of a gamma pdf, this can easily be filled in, and one obtains:
- p(λ)=Gamma(λ;α+n,β+nx¯).{displaystyle p(lambda )=mathrm {Gamma} (lambda ;alpha +n,beta +n{overline {x}}).}
Here the hyperparameter α can be interpreted as the number of prior observations, and β as the sum of the prior observations.
The posterior mean here is:
- α+nβ+nx¯.{displaystyle {frac {alpha +n}{beta +n{overline {x}}}}.}
Generating exponential variates
A conceptually very simple method for generating exponential variates is based on inverse transform sampling: Given a random variate U drawn from the uniform distribution on the unit interval (0, 1), the variate
- T=F−1(U){displaystyle T=F^{-1}(U)}
has an exponential distribution, where F −1 is the quantile function, defined by
- F−1(p)=−ln(1−p)λ.{displaystyle F^{-1}(p)={frac {-ln(1-p)}{lambda }}.}
Moreover, if U is uniform on (0, 1), then so is 1 − U. This means one can generate exponential variates as follows:
- T=−ln(U)λ.{displaystyle T={frac {-ln(U)}{lambda }}.}
Other methods for generating exponential variates are discussed by Knuth[9] and Devroye.[10]
A fast method for generating a set of ready-ordered exponential variates without using a sorting routine is also available.[10]
Related distributions
This section includes a list of references, but its sources remain unclear because it has insufficient inline citations. (March 2011) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
- Exponential distribution is closed under scaling by a positive factor. If X ~ Exp(λ) then kX ~ Exp(λ/k).
- If X ~ Exp(1/2) then X ∼ χ2
2, i.e. X has a chi-squared distribution with 2 degrees of freedom. Hence:
- Exp(λ)=12λExp(12)∼12λχ22⇒∑i=1nExp(λ)∼12λχ2n2{displaystyle operatorname {Exp} left(lambda right)={frac {1}{2lambda }}operatorname {Exp} left({frac {1}{2}}right)sim {frac {1}{2lambda }}chi _{2}^{2}Rightarrow sum limits _{i=1}^{n}operatorname {Exp} (lambda )sim {frac {1}{2lambda }}chi _{2n}^{2}}
- If Xi ~ Exp(λi) then min{X1, ..., Xn} ~ Exp(λ1+ ... +λn).
- The Benktander Weibull distribution reduces to a truncated exponential distribution. If X ~ Exp(λ) then 1 + X ~ BenktanderWeibull(λ, 1).
- The exponential distribution is a limit of a scaled beta distribution:
- limn→∞nBeta(1,n)=Exp(1).{displaystyle lim _{nto infty }noperatorname {Beta} (1,n)=operatorname {Exp} (1).}
- limn→∞nBeta(1,n)=Exp(1).{displaystyle lim _{nto infty }noperatorname {Beta} (1,n)=operatorname {Exp} (1).}
- If Xi ~ Exp(λ) then the sum X1 + ... + Xk = ∑iXi{displaystyle sum _{i}X_{i}}
~ Erlang(k, λ) which is just a Gamma(k, λ−1) (in (k, θ) parametrization) or Gamma(k, λ) (in (α,β) parametrization) with an integer shape parameter k.
- If X ~ Exp(1) then μ − σ log(X) ~ GEV(μ, σ, 0).
- If X ~ Exp(λ) then X ~ Gamma(1, λ−1) (in (k, θ) parametrization) or Gamma(1, λ) (in (α, β) parametrization).
- If X ~ Exp(λ) and Y ~ Exp(ν) then λX − νY ~ Laplace(0, 1).
- If X, Y ~ Exp(λ) then X − Y ~ Laplace(0, λ−1).
- If X ~ Laplace(μ, β−1) then |X − μ| ~ Exp(β).
- If X ~ Exp(1) then (logistic distribution):
- μ−βlog(e−X1−e−X)∼Logistic(μ,β){displaystyle mu -beta log left({tfrac {e^{-X}}{1-e^{-X}}}right)sim mathrm {Logistic} (mu ,beta )}
- μ−βlog(e−X1−e−X)∼Logistic(μ,β){displaystyle mu -beta log left({tfrac {e^{-X}}{1-e^{-X}}}right)sim mathrm {Logistic} (mu ,beta )}
- If X, Y ~ Exp(1) then (logistic distribution):
- μ−βlog(XY)∼Logistic(μ,β){displaystyle mu -beta log left({tfrac {X}{Y}}right)sim mathrm {Logistic} (mu ,beta )}
- μ−βlog(XY)∼Logistic(μ,β){displaystyle mu -beta log left({tfrac {X}{Y}}right)sim mathrm {Logistic} (mu ,beta )}
- If X ~ Exp(λ) then keX ~ Pareto(k, λ).
- If X ~ Pareto(1, λ) then log(X) ~ Exp(λ).
- Exponential distribution is a special case of type 3 Pearson distribution.
- If X ~ Exp(λ) then e−X ~ Beta(λ, 1).
- If X ~ Exp(λ) then e−Xk∼PowerLaw(k,λ){displaystyle {tfrac {e^{-X}}{k}}sim mathrm {PowerLaw} (k,lambda )}
(power law)
- If X ~ Exp(λ) then X∼Rayleigh(1/2λ).{displaystyle {sqrt {X}}sim operatorname {Rayleigh} left(1/{sqrt {2lambda }}right).}
(Rayleigh distribution)
- If X ~ Exp(λ) then X∼Weibull(1λ,1){displaystyle Xsim mathrm {Weibull} ({tfrac {1}{lambda }},1)}
(Weibull distribution)
- If Xi ~ U(0, 1) then
- limn→∞nmin(X1,…,Xn)∼Exp(1){displaystyle lim _{nto infty }nmin left(X_{1},ldots ,X_{n}right)sim {textrm {Exp}}(1)}
- limn→∞nmin(X1,…,Xn)∼Exp(1){displaystyle lim _{nto infty }nmin left(X_{1},ldots ,X_{n}right)sim {textrm {Exp}}(1)}
- If Y|X ~ Poisson(X) where X ~ Exp(λ−1) then Y∼Geometric(11+λ){displaystyle Ysim mathrm {Geometric} ({tfrac {1}{1+lambda }})}
(geometric distribution)
- If X ~ Exp(1) and Y∼Γ(α,βα){displaystyle Ysim Gamma (alpha ,{tfrac {beta }{alpha }})}
then XY∼K(α,β){displaystyle {sqrt {XY}}sim mathrm {K} (alpha ,beta )}
(K-distribution)
- The Hoyt distribution can be obtained from Exponential distribution and Arcsine distribution
- If X ~ Exp(λ) and Y ~ Erlang(n, λ) then:
- XY+1∼Pareto(1,n){displaystyle {frac {X}{Y}}+1sim mathrm {Pareto} (1,n)}
- XY+1∼Pareto(1,n){displaystyle {frac {X}{Y}}+1sim mathrm {Pareto} (1,n)}
- If X ~ Exp(λ) and Y∼Γ(n,1λ){displaystyle Ysim Gamma (n,{tfrac {1}{lambda }})}
then XY+1∼Pareto(1,n){displaystyle {tfrac {X}{Y}}+1sim mathrm {Pareto} (1,n)}
- If X ~ SkewLogistic(θ), then log(1 + e−X) ~ Exp(θ).
- If X ~ Exp(λ) and Y = μ − β log(Xλ) then Y ∼ Gumbel(μ, β).
- Let X ∼ Exp(λX) and Y ∼ Exp(λY) be independent. Then Z=λXXλYY{displaystyle Z={frac {lambda _{X}X}{lambda _{Y}Y}}}
has probability density function fZ(z)=1(z+1)2{displaystyle f_{Z}(z)={frac {1}{(z+1)^{2}}}}
. This can be used to obtain a confidence interval for λXλY{displaystyle {frac {lambda _{X}}{lambda _{Y}}}}
.
- Gamma mixture: If λ ~ Gamma(scale = k, shape = θ) and X ~ Exponential(rate = λ) then the marginal distribution of X is Lomax(scale = 1/k, shape = θ)
Other related distributions:
Hyper-exponential distribution – the distribution whose density is a weighted sum of exponential densities.
Hypoexponential distribution – the distribution of a general sum of exponential random variables.
exGaussian distribution – the sum of an exponential distribution and a normal distribution.
Applications of exponential distribution
Occurrence of events
The exponential distribution occurs naturally when describing the lengths of the inter-arrival times in a homogeneous Poisson process.
The exponential distribution may be viewed as a continuous counterpart of the geometric distribution, which describes the number of Bernoulli trials necessary for a discrete process to change state. In contrast, the exponential distribution describes the time for a continuous process to change state.
In real-world scenarios, the assumption of a constant rate (or probability per unit time) is rarely satisfied. For example, the rate of incoming phone calls differs according to the time of day. But if we focus on a time interval during which the rate is roughly constant, such as from 2 to 4 p.m. during work days, the exponential distribution can be used as a good approximate model for the time until the next phone call arrives. Similar caveats apply to the following examples which yield approximately exponentially distributed variables:
- The time until a radioactive particle decays, or the time between clicks of a geiger counter
- The time it takes before your next telephone call
- The time until default (on payment to company debt holders) in reduced form credit risk modeling
Exponential variables can also be used to model situations where certain events occur with a constant probability per unit length, such as the distance between mutations on a DNA strand, or between roadkills on a given road.
In queuing theory, the service times of agents in a system (e.g. how long it takes for a bank teller etc. to serve a customer) are often modeled as exponentially distributed variables. (The arrival of customers for instance is also modeled by the Poisson distribution if the arrivals are independent and distributed identically.) The length of a process that can be thought of as a sequence of several independent tasks follows the Erlang distribution (which is the distribution of the sum of several independent exponentially distributed variables).
Reliability theory and reliability engineering also make extensive use of the exponential distribution. Because of the memoryless property of this distribution, it is well-suited to model the constant hazard rate portion of the bathtub curve used in reliability theory. It is also very convenient because it is so easy to add failure rates in a reliability model. The exponential distribution is however not appropriate to model the overall lifetime of organisms or technical devices, because the "failure rates" here are not constant: more failures occur for very young and for very old systems.
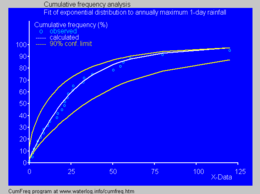
Fitted cumulative exponential distribution to annually maximum 1-day rainfalls using CumFreq[11]
In physics, if you observe a gas at a fixed temperature and pressure in a uniform gravitational field, the heights of the various molecules also follow an approximate exponential distribution, known as the Barometric formula. This is a consequence of the entropy property mentioned below.
In hydrology, the exponential distribution is used to analyze extreme values of such variables as monthly and annual maximum values of daily rainfall and river discharge volumes.[12]
- The blue picture illustrates an example of fitting the exponential distribution to ranked annually maximum one-day rainfalls showing also the 90% confidence belt based on the binomial distribution. The rainfall data are represented by plotting positions as part of the cumulative frequency analysis.
Prediction
Having observed a sample of n data points from an unknown exponential distribution a common task is to use these samples to make predictions about future data from the same source. A common predictive distribution over future samples is the so-called plug-in distribution, formed by plugging a suitable estimate for the rate parameter λ into the exponential density function. A common choice of estimate is the one provided by the principle of maximum likelihood, and using this yields the predictive density over a future sample xn+1, conditioned on the observed samples x = (x1, ..., xn) given by
- pML(xn+1∣x1,…,xn)=(1x¯)exp(−xn+1x¯){displaystyle p_{rm {ML}}(x_{n+1}mid x_{1},ldots ,x_{n})=left({frac {1}{overline {x}}}right)exp left(-{frac {x_{n+1}}{overline {x}}}right)}
The Bayesian approach provides a predictive distribution which takes into account the uncertainty of the estimated parameter, although this may depend crucially on the choice of prior.
A predictive distribution free of the issues of choosing priors that arise under the subjective Bayesian approach is
- pCNML(xn+1∣x1,…,xn)=nn+1(x¯)n(nx¯+xn+1)n+1,{displaystyle p_{rm {CNML}}(x_{n+1}mid x_{1},ldots ,x_{n})={frac {n^{n+1}left({overline {x}}right)^{n}}{left(n{overline {x}}+x_{n+1}right)^{n+1}}},}
which can be considered as
- (1) a frequentist confidence distribution, obtained from the distribution of the pivotal quantity xn+1/x¯{displaystyle {x_{n+1}}/{overline {x}}}
;[13]
- (2) a profile predictive likelihood, obtained by eliminating the parameter λ from the joint likelihood of xn+1 and λ by maximization;[14]
- (3) an objective Bayesian predictive posterior distribution, obtained using the non-informative Jeffreys prior 1/λ;
- (4) the Conditional Normalized Maximum Likelihood (CNML) predictive distribution, from information theoretic considerations.[15]
The accuracy of a predictive distribution may be measured using the distance or divergence between the true exponential distribution with rate parameter, λ0, and the predictive distribution based on the sample x. The Kullback–Leibler divergence is a commonly used, parameterisation free measure of the difference between two distributions. Letting Δ(λ0||p) denote the Kullback–Leibler divergence between an exponential with rate parameter λ0 and a predictive distribution p it can be shown that
- operatornameEλ0[Δ(λ0∣∣pML)]=ψ(n)+1n−1−log(n)operatornameEλ0[Δ(λ0∣∣pCNML)]=ψ(n)+1n−log(n){displaystyle {begin{aligned}operatorname{E}_{lambda _{0}}left[Delta (lambda _{0}mid mid p_{rm {ML}})right]&=psi (n)+{frac {1}{n-1}}-log(n)\operatorname{E}_{lambda _{0}}left[Delta (lambda _{0}mid mid p_{rm {CNML}})right]&=psi (n)+{frac {1}{n}}-log(n)end{aligned}}}
where the expectation is taken with respect to the exponential distribution with rate parameter λ0 ∈ (0, ∞), and ψ( · ) is the digamma function. It is clear that the CNML predictive distribution is strictly superior to the maximum likelihood plug-in distribution in terms of average Kullback–Leibler divergence for all sample sizes n > 0.
See also
Dead time – an application of exponential distribution to particle detector analysis.
Laplace distribution, or the "double exponential distribution".- Relationships among probability distributions
- Marshall–Olkin exponential distribution
References
^ David Olive, Chapter 4. Truncated Distributions, "Lemma 4.3", Southern Illinois University, February 18, 2010, p.107.
^ Park, Sung Y.; Bera, Anil K. (2009). "Maximum entropy autoregressive conditional heteroskedasticity model" (PDF). Journal of Econometrics. Elsevier: 219–230. Retrieved 2011-06-02..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ Michael, Lugo. "The expectation of the maximum of exponentials" (PDF). Retrieved 13 December 2016.
^ Richard Arnold Johnson; Dean W. Wichern (2007). Applied Multivariate Statistical Analysis. Pearson Prentice Hall. ISBN 978-0-13-187715-3. Retrieved 10 August 2012.
^ NIST/SEMATECH e-Handbook of Statistical Methods
^ Abdulaziz Elfessi and David M. Reineke, "A Bayesian Look at Classical Estimation: The Exponential Distribution", Journal of Statistics Education Volume 9, Number 1 (2001).
^ Ross, Sheldon M. (2009). Introduction to probability and statistics for engineers and scientists (4th ed.). Associated Press. p. 267. ISBN 978-0-12-370483-2.
^ Guerriero, V. (2012). "Power Law Distribution: Method of Multi-scale Inferential Statistics". Journal of Modern Mathematics Frontier (JMMF). 1: 21–28.
^ Donald E. Knuth (1998). The Art of Computer Programming, volume 2: Seminumerical Algorithms, 3rd edn. Boston: Addison–Wesley.
ISBN 0-201-89684-2. See section 3.4.1, p. 133.
^ ab Luc Devroye (1986). Non-Uniform Random Variate Generation. New York: Springer-Verlag.
ISBN 0-387-96305-7. See chapter IX, section 2, pp. 392–401.
^ "Cumfreq, a free computer program for cumulative frequency analysis".
^ Ritzema (ed.), H.P. (1994). Frequency and Regression Analysis (PDF). Chapter 6 in: Drainage Principles and Applications, Publication 16, International Institute for Land Reclamation and Improvement (ILRI), Wageningen, The Netherlands. pp. 175–224. ISBN 90-70754-33-9.CS1 maint: Extra text: authors list (link)
^ Lawless, J.F., Fredette, M.,"Frequentist predictions intervals and predictive distributions", Biometrika (2005), Vol 92, Issue 3, pp 529–542.
^ Bjornstad, J.F. (1990). "Predictive Likelihood: A Review". Statist. Sci. 5 (2): 242–254. doi:10.1214/ss/1177012175.
^ D. F. Schmidt and E. Makalic, "Universal Models for the Exponential Distribution", IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, Volume 55, Number 7, pp. 3087–3090, 2009 doi:10.1109/TIT.2009.2018331
External links
Hazewinkel, Michiel, ed. (2001) [1994], "Exponential distribution", Encyclopedia of Mathematics, Springer Science+Business Media B.V. / Kluwer Academic Publishers, ISBN 978-1-55608-010-4
- Online calculator of Exponential Distribution






![{displaystyle operatorname {Var} [X]={frac {1}{lambda ^{2}}}=beta ^{2},}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/e2db61d030b013b96776d081ed6e26b810b58c57)
![{displaystyle operatorname {E} left[X^{n}right]={frac {n!}{lambda ^{n}}}.}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/5f5d3a82fbcff5a294e5360fb05b1e5f2166ec09)

![{displaystyle operatorname {m} [X]={frac {ln(2)}{lambda }}<operatorname {E} [X],}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/7f19becbfbc702d8c33a9698c779384fe3f4dca1)
![{displaystyle |operatorname {E} [X]-operatorname {m} [X]|={frac {1-ln(2)}{lambda }}<{frac {1}{lambda }}={text{standard deviation}},}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/767d9e3df93d6e508eae348b687a6ee9e726313f)

![{displaystyle {begin{aligned}Pr left(T>s+tmid T>sright)&={frac {Pr left(T>s+tcap T>sright)}{Pr left(T>sright)}}\[4pt]&={frac {Pr left(T>s+tright)}{Pr left(T>sright)}}\[4pt]&={frac {e^{-lambda (s+t)}}{e^{-lambda s}}}\[4pt]&=e^{-lambda t}\[4pt]&=Pr(T>t).end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/126da1213459cde98ae372eae857a18183675f5a)







![{displaystyle E[X_{(i)}X_{(j)}]={frac {1}{(n-j+1)lambda }}E[X_{(i)}]+E[X_{(i)}^{2}]={frac {1}{(n-j+1)lambda }}{frac {1}{(n-i+1)lambda }}+{frac {2}{((n-i+1)lambda )^{2}}}.}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/90838ba27e31108ce08de3d949e228419f2f624c)
![{displaystyle {begin{aligned}operatorname {E} [X_{(i)}X_{(j)}]&=int _{0}^{infty }operatorname {E} [X_{(i)}X_{(j)}mid X_{(i)}=x]f_{X_{(i)}}(x),dx\&=int _{x=0}^{infty }xoperatorname {E} [X_{(j)}mid X_{(j)}geq x]f_{X_{(i)}}(x),dxqquad ({textrm {since}}~X_{(i)}=ximplies X_{(j)}geq x)\&=int _{x=0}^{infty }xleft[{frac {1}{(n-j+1)lambda }}+xright]f_{X_{(i)}}(x),dxqquad ({text{by the memoryless property}})\&={frac {1}{(n-j+1)lambda }}operatorname {E} [X_{(i)}]+operatorname {E} [X_{(i)}^{2}].end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/0200e17756c856d361cf21249d7cbf1f465df6ba)
![{displaystyle {begin{aligned}f_{Z}(z)=&int _{0}^{z}f_{X_{1}}(x_{1})f_{X_{2}}(z-x_{1}),dx_{1}\=&lambda _{1}lambda _{2}exp[-lambda _{2}z]int _{0}^{z}exp[(lambda _{2}-lambda _{1})x_{1}],dx_{1}\=&{frac {lambda _{1}lambda _{2}}{lambda _{2}-lambda _{1}}}left(exp[-lambda _{1}z]-exp[-lambda _{2}z]right)end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/8dffc55421f8961ff2340259c4d96a3aa8384800)
![{displaystyle {begin{aligned}operatorname {E} [Z]=&int z,df_{Z}(z)\[4pt]=&lambda _{1}^{-1}+lambda _{2}^{-1}\[4pt]operatorname {var} (Z)=&operatorname {E} [Z^{2}]-operatorname {E} [Z]^{2}\[4pt]=&int z^{2},df_{Z}(z)-(lambda _{1}^{-1}+lambda _{2}^{-1})^{2}\[4pt]=&lambda _{1}^{-2}+lambda _{2}^{-2}end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/593f22a8e037ea851f690a09eb3b42a7b49c2d17)
![{displaystyle {begin{aligned}F_{Z}(z)=Pr(Zleq z)=&int _{0}^{z}f_{Z}(t),dt\[4pt]=&1+{frac {lambda _{1}}{lambda _{2}-lambda _{1}}}exp[-lambda _{2}z]-{frac {lambda _{2}}{lambda _{2}-lambda _{1}}}exp[-lambda _{1}z]end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/1248725e45eb6dbc111538a46c018d51aa80c3c4)


![{frac {{mathrm {d}}}{{mathrm {d}}lambda }}ln(L(lambda ))={frac {{mathrm {d}}}{{mathrm {d}}lambda }}left(nln(lambda )-lambda noverline {x}right)={frac {n}{lambda }}-noverline {x} {begin{cases}>0,&0<lambda <{frac {1}{overline {x}}},\[8pt]=0,&lambda ={frac {1}{overline {x}}},\[8pt]<0,&lambda >{frac {1}{overline {x}}}.end{cases}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/fe786afa36e05947aacb710bd47910bffc029bd7)


![{displaystyle {mathcal {I}}(lambda )=operatorname {E} left[left.left({frac {partial }{partial lambda }}log f(x;lambda )right)^{2}right|lambda right]=int left({frac {partial }{partial lambda }}log f(x;lambda )right)^{2}f(x;lambda ),dx}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/2c70bd835b54bb1b7f344dbf1f04d170bd1d4852)





















![{displaystyle {begin{aligned}operatorname{E}_{lambda _{0}}left[Delta (lambda _{0}mid mid p_{rm {ML}})right]&=psi (n)+{frac {1}{n-1}}-log(n)\operatorname{E}_{lambda _{0}}left[Delta (lambda _{0}mid mid p_{rm {CNML}})right]&=psi (n)+{frac {1}{n}}-log(n)end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/bcae8e40ca2a21ceb824f7c28f51cfeca3a604c6)
Comments
Post a Comment