Rear admiral (Royal Navy)
| Rear Admiral | |
|---|---|
 Flag of a rear admiral, Royal Navy. | |
The sleeve lace, of a Royal Navy rear admiral. | |
The stars, and shoulder boards, of a Royal Navy rear admiral. | |
| Country | |
| Service branch |
|
| Abbreviation | RADM |
| Rank | two-star |
NATO rank | OF-7 |
| Non-NATO rank | 7 |
| Next higher rank | Vice Admiral |
| Next lower rank | Commodore |
| Equivalent ranks | Major-general, United Kingdom |
Rear admiral (RAdm) is a flag officer rank of the British Royal Navy. It is immediately superior to commodore and is subordinate to vice admiral. It is a two-star rank and has a NATO ranking code of OF-7.
Contents
1 History
2 Rank insignia and personal flag
3 Former command flags
4 See also
5 References
6 Sources
History
The rank originated in the days of naval sailing squadrons and each naval squadron would be assigned an admiral as its head. He would command from the centre vessel and direct the activities of the squadron. The admiral would in turn be assisted by a vice admiral, who commanded the lead ships which would bear the brunt of a naval battle. In the rear of the naval squadron, a third admiral would command the remaining ships and, as this section of the squadron was considered to be in the least danger, the admiral in command of the rear would typically be the most junior of the squadron admirals. This has survived into the modern age, with the rank of rear admiral the most-junior of the admiralty ranks of many navies.Prior to 1864 the Royal Navy was divided into colored squadrons which determined his career path. The command flags flown by Rear-Admiral changed a number of times during this period included.[1]
The Royal Navy rank of rear admiral should be distinguished from the office of Rear-Admiral of the United Kingdom, which is an Admiralty position usually held by a senior (and possibly retired) "full" admiral.
Rank insignia and personal flag

Royal Navy rear admiral sleeve insignia

Royal Navy rear admiral shoulder board
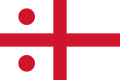
Royal Navy rear admiral command flag from 1864-present

Royal Navy rear admiral shoulder board prior to 2001[2]

World War II Royal Navy rear admiral's steel helmet with two-star insignia
Former command flags
See also
- List of Royal Navy rear admirals
References
^ Perrin, W. G. (William Gordon) (1922). "IV:Flags of Command". British flags, their early history, and their development at sea; with an account of the origin of the flag as a national device. Cambridge, England: Cambridge : The University Press. pp. 73–109..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ Refer UK DCI (Joint Service) 125/2001
Sources
- Perrin, W. G. (William Gordon) (1922). "IV:Flags of Command". British flags, their early history, and their development at sea; with an account of the origin of the flag as a national device. Cambridge, England: Cambridge : The University Press.
Commissioned officer ranks of the British Armed Forces | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
NATO rank code | Student officer | OF-1 | OF-2 | OF-3 | OF-4 | OF-5 | OF-6 * | OF-7 ** | OF-8 *** | OF-9 **** | OF-10 ***** | ||
Royal Navy | O Cdt | Mid | SLt | Lt | Lt Cdr | Cdr | Capt | Cdre | RAdm (list) | VAdm (list) | Adm (list) | Adm of the Fleet | |
Royal Marines | O Cdt | 2Lt | Lt | Capt | Maj | Lt Col | Col | Brig | Maj-Gen | Lt-Gen | Gen (list) | Capt-Gen | |
Army | O Cdt | 2Lt | Lt | Capt | Maj | Lt Col | Col | Brig | Maj-Gen (list) | Lt-Gen (list) | Gen (list) | Fd Mshl | |
Royal Air Force | Off Cdt / SO | APO / Plt Off | Fg Off | Flt Lt | Sqn Ldr | Wg Cdr | Gp Capt | Air Cdre | AVM | Air Mshl | Air Chf Mshl (list) | Mshl of the RAF | |





Comments
Post a Comment