| Ventral posterolateral nucleus |
|---|
 Thalamic nuclei:
MNG = Midline nuclear group
AN = Anterior nuclear group
MD = Medial dorsal nucleus
VNG = Ventral nuclear group
VA = Ventral anterior nucleus
VL = Ventral lateral nucleus
VPL = Ventral posterolateral nucleus
VPM = Ventral posteromedial nucleus
LNG = Lateral nuclear group
PUL = Pulvinar
MTh = Metathalamus
LG = Lateral geniculate nucleus
MG = Medial geniculate nucleus
|
 Thalamic nuclei
|
| Details |
|---|
| Part of |
Ventral posterior nucleus |
| Identifiers |
|---|
| Latin |
nucleus ventralis posterolateralis thalami |
| NeuroNames |
344 |
NeuroLex ID |
birnlex_737 |
| TA |
A14.1.08.641
A14.1.08.656
|
| FMA |
62200 |
Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy[edit on Wikidata]
|
The ventral posterolateral nucleus (VPL) is a nucleus of the thalamus. Together with the ventral posteromedial nucleus (VPM), ventral posterior inferior nucleus (VPI) and ventromedial posterior nucleus (VMpo), it constitutes the ventral posterior nucleus. There is uncertainty in the location of VMpo, as determined by spinothalamic tract (STT) terminations and staining for calcium-binding proteins, and several authorities do not consider its existence as being proved.[1]
Input and output
The VPL receives information from the neospinothalamic tract and the medial lemniscus of the posterior column-medial lemniscus pathway. It then projects this sensory information to Brodmann's Areas 3, 1 and 2 in the postcentral gyrus. Collectively, Brodmann areas 3, 1 and 2 make up the primary somatosensory cortex of the brain.
Additional images
Anatomy of the diencephalon of the human brain
|
|---|
| Epithalamus |
| Surface |
- Pineal gland
- Habenula
- Habenular trigone
- Habenular commissure
|
| Grey matter |
- Pretectal area
- Habenular nuclei
- Subcommissural organ
|
|
| Thalamus |
| Surface |
- Stria medullaris of thalamus
- Thalamic reticular nucleus
- Taenia thalami
|
Grey matter/
nuclei
|
paired: AN
Ventral
Lateral
Metathalamus
midline: MD
Intralaminar
- Midline nuclear group
- Interthalamic adhesion
|
| White matter |
- Mammillothalamic tract
Pallidothalamic tracts
- Ansa lenticularis
- Lenticular fasciculus
- Thalamic fasciculus
PCML
- Medial lemniscus
- Trigeminal lemniscus
- Spinothalamic tract
- Lateral lemniscus
- Dentatothalamic tract
- Acoustic radiation
- Optic radiation
- Subthalamic fasciculus
- Anterior trigeminothalamic tract
|
|
| Hypothalamus |
| Surface |
Median eminence/Tuber cinereum
- Mammillary body
- Infundibulum
|
| Grey matter |
Autonomic zones |
- Anterior (parasympathetic/heat loss)
- Posterior (sympathetic/heat conservation)
|
| Endocrine |
posterior pituitary: Paraventricular
- Magnocellular neurosecretory cell
- Parvocellular neurosecretory cell
Supraoptic
other: Arcuate (dopamine/GHRH)
- Preoptic (GnRH)
- Suprachiasmatic (melatonin)
|
| Emotion |
- Lateral
- Ventromedial
- Dorsomedial
|
|
| White matter |
afferent
- Medial forebrain bundle
- Retinohypothalamic tract
efferent
- Mammillothalamic tract
- Stria terminalis
- Dorsal longitudinal fasciculus
|
| Pituitary |
Posterior is diencephalon, but anterior is glandular
|
|
| Subthalamus |
- Subthalamic nucleus
- Zona incerta
Nuclei campi perizonalis (Fields of Forel)
|
Brain and spinal cord: neural tracts and fasciculi
|
|---|
Sensory/
ascending |
| DCML |
1°: |
Pacinian corpuscle/Meissner's corpuscle → Posterior column (Gracile fasciculus/Cuneate fasciculus) → Gracile nucleus/Cuneate nucleus
|
2°: |
- → sensory decussation/arcuate fibers (Posterior external arcuate fibers, Internal arcuate fibers) → Medial lemniscus/Trigeminal lemniscus → Thalamus (VPL, VPM)
|
3°: |
- → Posterior limb of internal capsule → Postcentral gyrus
|
|
Anterolateral/
pain
|
Fast/lateral |
- 1° (Free nerve ending → A delta fiber) → 2° (Anterior white commissure → Lateral and Anterior Spinothalamic tract → Spinal lemniscus → VPL of Thalamus) → 3° (Postcentral gyrus) → 4° (Posterior parietal cortex)
2° (Spinomesencephalic tract → Superior colliculus of Midbrain tectum)
|
Slow/medial |
- 1° (Group C nerve fiber → Spinoreticular tract → Reticular formation) → 2° (MD of Thalamus) → 3° (Cingulate cortex)
|
|
|
Motor/
descending |
| Pyramidal |
flexion: Primary motor cortex → Posterior limb of internal capsule → Decussation of pyramids → Corticospinal tract (Lateral, Anterior) → Neuromuscular junction
|
| Extrapyramidal |
.mw-parser-output .nobold{font-weight:normal}
flexion:
|
Primary motor cortex → Genu of internal capsule → Corticobulbar tract → Facial motor nucleus → Facial muscles
|
flexion:
|
Red nucleus → Rubrospinal tract
|
extension:
|
Vestibulocerebellum → Vestibular nuclei → Vestibulospinal tract
|
extension:
|
Vestibulocerebellum → Reticular formation → Reticulospinal tract
|
Midbrain tectum → Tectospinal tract → muscles of neck
|
|
| Basal ganglia |
direct:
|
1° (Motor cortex → Striatum) → 2° (GPi) → 3° (Lenticular fasciculus/Ansa lenticularis → Thalamic fasciculus → VL of Thalamus) → 4° (Thalamocortical radiations → Supplementary motor area) → 5° (Motor cortex) |
indirect:
|
1° (Motor cortex → Striatum) → 2° (GPe) → 3° (Subthalamic fasciculus → Subthalamic nucleus) → 4° (Subthalamic fasciculus → GPi) → 5° (Lenticular fasciculus/Ansa lenticularis → Thalamic fasciculus → VL of Thalamus) → 6° (Thalamocortical radiations → Supplementary motor area) → 7° (Motor cortex) |
nigrostriatal pathway:
|
|
|
|
| Cerebellar |
| Afferent |
Vestibular nuclei → Vestibulocerebellar tract → ICP → Cerebellum → Granule cell
Pontine nuclei → Pontocerebellar fibers → MCP → Deep cerebellar nuclei → Granule cell
Inferior olivary nucleus → Olivocerebellar tract → ICP → Hemisphere → Purkinje cell → Deep cerebellar nuclei
|
| Efferent |
Dentate nucleus in Lateral hemisphere/pontocerebellum → SCP → Dentatothalamic tract → Thalamus (VL) → Motor cortex
Interposed nucleus in Intermediate hemisphere/spinocerebellum → SCP → Reticular formation, or → Cerebellothalamic tract → Red nucleus → Thalamus (VL) → Motor cortex
Fastigial nucleus in Flocculonodular lobe/vestibulocerebellum → Vestibulocerebellar tract → Vestibular nuclei
|
Bidirectional:
Spinocerebellar
|
Unconscious
proprioception |
lower limb → 1° (muscle spindles → DRG) → 2° (Posterior thoracic nucleus → Dorsal/posterior spinocerebellar tract → ICP → Cerebellar vermis)
upper limb → 1° (muscle spindles → DRG) → 2° (Accessory cuneate nucleus → Cuneocerebellar tract → ICP → Anterior lobe of cerebellum)
|
| Reflex arc |
lower limb → 1° (Golgi tendon organ) → 2° (Ventral/anterior spinocerebellar tract→ SCP → Cerebellar vermis)
upper limb → 1° (Golgi tendon organ) → 2° (Rostral spinocerebellar tract → ICP → Cerebellum)
|
|
|
Physiology of balance and hearing
|
|---|
| Hearing |
| General |
- Auditory system
- Bone conduction
- Otoacoustic emission
- Tullio phenomenon
|
| Pathway |
inner ear: Hair cells → Spiral ganglion → Cochlear nerve VIII →
pons: Cochlear nucleus (Anterior, Dorsal) → Trapezoid body → Superior olivary nuclei →
midbrain: Lateral lemniscus → Inferior colliculi →
thalamus: Medial geniculate nuclei →
cerebrum: Acoustic radiation → Primary auditory cortex
|
|
| Balance |
| General |
|
| Pathway |
inner ear: Vestibular nerve VIII →
pons: Vestibular nuclei (Medial vestibular nucleus, Lateral vestibular nucleus)
cerebellum: Flocculonodular lobe
spinal cord: Vestibulospinal tract (Medial vestibulospinal tract, Lateral vestibulospinal tract)
thalamus: Ventral posterolateral nucleus
cerebrum: Vestibular cortex
- Vestibulo-oculomotor fibers
|
|
References
^ Willis et al The Journal of Pain 2002;3:79-94; Graziano and Jones, The Journal of Neuroscience 2004;24:248–256
Authority control 
|
|


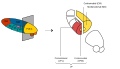


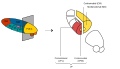

Comments
Post a Comment