Exhaustive ballot
| Part of the Politics series |
| Electoral systems |
|---|
Plurality/majoritarian
|
Proportional representation
|
Mixed systems
|
Other systems & related theory
|
The exhaustive ballot is a voting system used to elect a single winner. Under the exhaustive ballot the elector simply casts a single vote for their chosen candidate. However, if no candidate is supported by an overall majority of votes then the candidate with the fewest votes is eliminated and a further round of voting occurs. This process is repeated for as many rounds as necessary until one candidate has a majority.
The exhaustive ballot is similar to the two-round system but with key differences. Under the two round system if no candidate wins a majority on the first round, only the top two recipients of votes advance to the second (and final) round of voting, and a majority winner is determined in the second round. By contrast, on the exhaustive ballot only one candidate is eliminated per round; thus, several rounds of voting may be required until a candidate reaches a majority. (In some circumstances, the two or more lowest candidates can be eliminated simultaneously if together they have fewer votes than the lowest candidate above them. In other words, this "bulk exclusion" cannot change the order of elimination, unlike a two-round system.)
Because voters may have to cast votes several times, the exhaustive ballot is not used in large-scale public elections. Instead it is usually used in elections involving, at most, a few hundred voters, such as the election of a prime minister or the presiding officer of an assembly. The exhaustive ballot is currently used, in different forms, to elect the members of the Swiss Federal Council, the First Minister of Scotland, the President of the European Parliament, and the speakers of the House of Commons of Canada, the British House of Commons and the Scottish Parliament, the various party nominees for President of the United States, the host city of the Olympic Games and the host of the FIFA World Cup, and, formerly, to elect the President and the State Comptroller of Israel, which are now elected – though still indirectly by the Knesset – using a two-round system.
Contents
1 Voting and counting
1.1 Variations
2 Example
3 Use in practice
4 Similar systems
4.1 The two-round system
4.2 Primary two-round system
4.3 Instant-runoff voting
5 Tactical voting
5.1 Examples
5.1.1 Compromise
5.1.2 Push over
6 Strategic nomination
7 Effect on candidates and factions
8 Notes
9 External links
Voting and counting

An example of a ballot paper.
In each round of an exhaustive ballot the voter simply marks an 'x' beside his or her favourite candidate. If no candidate has an absolute majority of votes (i.e., more than half) in the first round, then the candidate with the fewest votes is eliminated while all other candidates advance to a second round. If there is still no candidate with a majority then the candidate with the fewest votes is again eliminated and there is a third round. The process repeats itself for as many rounds as are necessary for one candidate to achieve a majority. If necessary, the election will continue until only two candidates remain. When this occurs one of the two must achieve an absolute majority.
Between rounds, the voter is entirely free to change his/her preferred candidate for whatever reason, even if his/her preferred candidate has not yet been eliminated from voting.
Variations
- Under some variants of the exhaustive ballot there is no formal rule for eliminating candidates from one round to another; rather, candidates are expected to withdraw voluntarily.
- Some variations slowly raise an elimination threshold in to encourage compromise. For example, the Minnesota Democratic-Farmer-Labor Party for U.S. Senate endorsement 2008 used an exhaustive ballot with a dropoff rule starting at 5% and increasing to 25% after round 5, after which one candidate with the lowest votes was eliminated per round until no more than two remained.[1]
- There are also variants which exclude more than one candidate at a time. For example, in elections for the speakers of the Canadian and British Houses of Commons any candidate with fewer than 5% of all votes in the first round is immediately eliminated.
Example
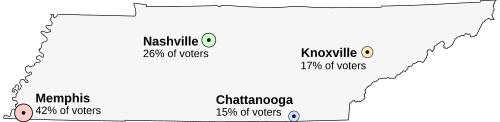
Imagine that the population of Tennessee, a state in the United States, is voting on the location of its capital. The population of Tennessee is concentrated around its four major cities, which are spread throughout the state. For this example, suppose that the entire electorate live in one of these four cities, and that they would like the capital to be established as close to their city as possible.
The candidates for the capital are:
Memphis, the state's largest city, with 42% of the voters, but located far from the other cities
Nashville, with 26% of the voters[2]
Knoxville, with 17% of the voters
Chattanooga, with 15% of the voters
Round 1: In the first round of voting the results will be as follows:
- Memphis: 42%
- Nashville: 26%
- Knoxville: 17%
- Chattanooga: 15%
Round 2: No candidate has an absolute majority in the first round (this would be greater than 50%), so Chattanooga, which has the fewest votes, is eliminated and the remaining three candidates proceed to Round 2. In this round the Chattanooga supporters vote instead for Knoxville, the next nearest city to their own. None of the other voters need change their votes. The results are therefore:
- Memphis: 42%
- Nashville: 26%
- Knoxville: 32%
Round 3: Nashville is now eliminated, so that only two candidates remain for the final round. The Nashville supporters change their vote to Knoxville, the next nearest city to their own. The result of the third round is therefore:
- Memphis: 42%
- Knoxville: 58%
Result: After round three Knoxville has an absolute majority so is the winner.
Use in practice
Scottish government: The First Minister, and the Presiding Officer and Deputy Presiding Officers of the Scottish Parliament are elected by the exhaustive ballot method.- The host city of the Olympic Games is chosen by an exhaustive ballot of members of the International Olympic Committee. Members from a country which has a city competing in the election are forbidden from voting unless the city has been eliminated.
- The President of the European Parliament is elected by all members of the body to be its 'speaker' or chairperson. In the election if no candidate receives an absolute majority in the first round then there are up to three more rounds. In the second and third rounds anyone who wants to is free to stand, but candidates who perform poorly sometimes withdraw to help others be elected. If no-one achieves an absolute majority in the third round then only the two candidates with most votes are allowed to proceed to the fourth and final round of voting.
- The Speaker of the British House of Commons is elected by secret ballot by members of the house. If no candidate achieves an absolute majority in the first round then the candidate with fewest votes and any other candidate who has received less than 5% of all votes is immediately eliminated. Subsequent rounds proceed according to the ordinary rules of the exhaustive ballot.
- The Speaker of the House of Commons of Canada is elected under essentially the same variant of the exhaustive ballot used for the British counterpart, with candidates on less than 5% in the first round immediately excluded.
Party nominees for the President of the United States: Delegates to the Democratic and Republican Parties' respective nominating conventions cast votes for their preferred candidate, and if no majority is reached on the first ballot, additional rounds follow until one candidate reaches a majority. In the past this process could be long and acrimonious, ending only with brokered deals made in a proverbial smoke-filled room. In the modern day the actual voting process is a perfunctory exercise, as primary elections encourage the emergence of a clear front-runner long before the conventions.- The Leader of the New Democratic Party of Canada is elected by the party membership under a mixture of instant runoff voting (IRV), and exhaustive voting, depending on the member's preferences. Those who want to vote only once may cast a single ballot filled out in the IRV format, while other members may cast separate ballots after each round of balloting. The party used this format for the 2012, and 2017 leadership elections.
Similar systems
The two-round system
As noted above the exhaustive ballot is similar to the two-round system. However under the two-round system if no candidate achieves an absolute majority in the first round then, rather than just a single candidate being eliminated, all candidates are immediately excluded except the two with the most votes. There is then a second and final round. Because, at most, it requires voters to return to the polls only once, the two-round system is considered more practical for large public elections than the exhaustive ballot, and is used in many countries for the election of presidents and legislative bodies. However the two systems often produce different winners. This is because, under the two-round system, a candidate may be eliminated in the first round who would have gone on to win the contest if they had been permitted to survive to the second round. In Example I above the winner would not have changed if the two rounds system had been used instead of the exhaustive ballot. However, in Example II the two round system would have elected Nashville instead of Knoxville.
Primary two-round system
A nonpartisan primary election system is a variation of the two-round system which holds a pre-election, and allows the top two candidates to pass to the general election. It generally differs from the two-round system in two ways: (1) the first election isn't allowed to pick a winner, and (2) political parties are not allowed to limit their field using a convention or caucus.
Instant-runoff voting
In some respects the exhaustive ballot closely resembles instant-runoff voting (also known as the 'Alternative Vote'). Under both systems if no candidate has an absolute majority in the first round then there are further rounds, with the candidate with the fewest votes being eliminated after each round. However while under the exhaustive ballot each round involves voters returning to cast a new vote, under instant-runoff, voters vote only once. This is possible because, rather than voting for only a single candidate, the voter ranks all of the candidates in order of preference. These preferences are then used to 'transfer' the votes of those whose first preference has been eliminated during the course of the count.
Because the exhaustive ballot involves separate rounds of voting, voters can use the results of one round to inform how they will vote in the next, whereas this is not possible under IRV. Furthermore, because it is necessary to vote only once, instant-runoff voting has been used for large-scale elections in many places.
Tactical voting
Like instant-runoff voting, the exhaustive ballot is intended to improve upon the simpler 'first-past-the-post' (plurality) system by reducing the potential for tactical voting by avoiding 'wasted' votes. Under the plurality system, which involves only one round, voters are encouraged to vote tactically by voting for only one of the two leading candidates, because a vote for any other candidate will not affect the result.[citation needed] Under the exhaustive ballot this tactic, known as 'compromising', is sometimes unnecessary because, even if the voter's first choice is unlikely to be elected, she will still have the opportunity to influence the outcome of the election by voting for more popular candidates once her favourite has been eliminated. However the exhaustive ballot is still vulnerable to tactical voting under some circumstances. Because of the similarity between the two systems it is open to the same forms of tactical voting as instant-runoff voting.
Although the exhaustive ballot is designed to avoid 'compromising' the tactic is still effective in some elections. Compromising is where a voter votes for a certain candidate, not because they necessarily support them, but as a way of avoiding the election of a candidate whom they dislike even more. The compromising tactic is sometimes effective because the exhaustive ballot eliminates candidates who are unpopular in early rounds, who might have had sufficient support to win the election had they survived a little longer. This can create strong incentives for voters to vote tactically.
Like instant-runoff voting, the exhaustive ballot is also vulnerable to the tactic of 'push over', where voters vote tactically for an unpopular 'push over' candidate in one round as a way of helping their true favourite candidate win in a later round. The purpose of voting for the 'push over' is to ensure that it is this weak candidate, rather than a stronger rival, who remains to challenge a voter's preferred candidate in later rounds. By supporting a 'push over' candidate it is hoped to eliminate a stronger candidate who might have gone on to win the election.[citation needed] The 'push over' tactic requires voters to be able to reliably predict how others will vote. It runs the risk of backfiring, because if the tactical voter miscalculates then the candidate intended as a 'push over' might end up actually beating the voter's preferred candidate.
Examples
Compromise
In Example I above, if Ice Cream supporters had voted tactically for Apple Pie in the first round then Apple Pie (their second choice) would have been elected instead of Fruit (their last choice). In Example II Knoxville wins, the last choice of both Nashville and Memphis supporters. If Memphis supporters had 'compromised' by voting for Nashville (their second choice) in the first round then Nashville would have been elected immediately, while if Nashville supporters had all 'compromised' by voting for their second choice of Chattanooga in the first round, then Chattanooga would have gone on to be elected in the second round.
Push over
Imagine an election, like the one at the start of this article, in which there are 100 voters who vote as follows:
- Ice Cream: 25 votes
- Apple Pie: 30 votes
- Fruit: 45 votes
No candidate has an absolute majority of votes so Ice Cream is eliminated in the first round. Ice Cream supporters prefer Apple Pie to Fruit so in the second round they vote for Apple Pie and Apple Pie is the winner. However, if only six Fruit supporters had used the tactic of 'push over' then they could have changed this outcome and ensured the election of Fruit. These six voters can do this by voting for Ice Cream in the first round as a 'push over'. If they do this then the votes cast in the first round will look like this:
- Ice Cream: 31
- Apple Pie: 30
- Fruit: 39
This time Apple Pie is eliminated in the first round and Ice Cream and Fruit survive to the second round. This outcome is deliberate. The tactical voters know that Ice Cream will be an easier candidate for Fruit to beat in the second round than Apple Pie–in other words, that Ice Cream will be a 'push-over'. In the second round the tactical voters vote for their real first preference, Fruit. Therefore, even if only 6 Apple Pie supporters prefer Fruit to Ice Cream, the result of the second round will be:
- Ice Cream: 49
- Fruit: 51
Fruit will therefore be elected. The success of this tactic relies on the Fruit supporters being able to predict that Ice Cream can be beaten by Fruit in the second round. If a large majority of Apple Pie supporters had voted for Ice Cream then the 'push over' tactic would have backfired, leading to the election of Ice Cream, which Fruit partisans like even less than Apple Pie.
Strategic nomination
The exhaustive ballot can also be influenced by strategic nomination; this is where candidates and political factions influence the result of an election by either nominating extra candidates or withdrawing a candidate who would otherwise have stood. The exhaustive ballot is vulnerable to strategic nomination for the same reasons that it is open to the voting tactic of 'compromising'. This is because a candidate who knows they are unlikely to win can bring about the election of a more desirable compromise candidate by withdrawing from the race, or by never standing in the first place. By the same token a candidate can bring about a less desirable result by unwisely choosing to stand in an election; this is because of the spoiler effect, by which a new candidate can 'split the vote' and cost another similar candidate the election.
The exhaustive vote's system of multiple rounds makes it less vulnerable to the spoiler effect than the plurality system or the two round system. This is because a potential spoiler candidate often has only minor support; therefore he will be eliminated early and his supporters will have the opportunity to influence the result of the election by voting for more popular candidates in later rounds. Voters can also counteract the effect of vote splitting by using the 'compromise' tactic.
The exhaustive vote is essentially vulnerable to the same forms of strategic nomination as instant-runoff voting, the difference being that under the exhaustive vote candidates can use the results of early rounds to inform whether or not they should strategically withdraw in later rounds. This is impossible under IRV. In IRV the electorate votes only once, so candidates must make the judgement of whether or not to participate in an election before the poll, and before even one round of counting has occurred.
Effect on candidates and factions
The exhaustive ballot encourages candidates to appeal to a broad cross-section of voters. This is because, in order to eventually receive an absolute majority of votes, it is necessary for a candidate to win the support of voters whose favourite candidate has been eliminated. Under the exhaustive ballot, eliminated candidates, and the factions who previously supported them, often issue recommendations to their supporters as to whom they should vote for in the remaining rounds of the contest. This means that eliminated candidates are still able to influence the result of the election.
Notes
^ DFL Call 2008/2009 Page 27: VIII. Endorsement for U.S. Senate: 22. GENERAL ENDORSEMENT RULES:
Dropoff rule: Candidates receiving less than 5% will be dropped after the first ballot. On subsequent ballots, the dropoff threshold will be raised by 5% each ballot to a maximum of 25%. After the fifth ballot and each subsequent ballot, the lowest remaining candidates will be dropped so that no more than two candidates remain. In the event that application of the dropoff rule would eliminate all but one candidate, then the two candidates who received the highest percent of the vote on the prior ballot shall be the remaining candidates.
^ Note: Nashville is in reality both the capital and most populous city of Tennessee, but please ignore this for the sake of example
External links
- Electoral Reform Society: Briefing on the electoral system for the Speaker of the British House of Commons

Comments
Post a Comment