Ultrafiltration (renal)
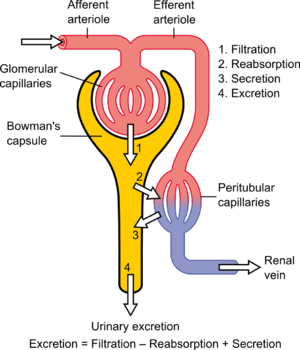
Diagram showing the basic physiologic mechanisms of the kidney
In renal physiology, ultrafiltration occurs at the barrier between the blood and the filtrate in the glomerular capsule (Bowman's capsule) in the kidneys. As in nonbiological examples of ultrafiltration, pressure (in this case blood pressure) and concentration gradients lead to a separation through a semipermeable membrane (provided by the podocytes). The Bowman's capsule contains a dense capillary network called the glomerulus. Blood flows into these capillaries through the afferent arterioles and leaves through the efferent arterioles.
The high hydrostatic pressure forces small molecules in the tubular fluid such as water, glucose, amino acids, sodium chloride and urea through the filter, from the blood in the glomerular capsule across the basement membrane of the Bowman's capsule and into the renal tubules. This process is called ultrafiltration; the resulting fluid, virtually free of large proteins and blood cells, is referred to as glomerular filtrate, or ultrafiltrate.[1] Further modification of ultrafiltrate, by reabsorption and secretion, transforms it into urine.
Glomerular pressure is about 75 millimeters of mercury (10 kPa). It is opposed by osmotic pressure (30 mmHg, 4.0 kPa) and hydrostatic pressure (20 mmHg, 2.7 kPa) of solutes present in capsular space. This difference in pressure is called effective pressure (25 mmHg, 3.3 kPa).
In hemodialysis centers, ultrafiltration takes place on the hemodialysis machines when the venous pressure is greater than the transmembrane pressure (TMP). This cleans whole blood while keeping its blood cells intact.
Contents
1 Selectivity
2 Slow continuous ultrafiltration
3 See also
4 References
Selectivity
The structures of the layers of the glomerulus determine their permeability-selectivity (permselectivity). For instance, small ions such as sodium and potassium pass freely, while larger plasma proteins, such as hemoglobin tetramers, haptoglobin bound hemoglobin and albumin have practically no permeability at all. Also, negatively charged molecules will pass through far less frequently than positively charged ones.
Slow continuous ultrafiltration
Slow Continuous Ultrafiltration (SCUF) is an artificial method which approximately mimics the ultrafiltration function of the kidneys. SCUF is a continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT) generally used to remove fluid from fluid overloaded patients suffering acute renal failure. During SCUF blood is removed from the body and is passed through an extracorporeal circuit through a hemofilter and a predetermined percentage of plasma water is removed based upon a prescription. Typically, no more than 2 liters an hour of fluid is removed. The remaining blood is returned to the patient. Unlike hemodialysis, hemofiltration and hemodiafiltration, no dialysate or replacement fluids are used in SCUF.[2]
See also
- Ultrafiltration (industrial)
- Ultrafiltration
- Aquapheresis
References
^ Koushanpour, Esmail (1986). Renal Physiology. New York: Springer-Verlag. pp. 53–72. ISBN 978-0-387-96304-4..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ Ronco C, Bellomo R, Ricci Z (2001). "Hemodynamic response to fluid withdrawal in overhydrated patients treated with intermittent ultrafiltration and slow continuous ultrafiltration: role of blood volume monitoring". Cardiology. 96 (3–4): 196–201. doi:10.1159/000047404. PMID 11805387.

Comments
Post a Comment