DNA sequencing
| Part of a series on |
| Genetics |
|---|
 |
Key components |
|
|
History and topics |
|
Research |
|
|
Personalized medicine |
Personalized medicine |
|
DNA sequencing is the process of determining the nucleic acid sequence – the order of nucleotides in DNA. It includes any method or technology that is used to determine the order of the four bases: adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine. The advent of rapid DNA sequencing methods has greatly accelerated biological and medical research and discovery.[1]
Knowledge of DNA sequences has become indispensable for basic biological research, and in numerous applied fields such as medical diagnosis, biotechnology, forensic biology, virology and biological systematics. The rapid speed of sequencing attained with modern DNA sequencing technology has been instrumental in the sequencing of complete DNA sequences, or genomes, of numerous types and species of life, including the human genome and other complete DNA sequences of many animal, plant, and microbial species.
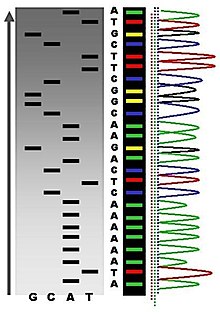
An example of the results of automated chain-termination DNA sequencing.
The first DNA sequences were obtained in the early 1970s by academic researchers using laborious methods based on two-dimensional chromatography. Following the development of fluorescence-based sequencing methods with a DNA sequencer,[2] DNA sequencing has become easier and orders of magnitude faster.[3]
Contents
1 Applications
1.1 Molecular biology
1.2 Evolutionary biology
1.3 Metagenomics
1.4 Medicine
1.5 Forensics
2 The four canonical bases
3 History
3.1 Discovery of DNA structure and function
3.2 RNA sequencing
3.3 Early DNA sequencing methods
3.4 Sequencing of full genomes
3.5 High-throughput sequencing (HTS) methods
4 Basic methods
4.1 Maxam-Gilbert sequencing
4.2 Chain-termination methods
5 Advanced methods and de novo sequencing
5.1 Shotgun sequencing
5.2 Bridge PCR
6 High-throughput methods
6.1 Massively parallel signature sequencing (MPSS)
6.2 Polony sequencing
6.3 454 pyrosequencing
6.4 Illumina (Solexa) sequencing
6.5 Combinatorial probe anchor synthesis (cPAS)
6.6 SOLiD sequencing
6.7 Ion Torrent semiconductor sequencing
6.8 DNA nanoball sequencing
6.9 Heliscope single molecule sequencing
6.10 Single molecule real time (SMRT) sequencing
6.11 Nanopore DNA sequencing
7 Methods in development
7.1 Tunnelling currents DNA sequencing
7.2 Sequencing by hybridization
7.3 Sequencing with mass spectrometry
7.4 Microfluidic Sanger sequencing
7.5 Microscopy-based techniques
7.6 RNAP sequencing
7.7 In vitro virus high-throughput sequencing
8 Sample preparation
9 Development initiatives
10 Computational challenges
10.1 Read trimming
11 Ethical issues
12 See also
13 Notes
14 References
15 External links
Applications
DNA sequencing may be used to determine the sequence of individual genes, larger genetic regions (i.e. clusters of genes or operons), full chromosomes, or entire genomes of any organism. DNA sequencing is also the most efficient way to indirectly sequence RNA or proteins (via their open reading frames). In fact, DNA sequencing has become a key technology in many areas of biology and other sciences such as medicine, forensics, and anthropology.
Molecular biology
Sequencing is used in molecular biology to study genomes and the proteins they encode. Information obtained using sequencing allows researchers to identify changes in genes, associations with diseases and phenotypes, and identify potential drug targets.
Evolutionary biology
Since DNA is an informative macromolecule in terms of transmission from one generation to another, DNA sequencing is used in evolutionary biology to study how different organisms are related and how they evolved.
Metagenomics
The field of metagenomics involves identification of organisms present in a body of water, sewage, dirt, debris filtered from the air, or swab samples from organisms. Knowing which organisms are present in a particular environment is critical to research in ecology, epidemiology, microbiology, and other fields. Sequencing enables researchers to determine which types of microbes may be present in a microbiome, for example.
Medicine
Medical technicians may sequence genes (or, theoretically, full genomes) from patients to determine if there is risk of genetic diseases. This is a form of genetic testing, though some genetic tests may not involve DNA sequencing.
Forensics
DNA sequencing may be used along with DNA profiling methods for forensic identification[4] and paternity testing. DNA testing has evolved tremendously in the last few decades to ultimately link a DNA print to what is under investigation. The DNA patterns in fingerprint, saliva, hair follicles, etc. uniquely separate each living organism from another. Testing DNA is a technique which can detect specific genomes in a DNA strand to produce a unique and individualized pattern. Every living organism ever created has a one of a kind DNA pattern, which can be determined through DNA testing. It is extremely rare that two people have exactly the same DNA pattern, therefore DNA testing is highly successful.
The four canonical bases
The canonical structure of DNA has four bases: thymine (T), adenine (A), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). DNA sequencing is the determination of the physical order of these bases in a molecule of DNA. However, there are many other bases that may be present in a molecule. In some viruses (specifically, bacteriophage), cytosine may be replaced by hydroxy methyl or hydroxy methyl glucose cytosine.[5] In mammalian DNA, variant bases with methyl groups or phosphosulfate may be found.[6][7] Depending on the sequencing technique, a particular modification, e.g., the 5mC (5 methyl cytosine) common in humans, may or may not be detected.[8]
History
Discovery of DNA structure and function
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) was first discovered and isolated by Friedrich Miescher in 1869, but it remained understudied for many decades because proteins, rather than DNA, were thought to hold the genetic blueprint to life. This situation changed after 1944 as a result of some experiments by Oswald Avery, Colin MacLeod, and Maclyn McCarty demonstrating that purified DNA could change one strain of bacteria into another. This was the first time that DNA was shown capable of transforming the properties of cells.
In 1953, James Watson and Francis Crick put forward their double-helix model of DNA, based on crystallized X-ray structures being studied by Rosalind Franklin – and without crediting her. According to the model, DNA is composed of two strands of nucleotides coiled around each other, linked together by hydrogen bonds and running in opposite directions. Each strand is composed of four complementary nucleotides – adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G) and thymine (T) – with an A on one strand always paired with T on the other, and C always paired with G. They proposed such a structure allowed each strand to be used to reconstruct the other, an idea central to the passing on of hereditary information between generations.[9]

Frederick Sanger, a pioneer of sequencing. Sanger is one of the few scientists who was awarded two Nobel prizes, one for the sequencing of proteins, and the other for the sequencing of DNA.
The foundation for sequencing proteins was first laid by the work of Frederick Sanger who by 1955 had completed the sequence of all the amino acids in insulin, a small protein secreted by the pancreas. This provided the first conclusive evidence that proteins were chemical entities with a specific molecular pattern rather than a random mixture of material suspended in fluid. Sanger's success in sequencing insulin greatly electrified x-ray crystallographers, including Watson and Crick who by now were trying to understand how DNA directed the formation of proteins within a cell. Soon after attending a series of lectures given by Frederick Sanger in October 1954, Crick began to develop a theory which argued that the arrangement of nucleotides in DNA determined the sequence of amino acids in proteins which in turn helped determine the function of a protein. He published this theory in 1958.[10]
RNA sequencing
RNA sequencing was one of the earliest forms of nucleotide sequencing. The major landmark of RNA sequencing is the sequence of the first complete gene and the complete genome of Bacteriophage MS2, identified and published by Walter Fiers and his coworkers at the University of Ghent (Ghent, Belgium), in 1972[11] and 1976.[12] Traditional RNA sequencing methods require the creation of a cDNA molecule which must be sequenced.[13]
Early DNA sequencing methods
The first method for determining DNA sequences involved a location-specific primer extension strategy established by Ray Wu at Cornell University in 1970.[14] DNA polymerase catalysis and specific nucleotide labeling, both of which figure prominently in current sequencing schemes, were used to sequence the cohesive ends of lambda phage DNA.[15][16][17] Between 1970 and 1973, Wu, R Padmanabhan and colleagues demonstrated that this method can be employed to determine any DNA sequence using synthetic location-specific primers.[18][19][20]Frederick Sanger then adopted this primer-extension strategy to develop more rapid DNA sequencing methods at the MRC Centre, Cambridge, UK and published a method for "DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors" in 1977.[21]Walter Gilbert and Allan Maxam at Harvard also developed sequencing methods, including one for "DNA sequencing by chemical degradation".[22][23] In 1973, Gilbert and Maxam reported the sequence of 24 basepairs using a method known as wandering-spot analysis.[24] Advancements in sequencing were aided by the concurrent development of recombinant DNA technology, allowing DNA samples to be isolated from sources other than viruses.
Sequencing of full genomes

The 5,386 bp genome of bacteriophage φX174. Each coloured block represents a gene.
The first full DNA genome to be sequenced was that of bacteriophage φX174 in 1977.[25]Medical Research Council scientists deciphered the complete DNA sequence of the Epstein-Barr virus in 1984, finding it contained 172,282 nucleotides. Completion of the sequence marked a significant turning point in DNA sequencing because it was achieved with no prior genetic profile knowledge of the virus.[26]
A non-radioactive method for transferring the DNA molecules of sequencing reaction mixtures onto an immobilizing matrix during electrophoresis was developed by Pohl and co-workers in the early 1980s.[27][28] Followed by the commercialization of the DNA sequencer "Direct-Blotting-Electrophoresis-System GATC 1500" by GATC Biotech, which was intensively used in the framework of the EU genome-sequencing programme, the complete DNA sequence of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosome II.[29]Leroy E. Hood's laboratory at the California Institute of Technology announced the first semi-automated DNA sequencing machine in 1986.[30] This was followed by Applied Biosystems' marketing of the first fully automated sequencing machine, the ABI 370, in 1987 and by Dupont's Genesis 2000[31] which used a novel fluorescent labeling technique enabling all four dideoxynucleotides to be identified in a single lane. By 1990, the U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH) had begun large-scale sequencing trials on Mycoplasma capricolum, Escherichia coli, Caenorhabditis elegans, and Saccharomyces cerevisiae at a cost of US$0.75 per base. Meanwhile, sequencing of human cDNA sequences called expressed sequence tags began in Craig Venter's lab, an attempt to capture the coding fraction of the human genome.[32] In 1995, Venter, Hamilton Smith, and colleagues at The Institute for Genomic Research (TIGR) published the first complete genome of a free-living organism, the bacterium Haemophilus influenzae. The circular chromosome contains 1,830,137 bases and its publication in the journal Science[33] marked the first published use of whole-genome shotgun sequencing, eliminating the need for initial mapping efforts.
By 2001, shotgun sequencing methods had been used to produce a draft sequence of the human genome.[34][35]
High-throughput sequencing (HTS) methods
Several new methods for DNA sequencing were developed in the mid to late 1990s and were implemented in commercial DNA sequencers by the year 2000. Together these were called the "next-generation" or "second-generation" sequencing (NGS) methods, in order to distinguish them from the aforementioned earlier methods, like Sanger Sequencing. In contrast to the first generation of sequencing, NGS technology is typically characterized by being highly scalable, allowing the entire genome to be sequenced at once. Usually, this is accomplished by fragmenting the genome into small pieces, randomly sampling for a fragment, and sequencing it using one of a variety of technologies, such as those described below. An entire genome is possible because multiple fragments are sequenced at once (giving it the name "massively parallel" sequencing) in an automated process.
NGS technology has tremendously empowered researchers to look for insights into health, anthropologists to investigate human origins, and is catalyzing the "Personalized Medicine" movement. However, it has also opened the door to more room for error. There are many software tools to carry out the computational analysis of NGS data, each with its own algorithm. Even the parameters within one software package can change the outcome of the analysis. In addition, the large quantities of data produced by DNA sequencing have also required development of new methods and programs for sequence analysis. Several efforts to develop standards in the NGS field have been attempted to address these challenges, most of which have been small-scale efforts arising from individual labs. Most recently, a large, organized, FDA-funded effort has culminated in the BioCompute standard.
On 26 October 1990, Roger Tsien, Pepi Ross, Margaret Fahnestock and Allan J Johnston filed a patent describing stepwise ("base-by-base") sequencing with removable 3' blockers on DNA arrays (blots and single DNA molecules).[36]
In 1996, Pål Nyrén and his student Mostafa Ronaghi at the Royal Institute of Technology in Stockholm published their method of pyrosequencing.[37]
On 1 April 1997, Pascal Mayer and Laurent Farinelli submitted patents to the World Intellectual Property Organization describing DNA colony sequencing.[38] The DNA sample preparation and random surface-PCR arraying methods described in this patent, coupled to Roger Tsien et al.'s "base-by-base" sequencing method, is now implemented in Illumina's Hi-Seq genome sequencers.
In 1998, Phil Green and Brent Ewing of the University of Washington described their phred quality score for sequencer data analysis,[39] a landmark analysis technique that gained widespread adoption, and which is still the most common metric for assessing the accuracy of a sequencing platform.[40]
Lynx Therapeutics published and marketed Massively parallel signature sequencing (MPSS), in 2000. This method incorporated a parallelized, adapter/ligation-mediated, bead-based sequencing technology and served as the first commercially available "next-generation" sequencing method, though no DNA sequencers were sold to independent laboratories.[41]
Basic methods
Maxam-Gilbert sequencing
Allan Maxam and Walter Gilbert published a DNA sequencing method in 1977 based on chemical modification of DNA and subsequent cleavage at specific bases.[22] Also known as chemical sequencing, this method allowed purified samples of double-stranded DNA to be used without further cloning. This method's use of radioactive labeling and its technical complexity discouraged extensive use after refinements in the Sanger methods had been made.
Maxam-Gilbert sequencing requires radioactive labeling at one 5' end of the DNA and purification of the DNA fragment to be sequenced. Chemical treatment then generates breaks at a small proportion of one or two of the four nucleotide bases in each of four reactions (G, A+G, C, C+T). The concentration of the modifying chemicals is controlled to introduce on average one modification per DNA molecule. Thus a series of labeled fragments is generated, from the radiolabeled end to the first "cut" site in each molecule. The fragments in the four reactions are electrophoresed side by side in denaturing acrylamide gels for size separation. To visualize the fragments, the gel is exposed to X-ray film for autoradiography, yielding a series of dark bands each corresponding to a radiolabeled DNA fragment, from which the sequence may be inferred.[22]
Chain-termination methods
The chain-termination method developed by Frederick Sanger and coworkers in 1977 soon became the method of choice, owing to its relative ease and reliability.[21][42] When invented, the chain-terminator method used fewer toxic chemicals and lower amounts of radioactivity than the Maxam and Gilbert method. Because of its comparative ease, the Sanger method was soon automated and was the method used in the first generation of DNA sequencers.
Sanger sequencing is the method which prevailed from the 1980s until the mid-2000s. Over that period, great advances were made in the technique, such as fluorescent labelling, capillary electrophoresis, and general automation. These developments allowed much more efficient sequencing, leading to lower costs. The Sanger method, in mass production form, is the technology which produced the first human genome in 2001, ushering in the age of genomics. However, later in the decade, radically different approaches reached the market, bringing the cost per genome down from $100 million in 2001 to $10,000 in 2011.[43]
Advanced methods and de novo sequencing
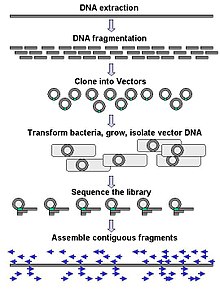
Genomic DNA is fragmented into random pieces and cloned as a bacterial library. DNA from individual bacterial clones is sequenced and the sequence is assembled by using overlapping DNA regions.(click to expand)
Large-scale sequencing often aims at sequencing very long DNA pieces, such as whole chromosomes, although large-scale sequencing can also be used to generate very large numbers of short sequences, such as found in phage display. For longer targets such as chromosomes, common approaches consist of cutting (with restriction enzymes) or shearing (with mechanical forces) large DNA fragments into shorter DNA fragments. The fragmented DNA may then be cloned into a DNA vector and amplified in a bacterial host such as Escherichia coli. Short DNA fragments purified from individual bacterial colonies are individually sequenced and assembled electronically into one long, contiguous sequence. Studies have shown that adding a size selection step to collect DNA fragments of uniform size can improve sequencing efficiency and accuracy of the genome assembly. In these studies, automated sizing has proven to be more reproducible and precise than manual gel sizing.[44][45][46]
The term "de novo sequencing" specifically refers to methods used to determine the sequence of DNA with no previously known sequence. De novo translates from Latin as "from the beginning". Gaps in the assembled sequence may be filled by primer walking. The different strategies have different tradeoffs in speed and accuracy; shotgun methods are often used for sequencing large genomes, but its assembly is complex and difficult, particularly with sequence repeats often causing gaps in genome assembly.
Most sequencing approaches use an in vitro cloning step to amplify individual DNA molecules, because their molecular detection methods are not sensitive enough for single molecule sequencing. Emulsion PCR[47] isolates individual DNA molecules along with primer-coated beads in aqueous droplets within an oil phase. A polymerase chain reaction (PCR) then coats each bead with clonal copies of the DNA molecule followed by immobilization for later sequencing. Emulsion PCR is used in the methods developed by Marguilis et al. (commercialized by 454 Life Sciences), Shendure and Porreca et al. (also known as "Polony sequencing") and SOLiD sequencing, (developed by Agencourt, later Applied Biosystems, now Life Technologies).[48][49][50] Emulsion PCR is also used in the GemCode and Chromium platforms developed by 10x Genomics.[51]
Shotgun sequencing
Shotgun sequencing is a sequencing method designed for analysis of DNA sequences longer than 1000 base pairs, up to and including entire chromosomes. This method requires the target DNA to be broken into random fragments. After sequencing individual fragments, the sequences can be reassembled on the basis of their overlapping regions.[52]
Bridge PCR
Another method for in vitro clonal amplification is bridge PCR, in which fragments are amplified upon primers attached to a solid surface[38][53][54] and form "DNA colonies" or "DNA clusters". This method is used in the Illumina Genome Analyzer sequencers. Single-molecule methods, such as that developed by Stephen Quake's laboratory (later commercialized by Helicos) are an exception: they use bright fluorophores and laser excitation to detect base addition events from individual DNA molecules fixed to a surface, eliminating the need for molecular amplification.[55]
High-throughput methods

Multiple, fragmented sequence reads must be assembled together on the basis of their overlapping areas.
High-throughput, or next-generation,[nt 1] sequencing applies to genome sequencing, genome resequencing, transcriptome profiling (RNA-Seq), DNA-protein interactions (ChIP-sequencing), and epigenome characterization.[56] Resequencing is necessary, because the genome of a single individual of a species will not indicate all of the genome variations among other individuals of the same species.
The high demand for low-cost sequencing has driven the development of high-throughput sequencing technologies that parallelize the sequencing process, producing thousands or millions of sequences concurrently.[57][58][59] High-throughput sequencing technologies are intended to lower the cost of DNA sequencing beyond what is possible with standard dye-terminator methods.[60] In ultra-high-throughput sequencing as many as 500,000 sequencing-by-synthesis operations may be run in parallel.[61][62][63] Such technologies led to the ability to sequence an entire human genome in as little as one day.[64] As of 2019[update], corporate leaders in the development of high-throughput sequencing products included Illumina, Qiagen and ThermoFisher Scientific.[64]
| Method | Read length | Accuracy (single read not consensus) | Reads per run | Time per run | Cost per 1 million bases (in US$) | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single-molecule real-time sequencing (Pacific Biosciences) | 30,000 bp (N50); maximum read length >100,000 bases[67][68][69] | 87% raw-read accuracy[70] | 500,000 per Sequel SMRT cell, 10–20 gigabases[67][71][72] | 30 minutes to 20 hours[67][73] | $0.05–$0.08 | Fast. Detects 4mC, 5mC, 6mA.[74] | Moderate throughput. Equipment can be very expensive. |
| Ion semiconductor (Ion Torrent sequencing) | up to 600 bp[75] | 99.6%[76] | up to 80 million | 2 hours | $1 | Less expensive equipment. Fast. | Homopolymer errors. |
| Pyrosequencing (454) | 700 bp | 99.9% | 1 million | 24 hours | $10 | Long read size. Fast. | Runs are expensive. Homopolymer errors. |
| Sequencing by synthesis (Illumina) | MiniSeq, NextSeq: 75–300 bp; MiSeq: 50–600 bp; HiSeq 2500: 50–500 bp; HiSeq 3/4000: 50–300 bp; HiSeq X: 300 bp | 99.9% (Phred30) | MiniSeq/MiSeq: 1–25 Million; NextSeq: 130-00 Million; HiSeq 2500: 300 million – 2 billion; HiSeq 3/4000 2.5 billion; HiSeq X: 3 billion | 1 to 11 days, depending upon sequencer and specified read length[77] | $0.05 to $0.15 | Potential for high sequence yield, depending upon sequencer model and desired application. | Equipment can be very expensive. Requires high concentrations of DNA. |
Combinatorial probe anchor synthesis (cPAS- BGI/MGI) | BGISEQ-50: 35-50bp; MGISEQ 200: 50-200bp; BGISEQ-500, MGISEQ-2000: 50-300bp[78] | 99.9% (Phred30) | BGISEQ-50: 160M; MGISEQ 200: 300M; BGISEQ-500: 1300M per flow cell; MGISEQ-2000: 375M FCS flow cell, 1500M FCL flow cell per flow cell. | 1 to 9 days depending on instrument, read length and number of flow cells run at a time. | $0.035- $0.12 | ||
| Sequencing by ligation (SOLiD sequencing) | 50+35 or 50+50 bp | 99.9% | 1.2 to 1.4 billion | 1 to 2 weeks | $0.13 | Low cost per base. | Slower than other methods. Has issues sequencing palindromic sequences.[79] |
| Nanopore Sequencing | Dependent on library prep, not the device, so user chooses read length. (up to 500 kb reported) | ~92–97% single read | dependent on read length selected by user | data streamed in real time. Choose 1 min to 48 hrs | $500–999 per Flow Cell, base cost dependent on expt | Longest individual reads. Accessible user community. Portable (Palm sized). | Lower throughput than other machines, Single read accuracy in 90s. |
| Chain termination (Sanger sequencing) | 400 to 900 bp | 99.9% | N/A | 20 minutes to 3 hours | $2400 | Useful for many applications. | More expensive and impractical for larger sequencing projects. This method also requires the time consuming step of plasmid cloning or PCR. |
Massively parallel signature sequencing (MPSS)
The first of the high-throughput sequencing technologies, massively parallel signature sequencing (or MPSS), was developed in the 1990s at Lynx Therapeutics, a company founded in 1992 by Sydney Brenner and Sam Eletr. MPSS was a bead-based method that used a complex approach of adapter ligation followed by adapter decoding, reading the sequence in increments of four nucleotides. This method made it susceptible to sequence-specific bias or loss of specific sequences. Because the technology was so complex, MPSS was only performed 'in-house' by Lynx Therapeutics and no DNA sequencing machines were sold to independent laboratories. Lynx Therapeutics merged with Solexa (later acquired by Illumina) in 2004, leading to the development of sequencing-by-synthesis, a simpler approach acquired from Manteia Predictive Medicine, which rendered MPSS obsolete. However, the essential properties of the MPSS output were typical of later high-throughput data types, including hundreds of thousands of short DNA sequences. In the case of MPSS, these were typically used for sequencing cDNA for measurements of gene expression levels.[41]
Polony sequencing
The Polony sequencing method, developed in the laboratory of George M. Church at Harvard, was among the first high-throughput sequencing systems and was used to sequence a full E. coli genome in 2005.[80] It combined an in vitro paired-tag library with emulsion PCR, an automated microscope, and ligation-based sequencing chemistry to sequence an E. coli genome at an accuracy of >99.9999% and a cost approximately 1/9 that of Sanger sequencing.[80] The technology was licensed to Agencourt Biosciences, subsequently spun out into Agencourt Personal Genomics, and eventually incorporated into the Applied Biosystems SOLiD platform. Applied Biosystems was later acquired by Life Technologies, now part of Thermo Fisher Scientific.
454 pyrosequencing
A parallelized version of pyrosequencing was developed by 454 Life Sciences, which has since been acquired by Roche Diagnostics. The method amplifies DNA inside water droplets in an oil solution (emulsion PCR), with each droplet containing a single DNA template attached to a single primer-coated bead that then forms a clonal colony. The sequencing machine contains many picoliter-volume wells each containing a single bead and sequencing enzymes. Pyrosequencing uses luciferase to generate light for detection of the individual nucleotides added to the nascent DNA, and the combined data are used to generate sequence reads.[48] This technology provides intermediate read length and price per base compared to Sanger sequencing on one end and Solexa and SOLiD on the other.[60]
Illumina (Solexa) sequencing
Solexa, now part of Illumina, was founded by Shankar Balasubramanian and David Klenerman in 1998, and developed a sequencing method based on reversible dye-terminators technology, and engineered polymerases.[81] The reversible terminated chemistry concept was invented by Bruno Canard and Simon Sarfati at the Pasteur Institute in Paris.[82][83] It was developed internally at Solexa by those named on the relevant patents. In 2004, Solexa acquired the company Manteia Predictive Medicine in order to gain a massively parallel sequencing technology invented in 1997 by Pascal Mayer and Laurent Farinelli.[38] It is based on "DNA Clusters" or "DNA colonies", which involves the clonal amplification of DNA on a surface. The cluster technology was co-acquired with Lynx Therapeutics of California. Solexa Ltd. later merged with Lynx to form Solexa Inc.

An Illumina HiSeq 2500 sequencer
In this method, DNA molecules and primers are first attached on a slide or flow cell and amplified with polymerase so that local clonal DNA colonies, later coined "DNA clusters", are formed. To determine the sequence, four types of reversible terminator bases (RT-bases) are added and non-incorporated nucleotides are washed away. A camera takes images of the fluorescently labeled nucleotides. Then the dye, along with the terminal 3' blocker, is chemically removed from the DNA, allowing for the next cycle to begin. Unlike pyrosequencing, the DNA chains are extended one nucleotide at a time and image acquisition can be performed at a delayed moment, allowing for very large arrays of DNA colonies to be captured by sequential images taken from a single camera.

An Illumina MiSeq sequencer
Decoupling the enzymatic reaction and the image capture allows for optimal throughput and theoretically unlimited sequencing capacity. With an optimal configuration, the ultimately reachable instrument throughput is thus dictated solely by the analog-to-digital conversion rate of the camera, multiplied by the number of cameras and divided by the number of pixels per DNA colony required for visualizing them optimally (approximately 10 pixels/colony). In 2012, with cameras operating at more than 10 MHz A/D conversion rates and available optics, fluidics and enzymatics, throughput can be multiples of 1 million nucleotides/second, corresponding roughly to 1 human genome equivalent at 1x coverage per hour per instrument, and 1 human genome re-sequenced (at approx. 30x) per day per instrument (equipped with a single camera).[84]
Combinatorial probe anchor synthesis (cPAS)
This method is an upgraded modification to combinatorial probe anchor ligation technology (cPAL) described by Complete Genomics[85] which has since become part of Chinese genomics company BGI in 2013.[86] The two companies have refined the technology to allow for longer read lengths, reaction time reductions and faster time to results. In addition, data are now generated as contiguous full-length reads in the standard FASTQ file format and can be used as-is in most short-read-based bioinformatics analysis pipelines.[87][citation needed]
The two technologies that form the basis for this high-throughput sequencing technology are DNA nanoballs (DNB) and patterned arrays for nanoball attachment to a solid surface.[85] DNA nanoballs are simply formed by denaturing double stranded, adapter ligated libraries and ligating the forward strand only to a splint oligonucleotide to form a ssDNA circle. Faithful copies of the circles containing the DNA insert are produced utilizing Rolling Circle Amplification that generates approximately 300–500 copies. The long strand of ssDNA folds upon itself to produce a three-dimensional nanoball structure that is approximately 220 nm in diameter. Making DNBs replaces the need to generate PCR copies of the library on the flow cell and as such can remove large proportions of duplicate reads, adapter-adapter ligations and PCR induced errors.[87][citation needed]

A BGI MGISEQ-2000RS sequencer
The patterned array of positively charged spots is fabricated through photolithography and etching techniques followed by chemical modification to generate a sequencing flow cell. Each spot on the flow cell is approximately 250 nm in diameter, are separated by 700 nm (centre to centre) and allows easy attachment of a single negatively charged DNB to the flow cell and thus reducing under or over-clustering on the flow cell.[85][citation needed]
Sequencing is then performed by addition of an oligonucleotide probe that attaches in combination to specific sites within the DNB. The probe acts as an anchor that then allows one of four single reversibly inactivated, labelled nucleotides to bind after flowing across the flow cell. Unbound nucleotides are washed away before laser excitation of the attached labels then emit fluorescence and signal is captured by cameras that is converted to a digital output for base calling. The attached base has its terminator and label chemically cleaved at completion of the cycle. The cycle is repeated with another flow of free, labelled nucleotides across the flow cell to allow the next nucleotide to bind and have its signal captured. This process is completed a number of times (usually 50 to 300 times) to determine the sequence of the inserted piece of DNA at a rate of approximately 40 million nucleotides per second as of 2018.[citation needed]
SOLiD sequencing

Library preparation for the SOLiD platform
Applied Biosystems' (now a Life Technologies brand) SOLiD technology employs sequencing by ligation. Here, a pool of all possible oligonucleotides of a fixed length are labeled according to the sequenced position. Oligonucleotides are annealed and ligated; the preferential ligation by DNA ligase for matching sequences results in a signal informative of the nucleotide at that position. Before sequencing, the DNA is amplified by emulsion PCR. The resulting beads, each containing single copies of the same DNA molecule, are deposited on a glass slide.[88] The result is sequences of quantities and lengths comparable to Illumina sequencing.[60] This sequencing by ligation method has been reported to have some issue sequencing palindromic sequences.[79]
Ion Torrent semiconductor sequencing
Ion Torrent Systems Inc. (now owned by Life Technologies) developed a system based on using standard sequencing chemistry, but with a novel, semiconductor-based detection system. This method of sequencing is based on the detection of hydrogen ions that are released during the polymerisation of DNA, as opposed to the optical methods used in other sequencing systems. A microwell containing a template DNA strand to be sequenced is flooded with a single type of nucleotide. If the introduced nucleotide is complementary to the leading template nucleotide it is incorporated into the growing complementary strand. This causes the release of a hydrogen ion that triggers a hypersensitive ion sensor, which indicates that a reaction has occurred. If homopolymer repeats are present in the template sequence, multiple nucleotides will be incorporated in a single cycle. This leads to a corresponding number of released hydrogens and a proportionally higher electronic signal.[89]

Sequencing of the TAGGCT template with IonTorrent, PacBioRS and GridION
DNA nanoball sequencing
DNA nanoball sequencing is a type of high throughput sequencing technology used to determine the entire genomic sequence of an organism. The company Complete Genomics uses this technology to sequence samples submitted by independent researchers. The method uses rolling circle replication to amplify small fragments of genomic DNA into DNA nanoballs. Unchained sequencing by ligation is then used to determine the nucleotide sequence.[90] This method of DNA sequencing allows large numbers of DNA nanoballs to be sequenced per run and at low reagent costs compared to other high-throughput sequencing platforms.[91] However, only short sequences of DNA are determined from each DNA nanoball which makes mapping the short reads to a reference genome difficult.[90] This technology has been used for multiple genome sequencing projects and is scheduled to be used for more.[92]
Heliscope single molecule sequencing
Heliscope sequencing is a method of single-molecule sequencing developed by Helicos Biosciences. It uses DNA fragments with added poly-A tail adapters which are attached to the flow cell surface. The next steps involve extension-based sequencing with cyclic washes of the flow cell with fluorescently labeled nucleotides (one nucleotide type at a time, as with the Sanger method). The reads are performed by the Heliscope sequencer.[93][94] The reads are short, averaging 35 bp.[95] In 2009 a human genome was sequenced using the Heliscope, however in 2012 the company went bankrupt.[96]
Single molecule real time (SMRT) sequencing
SMRT sequencing is based on the sequencing by synthesis approach. The DNA is synthesized in zero-mode wave-guides (ZMWs) – small well-like containers with the capturing tools located at the bottom of the well. The sequencing is performed with use of unmodified polymerase (attached to the ZMW bottom) and fluorescently labelled nucleotides flowing freely in the solution. The wells are constructed in a way that only the fluorescence occurring by the bottom of the well is detected. The fluorescent label is detached from the nucleotide upon its incorporation into the DNA strand, leaving an unmodified DNA strand. According to Pacific Biosciences (PacBio), the SMRT technology developer, this methodology allows detection of nucleotide modifications (such as cytosine methylation). This happens through the observation of polymerase kinetics. This approach allows reads of 20,000 nucleotides or more, with average read lengths of 5 kilobases.[71][97] In 2015, Pacific Biosciences announced the launch of a new sequencing instrument called the Sequel System, with 1 million ZMWs compared to 150,000 ZMWs in the PacBio RS II instrument.[98][99] SMRT sequencing is referred to as "third-generation" or "long-read" sequencing.
Nanopore DNA sequencing
The DNA passing through the nanopore changes its ion current. This change is dependent on the shape, size and length of the DNA sequence. Each type of the nucleotide blocks the ion flow through the pore for a different period of time. The method does not require modified nucleotides and is performed in real time. Nanopore sequencing is referred to as "third-generation" or "long-read" sequencing, along with SMRT sequencing.
Early industrial research into this method was based on a technique called 'Exonuclease sequencing', where the readout of electrical signals occurring at nucleotides passing by alpha(α)-hemolysin pores covalently bound with cyclodextrin.[100] However the subsequently commercial method, 'strand sequencing' sequencing DNA bases in an intact strand.
Two main areas of nanopore sequencing in development are solid state nanopore sequencing, and protein based nanopore sequencing. Protein nanopore sequencing utilizes membrane protein complexes such as α-hemolysin, MspA (Mycobacterium smegmatis Porin A) or CssG, which show great promise given their ability to distinguish between individual and groups of nucleotides.[101] In contrast, solid-state nanopore sequencing utilizes synthetic materials such as silicon nitride and aluminum oxide and it is preferred for its superior mechanical ability and thermal and chemical stability.[102] The fabrication method is essential for this type of sequencing given that the nanopore array can contain hundreds of pores with diameters smaller than eight nanometers.[101]
The concept originated from the idea that single stranded DNA or RNA molecules can be electrophoretically driven in a strict linear sequence through a biological pore that can be less than eight nanometers, and can be detected given that the molecules release an ionic current while moving through the pore. The pore contains a detection region capable of recognizing different bases, with each base generating various time specific signals corresponding to the sequence of bases as they cross the pore which are then evaluated.[102] Precise control over the DNA transport through the pore is crucial for success. Various enzymes such as exonucleases and polymerases have been used to moderate this process by positioning them near the pore’s entrance.[103]
Methods in development
DNA sequencing methods currently under development include reading the sequence as a DNA strand transits through nanopores (a method that is now commercial but subsequent generations such as solid-state nanopores are still in development),[104][105] and microscopy-based techniques, such as atomic force microscopy or transmission electron microscopy that are used to identify the positions of individual nucleotides within long DNA fragments (>5,000 bp) by nucleotide labeling with heavier elements (e.g., halogens) for visual detection and recording.[106][107]Third generation technologies aim to increase throughput and decrease the time to result and cost by eliminating the need for excessive reagents and harnessing the processivity of DNA polymerase.[108]
Tunnelling currents DNA sequencing
Another approach uses measurements of the electrical tunnelling currents across single-strand DNA as it moves through a channel. Depending on its electronic structure, each base affects the tunnelling current differently,[109] allowing differentiation between different bases.[110]
The use of tunnelling currents has the potential to sequence orders of magnitude faster than ionic current methods and the sequencing of several DNA oligomers and micro-RNA has already been achieved.[111]
Sequencing by hybridization
Sequencing by hybridization is a non-enzymatic method that uses a DNA microarray. A single pool of DNA whose sequence is to be determined is fluorescently labeled and hybridized to an array containing known sequences. Strong hybridization signals from a given spot on the array identifies its sequence in the DNA being sequenced.[112]
This method of sequencing utilizes binding characteristics of a library of short single stranded DNA molecules (oligonucleotides), also called DNA probes, to reconstruct a target DNA sequence. Non-specific hybrids are removed by washing and the target DNA is eluted.[113] Hybrids are re-arranged such that the DNA sequence can be reconstructed. The benefit of this sequencing type is its ability to capture a large number of targets with a homogenous coverage.[114] A large number of chemicals and starting DNA is usually required. However, with the advent of solution-based hybridization, much less equipment and chemicals are necessary.[113]
Sequencing with mass spectrometry
Mass spectrometry may be used to determine DNA sequences. Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry, or MALDI-TOF MS, has specifically been investigated as an alternative method to gel electrophoresis for visualizing DNA fragments. With this method, DNA fragments generated by chain-termination sequencing reactions are compared by mass rather than by size. The mass of each nucleotide is different from the others and this difference is detectable by mass spectrometry. Single-nucleotide mutations in a fragment can be more easily detected with MS than by gel electrophoresis alone. MALDI-TOF MS can more easily detect differences between RNA fragments, so researchers may indirectly sequence DNA with MS-based methods by converting it to RNA first.[115]
The higher resolution of DNA fragments permitted by MS-based methods is of special interest to researchers in forensic science, as they may wish to find single-nucleotide polymorphisms in human DNA samples to identify individuals. These samples may be highly degraded so forensic researchers often prefer mitochondrial DNA for its higher stability and applications for lineage studies. MS-based sequencing methods have been used to compare the sequences of human mitochondrial DNA from samples in a Federal Bureau of Investigation database[116] and from bones found in mass graves of World War I soldiers.[117]
Early chain-termination and TOF MS methods demonstrated read lengths of up to 100 base pairs.[118] Researchers have been unable to exceed this average read size; like chain-termination sequencing alone, MS-based DNA sequencing may not be suitable for large de novo sequencing projects. Even so, a recent study did use the short sequence reads and mass spectroscopy to compare single-nucleotide polymorphisms in pathogenic Streptococcus strains.[119]
Microfluidic Sanger sequencing
In microfluidic Sanger sequencing the entire thermocycling amplification of DNA fragments as well as their separation by electrophoresis is done on a single glass wafer (approximately 10 cm in diameter) thus reducing the reagent usage as well as cost.[120] In some instances researchers have shown that they can increase the throughput of conventional sequencing through the use of microchips.[121] Research will still need to be done in order to make this use of technology effective.
Microscopy-based techniques
This approach directly visualizes the sequence of DNA molecules using electron microscopy. The first identification of DNA base pairs within intact DNA molecules by enzymatically incorporating modified bases, which contain atoms of increased atomic number, direct visualization and identification of individually labeled bases within a synthetic 3,272 base-pair DNA molecule and a 7,249 base-pair viral genome has been demonstrated.[122]
RNAP sequencing
This method is based on use of RNA polymerase (RNAP), which is attached to a polystyrene bead. One end of DNA to be sequenced is attached to another bead, with both beads being placed in optical traps. RNAP motion during transcription brings the beads in closer and their relative distance changes, which can then be recorded at a single nucleotide resolution. The sequence is deduced based on the four readouts with lowered concentrations of each of the four nucleotide types, similarly to the Sanger method.[123] A comparison is made between regions and sequence information is deduced by comparing the known sequence regions to the unknown sequence regions.[124]
In vitro virus high-throughput sequencing
A method has been developed to analyze full sets of protein interactions using a combination of 454 pyrosequencing and an in vitro virus mRNA display method. Specifically, this method covalently links proteins of interest to the mRNAs encoding them, then detects the mRNA pieces using reverse transcription PCRs. The mRNA may then be amplified and sequenced. The combined method was titled IVV-HiTSeq and can be performed under cell-free conditions, though its results may not be representative of in vivo conditions.[125]
Sample preparation
The success of any DNA sequencing protocol relies upon the DNA or RNA sample extraction and preparation from the biological material of interest.
- A successful DNA extraction will yield a DNA sample with long, non-degraded strands.
- A successful RNA extraction will yield a RNA sample that should be converted to complementary DNA (cDNA) using reverse transcriptase—a DNA polymerase that synthesizes a complementary DNA based on existing strands of RNA in a PCR-like manner.[126] Complementary DNA can then be processed the same way as genomic DNA.
According to the sequencing technology to be used, the samples resulting from either the DNA or the RNA extraction require further preparation. For Sanger sequencing, either cloning procedures or PCR are required prior to sequencing. In the case of next-generation sequencing methods, library preparation is required before processing.[127] Assessing the quality and quantity of nucleic acids both after extraction and after library preparation identifies degraded, fragmented, and low-purity samples and yields high-quality sequencing data.[128]
Development initiatives

Total cost of sequencing a human genome over time as calculated by the NHGRI.
In October 2006, the X Prize Foundation established an initiative to promote the development of full genome sequencing technologies, called the Archon X Prize, intending to award $10 million to "the first Team that can build a device and use it to sequence 100 human genomes within 10 days or less, with an accuracy of no more than one error in every 100,000 bases sequenced, with sequences accurately covering at least 98% of the genome, and at a recurring cost of no more than $10,000 (US) per genome."[129]
Each year the National Human Genome Research Institute, or NHGRI, promotes grants for new research and developments in genomics. 2010 grants and 2011 candidates include continuing work in microfluidic, polony and base-heavy sequencing methodologies.[130]
Computational challenges
The sequencing technologies described here produce raw data that needs to be assembled into longer sequences such as complete genomes (sequence assembly). There are many computational challenges to achieve this, such as the evaluation of the raw sequence data which is done by programs and algorithms such as Phred and Phrap. Other challenges have to deal with repetitive sequences that often prevent complete genome assemblies because they occur in many places of the genome. As a consequence, many sequences may not be assigned to particular chromosomes. The production of raw sequence data is only the beginning of its detailed bioinformatical analysis.[131] Yet new methods for sequencing and correcting sequencing errors were developed.[132]
Read trimming
Sometimes, the raw reads produced by the sequencer are correct and precise only in a fraction of their length. Using the entire read may introduce artifacts in the downstream analyses like genome assembly, snp calling, or gene expression estimation. Two classes of trimming programs have been introduced, based on the window-based or the running-sum classes of algorithms.[133] This is a partial list of the trimming algorithms currently available, specifying the algorithm class they belong to:
| Name of algorithm | Type of algorithm | Link |
|---|---|---|
| Cutadapt[134] | Running sum | Cutadapt |
| ConDeTri[135] | Window based | ConDeTri |
| ERNE-FILTER[136] | Running sum | ERNE-FILTER |
| FASTX quality trimmer | Window based | FASTX quality trimmer |
| PRINSEQ[137] | Window based | PRINSEQ |
| Trimmomatic[138] | Window based | Trimmomatic |
| SolexaQA[139] | Window based | SolexaQA |
| SolexaQA-BWA | Running sum | SolexaQA-BWA |
| Sickle | Window based | Sickle |
Ethical issues
Human genetics have been included within the field of bioethics since the early 1970s[140] and the growth in the use of DNA sequencing (particularly high-throughput sequencing) has introduced a number of ethical issues. One key issue is the ownership of an individual's DNA and the data produced when that DNA is sequenced.[141] Regarding the DNA molecule itself, the leading legal case on this topic, Moore v. Regents of the University of California (1990) ruled that individuals have no property rights to discarded cells or any profits made using these cells (for instance, as a patented cell line). However, individuals have a right to informed consent regarding removal and use of cells. Regarding the data produced through DNA sequencing, Moore gives the individual no rights to the information derived from their DNA.[141]
As DNA sequencing becomes more widespread, the storage, security and sharing of genomic data has also become more important.[141][142] For instance, one concern is that insurers may use an individual's genomic data to modify their quote, depending on the perceived future health of the individual based on their DNA.[142][143] In May 2008, the Genetic Information Nondiscrimination Act (GINA) was signed in the United States, prohibiting discrimination on the basis of genetic information with respect to health insurance and employment.[144][145] In 2012, the US Presidential Commission for the Study of Bioethical Issues reported that existing privacy legislation for DNA sequencing data such as GINA and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act were insufficient, noting that whole-genome sequencing data was particularly sensitive, as it could be used to identify not only the individual from which the data was created, but also their relatives.[146][147]
Ethical issues have also been raised by the increasing use of genetic variation screening, both in newborns, and in adults by companies such as 23andMe.[148][149] It has been asserted that screening for genetic variations can be harmful, increasing anxiety in individuals who have been found to have an increased risk of disease.[150] For example, in one case noted in Time, doctors screening an ill baby for genetic variants chose not to inform the parents of an unrelated variant linked to dementia due to the harm it would cause to the parents.[151] However, a 2011 study in The New England Journal of Medicine has shown that individuals undergoing disease risk profiling did not show increased levels of anxiety.[150]
See also
|
|
Notes
^ "Next-generation" remains in broad use as of 2019. For instance, Straiton J, Free T, Sawyer A, Martin J (February 2019). "From Sanger Sequencing to Genome Databases and Beyond". BioTechniques. 66 (2): 60. doi:10.2144/btn-2019-0011.Next-generation sequencing (NGS) technologies have revolutionized genomic research. (opening sentence of the article)
.mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
References
^ "Introducing 'dark DNA' – the phenomenon that could change how we think about evolution".
^ Olsvik O, Wahlberg J, Petterson B, Uhlén M, Popovic T, Wachsmuth IK, Fields PI (January 1993). "Use of automated sequencing of polymerase chain reaction-generated amplicons to identify three types of cholera toxin subunit B in Vibrio cholerae O1 strains". J. Clin. Microbiol. 31 (1): 22–25. PMC 262614. PMID 7678018.

^ Pettersson E, Lundeberg J, Ahmadian A (February 2009). "Generations of sequencing technologies". Genomics. 93 (2): 105–11. doi:10.1016/j.ygeno.2008.10.003. PMID 18992322.
^ Curtis, Caitlin; Hereward, James (29 August 2017). "From the crime scene to the courtroom: the journey of a DNA sample". The Conversation.
^ Moréra, Solange; Larivière, Laurent; Kurzeck, Jürgen; Aschke-Sonnenborn, Ursula; Freemont, Paul S; Janin, Joël; Rüger, Wolfgang (August 2001). "High resolution crystal structures of T4 phage β-glucosyltransferase: induced fit and effect of substrate and metal binding". Journal of Molecular Biology. 311 (3): 569–77. doi:10.1006/jmbi.2001.4905. PMID 11493010.
^ Ehrlich, Melanie; Gama-Sosa, Miguel A.; Huang, Lan-Hsiang; Midgett, Rose Marie; Kuo, Kenneth C.; McCune, Roy A.; Gehrke, Charles (1982). "Amount and distribution of 5-methylcytosine in human DNA from different types of tissues or cells". Nucleic Acids Research. 10 (8): 2709–21. doi:10.1093/nar/10.8.2709. PMC 320645. PMID 7079182.
^ Ehrlich, M; Wang, R. (19 June 1981). "5-Methylcytosine in eukaryotic DNA". Science. 212 (4501): 1350–57. Bibcode:1981Sci...212.1350E. doi:10.1126/science.6262918. PMID 6262918.
^ Song, Chun-Xiao; Clark, Tyson A; Lu, Xing-Yu; Kislyuk, Andrey; Dai, Qing; Turner, Stephen W; He, Chuan; Korlach, Jonas (20 November 2011). "Sensitive and specific single-molecule sequencing of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine". Nature Methods. 9 (1): 75–77. doi:10.1038/nmeth.1779. PMC 3646335. PMID 22101853.
^ Watson JD, Crick FH (1953). "The structure of DNA". Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 18: 123–31. doi:10.1101/SQB.1953.018.01.020. PMID 13168976.
^ Marks, L, The path to DNA sequencing: The life and work of Frederick Sanger.
^ Min Jou W, Haegeman G, Ysebaert M, Fiers W (May 1972). "Nucleotide sequence of the gene coding for the bacteriophage MS2 coat protein". Nature. 237 (5350): 82–8. Bibcode:1972Natur.237...82J. doi:10.1038/237082a0. PMID 4555447.
^ Fiers W, Contreras R, Duerinck F, Haegeman G, Iserentant D, Merregaert J, Min Jou W, Molemans F, Raeymaekers A, Van den Berghe A, Volckaert G, Ysebaert M (April 1976). "Complete nucleotide sequence of bacteriophage MS2 RNA: primary and secondary structure of the replicase gene". Nature. 260 (5551): 500–7. Bibcode:1976Natur.260..500F. doi:10.1038/260500a0. PMID 1264203.
^ Ozsolak, Fatih; Milos, Patrice M. (2011-02-01). "RNA sequencing: advances, challenges and opportunities". Nature Reviews Genetics. 12 (2): 87–98. doi:10.1038/nrg2934. ISSN 1471-0056. PMC 3031867. PMID 21191423.
^ "Ray Wu Faculty Profile". Cornell University. Archived from the original on 2009-03-04.
^ Padmanabhan, R; Ray Wu; Ernest Jay (June 1974). "Chemical Synthesis of a Primer and Its Use in the Sequence Analysis of the Lysozyme Gene of Bacteriophage T4". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 71 (6): 2510–14. Bibcode:1974PNAS...71.2510P. doi:10.1073/pnas.71.6.2510. PMC 388489. PMID 4526223.
^ Onaga LA (June 2014). "Ray Wu as Fifth Business: Demonstrating Collective Memory in the History of DNA Sequencing". Studies in the History and Philosophy of Science. Part C. 46: 1–14. doi:10.1016/j.shpsc.2013.12.006. PMID 24565976.
^ Wu R (1972). "Nucleotide sequence analysis of DNA". Nature New Biology. 236 (68): 198–200. doi:10.1038/newbio236198a0. PMID 4553110.
^ Padmanabhan R, Wu R (1972). "Nucleotide sequence analysis of DNA. IX. Use of oligonucleotides of defined sequence as primers in DNA sequence analysis". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 48 (5): 1295–302. doi:10.1016/0006-291X(72)90852-2. PMID 4560009.
^ Wu R, Tu CD, Padmanabhan R (1973). "Nucleotide sequence analysis of DNA. XII. The chemical synthesis and sequence analysis of a dodecadeoxynucleotide which binds to the endolysin gene of bacteriophage lambda". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 55 (4): 1092–99. doi:10.1016/S0006-291X(73)80007-5. PMID 4358929.
^ Jay E, Bambara R, Padmanabhan R, Wu R (March 1974). "DNA sequence analysis: a general, simple and rapid method for sequencing large oligodeoxyribonucleotide fragments by mapping". Nucleic Acids Research. 1 (3): 331–53. doi:10.1093/nar/1.3.331. PMC 344020. PMID 10793670.
^ ab Sanger F, Nicklen S, Coulson AR (December 1977). "DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 74 (12): 5463–77. Bibcode:1977PNAS...74.5463S. doi:10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. PMC 431765. PMID 271968.
^ abc Maxam AM, Gilbert W (February 1977). "A new method for sequencing DNA". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 74 (2): 560–64. Bibcode:1977PNAS...74..560M. doi:10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. PMC 392330. PMID 265521.
^ Gilbert, W. DNA sequencing and gene structure. Nobel lecture, 8 December 1980.
^ Gilbert W, Maxam A (December 1973). "The Nucleotide Sequence of the lac Operator". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 70 (12): 3581–84. Bibcode:1973PNAS...70.3581G. doi:10.1073/pnas.70.12.3581. PMC 427284. PMID 4587255.
^ Sanger F, Air GM, Barrell BG, Brown NL, Coulson AR, Fiddes CA, Hutchison CA, Slocombe PM, Smith M (February 1977). "Nucleotide sequence of bacteriophage phi X174 DNA". Nature. 265 (5596): 687–95. Bibcode:1977Natur.265..687S. doi:10.1038/265687a0. PMID 870828.
^ "The Next Frontier: Human Viruses" , whatisbiotechnology.org, Retrieved 3 May 2017
^ Beck S, Pohl FM (1984). "DNA sequencing with direct blotting electrophoresis". EMBO J. 3 (12): 2905–09. PMC 557787. PMID 6396083.
^ United States Patent 4,631,122 (1986)
^ Feldmann H, et al. (1994). "Complete DNA sequence of yeast chromosome II". EMBO J. 13 (24): 5795–809. PMC 395553. PMID 7813418.
^ Smith LM, Sanders JZ, Kaiser RJ, Hughes P, Dodd C, Connell CR, Heiner C, Kent SB, Hood LE (12 June 1986). "Fluorescence Detection in Automated DNA Sequence Analysis". Nature. 321 (6071): 674–79. Bibcode:1986Natur.321..674S. doi:10.1038/321674a0. PMID 3713851.
^ Prober JM, Trainor GL, Dam RJ, Hobbs FW, Robertson CW, Zagursky RJ, Cocuzza AJ, Jensen MA, Baumeister K (16 Oct 1987). "A system for rapid DNA sequencing with fluorescent chain-terminating dideoxynucleotides". Science. 238 (4825): 336–41. Bibcode:1987Sci...238..336P. doi:10.1126/science.2443975. PMID 2443975.
^ Adams MD, Kelley JM, Gocayne JD, Dubnick M, Polymeropoulos MH, Xiao H, Merril CR, Wu A, Olde B, Moreno RF (June 1991). "Complementary DNA sequencing: expressed sequence tags and human genome project". Science. 252 (5013): 1651–56. Bibcode:1991Sci...252.1651A. doi:10.1126/science.2047873. PMID 2047873.
^ Fleischmann RD, Adams MD, White O, Clayton RA, Kirkness EF, Kerlavage AR, Bult CJ, Tomb JF, Dougherty BA, Merrick JM (July 1995). "Whole-genome random sequencing and assembly of Haemophilus influenzae Rd". Science. 269 (5223): 496–512. Bibcode:1995Sci...269..496F. doi:10.1126/science.7542800. PMID 7542800.
^ Lander ES, Linton LM, Birren B, Nusbaum C, Zody MC, et al. (February 2001). "Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome" (PDF). Nature. 409 (6822): 860–921. Bibcode:2001Natur.409..860L. doi:10.1038/35057062. PMID 11237011.
^ Venter JC, Adams MD, et al. (February 2001). "The sequence of the human genome". Science. 291 (5507): 1304–51. Bibcode:2001Sci...291.1304V. doi:10.1126/science.1058040. PMID 11181995.
^ "Espacenet – Bibliographic data". worldwide.espacenet.com.
^ Ronaghi M, Karamohamed S, Pettersson B, Uhlén M, Nyrén P (1996). "Real-time DNA sequencing using detection of pyrophosphate release". Analytical Biochemistry. 242 (1): 84–89. doi:10.1006/abio.1996.0432. PMID 8923969.
^ abc Kawashima, Eric H.; Laurent Farinelli; Pascal Mayer (2005-05-12). "Patent: Method of nucleic acid amplification". Retrieved 2012-12-22.
^ Ewing B, Green P (March 1998). "Base-calling of automated sequencer traces using phred. II. Error probabilities". Genome Res. 8 (3): 186–94. doi:10.1101/gr.8.3.186. PMID 9521922.
^ "Quality Scores for Next-Generation Sequencing" (PDF). Illumina. 31 October 2011. Retrieved 8 May 2018.
^ ab Brenner S, Johnson M, Bridgham J, Golda G, Lloyd DH, Johnson D, Luo S, McCurdy S, Foy M, Ewan M, Roth R, George D, Eletr S, Albrecht G, Vermaas E, Williams SR, Moon K, Burcham T, Pallas M, DuBridge RB, Kirchner J, Fearon K, Mao J, Corcoran K (2000). "Gene expression analysis by massively parallel signature sequencing (MPSS) on microbead arrays". Nature Biotechnology. 18 (6): 630–34. doi:10.1038/76469. PMID 10835600.
^ Sanger F, Coulson AR (May 1975). "A rapid method for determining sequences in DNA by primed synthesis with DNA polymerase". J. Mol. Biol. 94 (3): 441–48. doi:10.1016/0022-2836(75)90213-2. PMID 1100841.
^ Wetterstrand, Kris. "DNA Sequencing Costs: Data from the NHGRI Genome Sequencing Program (GSP)". National Human Genome Research Institute. Retrieved 30 May 2013.
^ Quail MA, Gu Y, Swerdlow H, Mayho M (2012). "Evaluation and optimisation of preparative semi-automated electrophoresis systems for Illumina library preparation". Electrophoresis. 33 (23): 3521–28. doi:10.1002/elps.201200128. PMID 23147856.
^ Duhaime MB, Deng L, Poulos BT, Sullivan MB (2012). "Towards quantitative metagenomics of wild viruses and other ultra-low concentration DNA samples: a rigorous assessment and optimization of the linker amplification method". Environ. Microbiol. 14 (9): 2526–37. doi:10.1111/j.1462-2920.2012.02791.x. PMC 3466414. PMID 22713159.
^ Peterson BK, Weber JN, Kay EH, Fisher HS, Hoekstra HE (2012). "Double digest RADseq: an inexpensive method for de novo SNP discovery and genotyping in model and non-model species". PLoS ONE. 7 (5): e37135. Bibcode:2012PLoSO...737135P. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0037135. PMC 3365034. PMID 22675423.
^ Williams R, Peisajovich SG, Miller OJ, Magdassi S, Tawfik DS, Griffiths AD (2006). "Amplification of complex gene libraries by emulsion PCR". Nature Methods. 3 (7): 545–50. doi:10.1038/nmeth896. PMID 16791213.
^ ab Margulies M, Egholm M, et al. (September 2005). "Genome Sequencing in Open Microfabricated High Density Picoliter Reactors". Nature. 437 (7057): 376–80. Bibcode:2005Natur.437..376M. doi:10.1038/nature03959. PMC 1464427. PMID 16056220.
^ Shendure J, Porreca GJ, Reppas NB, Lin X, McCutcheon JP, Rosenbaum AM, Wang MD, Zhang K, Mitra RD, Church GM (2005). "Accurate Multiplex Polony Sequencing of an Evolved Bacterial Genome". Science. 309 (5741): 1728–32. Bibcode:2005Sci...309.1728S. doi:10.1126/science.1117389. PMID 16081699.
^ "Applied Biosystems – File Not Found (404 Error)". 16 May 2008. Archived from the original on 2008-05-16.
^ Goodwin, Sara; McPherson, John D.; McCombie, W. Richard (17 May 2016). "Coming of age: ten years of next-generation sequencing technologies". Nature Reviews Genetics. 17 (6): 333–51. doi:10.1038/nrg.2016.49. PMID 27184599.
^ Staden R (11 Jun 1979). "A strategy of DNA sequencing employing computer programs". Nucleic Acids Research. 6 (7): 2601–10. doi:10.1093/nar/6.7.2601. PMC 327874. PMID 461197.
^ P. Mayer,L. Farinelli, G. Matton, C. Adessi, G. Turcatti, J. J. Mermod, E. Kawashima.DNA colony massively parallel sequencing ams98 presentation
^ U.S. Patent 5,641,658
^ Braslavsky I, Hebert B, Kartalov E, Quake SR (April 2003). "Sequence information can be obtained from single DNA molecules". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 100 (7): 3960–64. Bibcode:2003PNAS..100.3960B. doi:10.1073/pnas.0230489100. PMC 153030. PMID 12651960.
^ de Magalhães JP, Finch CE, Janssens G (2010). "Next-generation sequencing in aging research: emerging applications, problems, pitfalls and possible solutions". Ageing Research Reviews. 9 (3): 315–23. doi:10.1016/j.arr.2009.10.006. PMC 2878865. PMID 19900591.
^ Grada A (August 2013). "Next-generation sequencing: methodology and application". J Invest Dermatol. 133 (8): 1–4. doi:10.1038/jid.2013.248. PMID 23856935.
^ Hall N (May 2007). "Advanced sequencing technologies and their wider impact in microbiology". J. Exp. Biol. 210 (Pt 9): 1518–25. doi:10.1242/jeb.001370. PMID 17449817.

^ Church GM (January 2006). "Genomes for all". Sci. Am. 294 (1): 46–54. Bibcode:2006SciAm.294a..46C. doi:10.1038/scientificamerican0106-46. PMID 16468433.
(subscription required)
^ abc Schuster SC (January 2008). "Next-generation sequencing transforms today's biology". Nat. Methods. 5 (1): 16–18. doi:10.1038/nmeth1156. PMID 18165802.
^ Kalb, Gilbert; Moxley, Robert (1992). Massively Parallel, Optical, and Neural Computing in the United States. IOS Press. ISBN 978-90-5199-097-3.
[page needed]
^ ten Bosch JR, Grody WW (2008). "Keeping Up with the Next Generation". The Journal of Molecular Diagnostics. 10 (6): 484–92. doi:10.2353/jmoldx.2008.080027. PMC 2570630. PMID 18832462.

^ Tucker T, Marra M, Friedman JM (2009). "Massively Parallel Sequencing: The Next Big Thing in Genetic Medicine". The American Journal of Human Genetics. 85 (2): 142–54. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2009.06.022. PMC 2725244. PMID 19679224.

^ ab Straiton, Jenny; Free, Tristan; Sawyer, Abigail; Martin, Joseph (February 2019). "From Sanger Sequencing to Genome Databases and Beyond". BioTechniques. Future Science. 66 (2): 60–63. doi:10.2144/btn-2019-0011.
^ Quail MA, Smith M, Coupland P, Otto TD, Harris SR, Connor TR, Bertoni A, Swerdlow HP, Gu Y (1 January 2012). "A tale of three next generation sequencing platforms: comparison of Ion Torrent, Pacific Biosciences and illumina MiSeq sequencers". BMC Genomics. 13 (1): 341. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-13-341. PMC 3431227. PMID 22827831.

^ Liu L, Li Y, Li S, Hu N, He Y, Pong R, Lin D, Lu L, Law M (1 January 2012). "Comparison of Next-Generation Sequencing Systems". Journal of Biomedicine and Biotechnology. 2012: 1–11. doi:10.1155/2012/251364. PMC 3398667. PMID 22829749.

^ abc "New Software, Polymerase for Sequel System Boost Throughput and Affordability – PacBio". 7 March 2018.
^ "After a Year of Testing, Two Early PacBio Customers Expect More Routine Use of RS Sequencer in 2012". GenomeWeb. 10 January 2012.
(registration required)
^ Inc., Pacific Biosciences (2013). "Pacific Biosciences Introduces New Chemistry With Longer Read Lengths to Detect Novel Features in DNA Sequence and Advance Genome Studies of Large Organisms".
^ Chin CS, Alexander DH, Marks P, Klammer AA, Drake J, Heiner C, Clum A, Copeland A, Huddleston J, Eichler EE, Turner SW, Korlach J (2013). "Nonhybrid, finished microbial genome assemblies from long-read SMRT sequencing data". Nat. Methods. 10 (6): 563–69. doi:10.1038/nmeth.2474. PMID 23644548.
^ ab "De novo bacterial genome assembly: a solved problem?". 5 July 2013.
^ Rasko DA, Webster DR, Sahl JW, Bashir A, Boisen N, Scheutz F, Paxinos EE, Sebra R, Chin CS, Iliopoulos D, Klammer A, Peluso P, Lee L, Kislyuk AO, Bullard J, Kasarskis A, Wang S, Eid J, Rank D, Redman JC, Steyert SR, Frimodt-Møller J, Struve C, Petersen AM, Krogfelt KA, Nataro JP, Schadt EE, Waldor MK (25 August 2011). "Origins of the Strain Causing an Outbreak of Hemolytic–Uremic Syndrome in Germany". N Engl J Med. 365 (8): 709–17. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1106920. PMC 3168948. PMID 21793740.

^ Tran B, Brown AM, Bedard PL, Winquist E, Goss GD, Hotte SJ, Welch SA, Hirte HW, Zhang T, Stein LD, Ferretti V, Watt S, Jiao W, Ng K, Ghai S, Shaw P, Petrocelli T, Hudson TJ, Neel BG, Onetto N, Siu LL, McPherson JD, Kamel-Reid S, Dancey JE (1 January 2012). "Feasibility of real time next generation sequencing of cancer genes linked to drug response: Results from a clinical trial". Int. J. Cancer. 132 (7): 1547–55. doi:10.1002/ijc.27817. PMID 22948899.
(subscription required)
^ Murray IA, Clark TA, Morgan RD, Boitano M, Anton BP, Luong K, Fomenkov A, Turner SW, Korlach J, Roberts RJ (2 October 2012). "The methylomes of six bacteria". Nucleic Acids Research. 40 (22): 11450–62. doi:10.1093/nar/gks891. PMC 3526280. PMID 23034806.
^ "Ion 520 & Ion 530 ExT Kit-Chef – Thermo Fisher Scientific". www.thermofisher.com.
^ [1][dead link]
^ van Vliet AH (1 January 2010). "Next generation sequencing of microbial transcriptomes: challenges and opportunities". FEMS Microbiology Letters. 302 (1): 1–7. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6968.2009.01767.x. PMID 19735299.

^ "BGI and MGISEQ". en.mgitech.cn. Retrieved 2018-07-05.
^ ab Huang YF, Chen SC, Chiang YS, Chen TH, Chiu KP (2012). "Palindromic sequence impedes sequencing-by-ligation mechanism". BMC Systems Biology. 6 Suppl 2: S10. doi:10.1186/1752-0509-6-S2-S10. PMC 3521181. PMID 23281822.
^ ab Shendure J, Porreca GJ, Reppas NB, Lin X, McCutcheon JP, Rosenbaum AM, Wang MD, Zhang K, Mitra RD, Church GM (9 Sep 2005). "Accurate multiplex polony sequencing of an evolved bacterial genome". Science. 309 (5741): 1728–32. Bibcode:2005Sci...309.1728S. doi:10.1126/science.1117389. PMID 16081699.
^ Bentley DR, Balasubramanian S, et al. (2008). "Accurate whole human genome sequencing using reversible terminator chemistry". Nature. 456 (7218): 53–59. Bibcode:2008Natur.456...53B. doi:10.1038/nature07517. PMC 2581791. PMID 18987734.
^ Canard, Bruno; Sarfati, Simon (13 Oct 1994), Novel derivatives usable for the sequencing of nucleic acids, retrieved 2016-03-09
^ Canard, Bruno; Sarfati, Robert S. (1994-10-11). "DNA polymerase fluorescent substrates with reversible 3′-tags". Gene. 148 (1): 1–6. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(94)90226-7. PMID 7523248.
^ Mardis ER (2008). "Next-generation DNA sequencing methods". Annu Rev Genom Hum Genet. 9: 387–402. doi:10.1146/annurev.genom.9.081307.164359. PMID 18576944.
^ abc Drmanac, Radoje; Sparks, Andrew B.; Callow, Matthew J.; Halpern, Aaron L.; Burns, Norman L.; Kermani, Bahram G.; Carnevali, Paolo; Nazarenko, Igor; Nilsen, Geoffrey B. (2010-01-01). "Human Genome Sequencing Using Unchained Base Reads on Self-Assembling DNA Nanoarrays". Science. 327 (5961): 78–81. Bibcode:2010Sci...327...78D. doi:10.1126/science.1181498. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 19892942.
^ brandonvd. "About Us - Complete Genomics". Complete Genomics. Retrieved 2018-07-02.
^ ab Huang, Jie; Liang, Xinming; Xuan, Yuankai; Geng, Chunyu; Li, Yuxiang; Lu, Haorong; Qu, Shoufang; Mei, Xianglin; Chen, Hongbo (2017-05-01). "A reference human genome dataset of the BGISEQ-500 sequencer". GigaScience. 6 (5): 1–9. doi:10.1093/gigascience/gix024. PMC 5467036. PMID 28379488.
^ Valouev A, Ichikawa J, Tonthat T, Stuart J, Ranade S, Peckham H, Zeng K, Malek JA, Costa G, McKernan K, Sidow A, Fire A, Johnson SM (July 2008). "A high-resolution, nucleosome position map of C. elegans reveals a lack of universal sequence-dictated positioning". Genome Res. 18 (7): 1051–63. doi:10.1101/gr.076463.108. PMC 2493394. PMID 18477713.
^ Rusk N (2011). "Torrents of sequence". Nat Methods. 8 (1): 44. doi:10.1038/nmeth.f.330.
^ ab Drmanac R, Sparks AB, et al. (2010). "Human Genome Sequencing Using Unchained Base Reads in Self-Assembling DNA Nanoarrays". Science. 327 (5961): 78–81. Bibcode:2010Sci...327...78D. doi:10.1126/science.1181498. PMID 19892942.
^ Porreca GJ (2010). "Genome Sequencing on Nanoballs". Nature Biotechnology. 28 (1): 43–44. doi:10.1038/nbt0110-43. PMID 20062041.
^ Complete Genomics Press release, 2010
^ "HeliScope Gene Sequencing / Genetic Analyzer System : Helicos BioSciences". 2 November 2009. Archived from the original on 2009-11-02.
^ Thompson JF, Steinmann KE (October 2010). Single molecule sequencing with a HeliScope genetic analysis system. Current Protocols in Molecular Biology. Chapter 7. pp. Unit7.10. doi:10.1002/0471142727.mb0710s92. ISBN 978-0471142720. PMC 2954431. PMID 20890904.
^ "tSMS SeqLL Technical Explanation". SeqLL. Archived from the original on 8 August 2014. Retrieved 9 Aug 2015.
^ Sara El-Metwally; Osama M. Ouda; Mohamed Helmy (2014). "New Horizons in Next-Generation Sequencing". Next Generation Sequencing Technologies and Challenges in Sequence Assembly. Next Generation Sequencing Technologies and Challenges in Sequence Assembly, Springer Briefs in Systems Biology Volume 7. SpringerBriefs in Systems Biology. 7. pp. 51–59. doi:10.1007/978-1-4939-0715-1_6. ISBN 978-1-4939-0714-4.
^ "PacBio Sales Start to Pick Up as Company Delivers on Product Enhancements".
^ "Bio-IT World". www.bio-itworld.com.
^ "PacBio Launches Higher-Throughput, Lower-Cost Single-Molecule Sequencing System".
^ Clarke, James; Wu, Hai-Chen; Jayasinghe, Lakmal; Patel, Alpesh; Reid, Stuart; Bayley, Hagan (2009-04-01). "Continuous base identification for single-molecule nanopore DNA sequencing". Nature Nanotechnology. 4 (4): 265–70. Bibcode:2009NatNa...4..265C. doi:10.1038/nnano.2009.12. ISSN 1748-3387. PMID 19350039.
^ ab dela Torre R, Larkin J, Singer A, Meller A (2012). "Fabrication and characterization of solid-state nanopore arrays for high-throughput DNA sequencing". Nanotechnology. 23 (38): 385308. Bibcode:2012Nanot..23L5308D. doi:10.1088/0957-4484/23/38/385308. PMC 3557807. PMID 22948520.
^ ab Pathak B, Lofas H, Prasongkit J, Grigoriev A, Ahuja R, Scheicher RH (2012). "Double-functionalized nanopore-embedded gold electrodes for rapid DNA sequencing". Applied Physics Letters. 100 (2): 023701. Bibcode:2012ApPhL.100b3701P. doi:10.1063/1.3673335.
^ Korlach J, Marks PJ, Cicero RL, Gray JJ, Murphy DL, Roitman DB, Pham TT, Otto GA, Foquet M, Turner SW (2008). "Selective aluminum passivation for targeted immobilization of single DNA polymerase molecules in zero-mode waveguide nanostructures". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 105 (4): 1176–81. Bibcode:2008PNAS..105.1176K. doi:10.1073/pnas.0710982105. PMC 2234111. PMID 18216253.
^ "The Harvard Nanopore Group". Mcb.harvard.edu. Archived from the original on 21 February 2002. Retrieved 15 November 2009.
^ "Nanopore Sequencing Could Slash DNA Analysis Costs".
^ US patent 20060029957, ZS Genetics, "Systems and methods of analyzing nucleic acid polymers and related components", issued 2005-07-14
^ Xu M, Fujita D, Hanagata N (December 2009). "Perspectives and challenges of emerging single-molecule DNA sequencing technologies". Small. 5 (23): 2638–49. doi:10.1002/smll.200900976. PMID 19904762.
^ Schadt EE, Turner S, Kasarskis A (2010). "A window into third-generation sequencing". Human Molecular Genetics. 19 (R2): R227–40. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddq416. PMID 20858600.
^ Xu M, Endres RG, Arakawa Y (2007). "The electronic properties of DNA bases". Small. 3 (9): 1539–43. doi:10.1002/smll.200600732. PMID 17786897.
^ Di Ventra M (2013). "Fast DNA sequencing by electrical means inches closer". Nanotechnology. 24 (34): 342501. Bibcode:2013Nanot..24H2501D. doi:10.1088/0957-4484/24/34/342501. PMID 23899780.
^ Ohshiro T, Matsubara K, Tsutsui M, Furuhashi M, Taniguchi M, Kawai T (2012). "Single-molecule electrical random resequencing of DNA and RNA". Sci Rep. 2: 501. Bibcode:2012NatSR...2E.501O. doi:10.1038/srep00501. PMC 3392642. PMID 22787559.
^ Hanna GJ, Johnson VA, Kuritzkes DR, Richman DD, Martinez-Picado J, Sutton L, Hazelwood JD, D'Aquila RT (1 July 2000). "Comparison of Sequencing by Hybridization and Cycle Sequencing for Genotyping of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Reverse Transcriptase". J. Clin. Microbiol. 38 (7): 2715–21. PMC 87006. PMID 10878069.
^ ab Morey M, Fernández-Marmiesse A, Castiñeiras D, Fraga JM, Couce ML, Cocho JA (2013). "A glimpse into past, present, and future DNA sequencing". Molecular Genetics and Metabolism. 110 (1–2): 3–24. doi:10.1016/j.ymgme.2013.04.024. PMID 23742747.
^ Qin Y, Schneider TM, Brenner MP (2012). Gibas C, ed. "Sequencing by Hybridization of Long Targets". PLoS ONE. 7 (5): e35819. Bibcode:2012PLoSO...735819Q. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0035819. PMC 3344849. PMID 22574124.
^ Edwards JR, Ruparel H, Ju J (2005). "Mass-spectrometry DNA sequencing". Mutation Research. 573 (1–2): 3–12. doi:10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2004.07.021. PMID 15829234.
^ Hall TA, Budowle B, Jiang Y, Blyn L, Eshoo M, Sannes-Lowery KA, Sampath R, Drader JJ, Hannis JC, Harrell P, Samant V, White N, Ecker DJ, Hofstadler SA (2005). "Base composition analysis of human mitochondrial DNA using electrospray ionization mass spectrometry: A novel tool for the identification and differentiation of humans". Analytical Biochemistry. 344 (1): 53–69. doi:10.1016/j.ab.2005.05.028. PMID 16054106.
^ Howard R, Encheva V, Thomson J, Bache K, Chan YT, Cowen S, Debenham P, Dixon A, Krause JU, Krishan E, Moore D, Moore V, Ojo M, Rodrigues S, Stokes P, Walker J, Zimmermann W, Barallon R (15 Jun 2011). "Comparative analysis of human mitochondrial DNA from World War I bone samples by DNA sequencing and ESI-TOF mass spectrometry". Forensic Science International: Genetics. 7 (1): 1–9. doi:10.1016/j.fsigen.2011.05.009. PMID 21683667.
^ Monforte JA, Becker CH (1 March 1997). "High-throughput DNA analysis by time-of-flight mass spectrometry". Nature Medicine. 3 (3): 360–62. doi:10.1038/nm0397-360. PMID 9055869.
^ Beres SB, Carroll RK, Shea PR, Sitkiewicz I, Martinez-Gutierrez JC, Low DE, McGeer A, Willey BM, Green K, Tyrrell GJ, Goldman TD, Feldgarden M, Birren BW, Fofanov Y, Boos J, Wheaton WD, Honisch C, Musser JM (8 February 2010). "Molecular complexity of successive bacterial epidemics deconvoluted by comparative pathogenomics". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 107 (9): 4371–76. Bibcode:2010PNAS..107.4371B. doi:10.1073/pnas.0911295107. PMC 2840111. PMID 20142485.
^ Kan CW, Fredlake CP, Doherty EA, Barron AE (1 November 2004). "DNA sequencing and genotyping in miniaturized electrophoresis systems". Electrophoresis. 25 (21–22): 3564–88. doi:10.1002/elps.200406161. PMID 15565709.
^ Chen YJ, Roller EE, Huang X (2010). "DNA sequencing by denaturation: experimental proof of concept with an integrated fluidic device". Lab on a Chip. 10 (9): 1153–59. doi:10.1039/b921417h. PMC 2881221. PMID 20390134.
^ Bell DC, Thomas WK, Murtagh KM, Dionne CA, Graham AC, Anderson JE, Glover WR (9 Oct 2012). "DNA Base Identification by Electron Microscopy". Microscopy and Microanalysis : The Official Journal of Microscopy Society of America, Microbeam Analysis Society, Microscopical Society of Canada. 18 (5): 1049–53. Bibcode:2012MiMic..18.1049B. doi:10.1017/S1431927612012615. PMID 23046798.
^ Pareek CS, Smoczynski R, Tretyn A (November 2011). "Sequencing technologies and genome sequencing". Journal of Applied Genetics. 52 (4): 413–35. doi:10.1007/s13353-011-0057-x. PMC 3189340. PMID 21698376.
^ Pareek CS, Smoczynski R, Tretyn A (2011). "Sequencing technologies and genome sequencing". Journal of Applied Genetics. 52 (4): 413–35. doi:10.1007/s13353-011-0057-x. PMC 3189340. PMID 21698376.
^ Fujimori S, Hirai N, Ohashi H, Masuoka K, Nishikimi A, Fukui Y, Washio T, Oshikubo T, Yamashita T, Miyamoto-Sato E (2012). "Next-generation sequencing coupled with a cell-free display technology for high-throughput production of reliable interactome data". Scientific Reports. 2: 691. Bibcode:2012NatSR...2E.691F. doi:10.1038/srep00691. PMC 3466446. PMID 23056904.
^ Harbers M (2008). "The Current Status of cDNA Cloning". Genomics. 91 (3): 232–42. doi:10.1016/j.ygeno.2007.11.004. PMID 18222633.
^ Alberti A, Belser C, Engelen S, Bertrand L, Orvain C, Brinas L, Cruaud C, et al. (2014). "Comparison of Library Preparation Methods Reveals Their Impact on Interpretation of Metatranscriptomic Data". BMC Genomics. 15: 912–12. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-15-912. PMC 4213505. PMID 25331572.
^ "Scalable Nucleic Acid Quality Assessments for Illumina Next-Generation Sequencing Library Prep" (PDF). Retrieved 2017-12-27.
^ "Archon Genomics XPRIZE". Archon Genomics XPRIZE.
^ "Grant Information". National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI).
^ Severin J, Lizio M, Harshbarger J, Kawaji H, Daub CO, Hayashizaki Y, Bertin N, Forrest AR (2014). "Interactive visualization and analysis of large-scale sequencing datasets using ZENBU". Nat. Biotechnol. 32 (3): 217–19. doi:10.1038/nbt.2840. PMID 24727769.
^ Shmilovici A, Ben-Gal I (2007). "Using a VOM model for reconstructing potential coding regions in EST sequences" (PDF). Computational Statistics. 22 (1): 49–69. doi:10.1007/s00180-007-0021-8.
^ Del Fabbro C, Scalabrin S, Morgante M, Giorgi FM (2013). "An Extensive Evaluation of Read Trimming Effects on Illumina NGS Data Analysis". PLoS ONE. 8 (12): e85024. Bibcode:2013PLoSO...885024D. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0085024. PMC 3871669. PMID 24376861.
^ Martin, Marcel (2 May 2011). "Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads". EMBnet.journal. 17 (1): 10. doi:10.14806/ej.17.1.200.
^ Smeds, Linnéa; Künstner, Axel; Donlin, Maureen J. (19 October 2011). "ConDeTri - A Content Dependent Read Trimmer for Illumina Data". PLoS ONE. 6 (10): e26314. Bibcode:2011PLoSO...626314S. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0026314. PMC 3198461. PMID 22039460.
^ Spandow, O; Hellström, S; Schmidt, SH; De Paoli, Emanuale; Policriti, Alberto (2012). ERNE-BS5: Aligning BS-treated Sequences by Multiple Hits on a 5-letters Alphabet. Proceedings of the ACM Conference on Bioinformatics, Computational Biology and Biomedicine. 12. pp. 12–19. doi:10.1145/2382936.2382938. ISBN 9781450316705.
^ Schmieder, R.; Edwards, R. (28 January 2011). "Quality control and preprocessing of metagenomic datasets". Bioinformatics. 27 (6): 863–64. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btr026. PMC 3051327. PMID 21278185.
^ Bolger, A. M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. (1 April 2014). "Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data". Bioinformatics. 30 (15): 2114–20. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btu170. PMC 4103590. PMID 24695404.
^ Cox, Murray P; Peterson, Daniel A; Biggs, Patrick J (2010). "SolexaQA: At-a-glance quality assessment of Illumina second-generation sequencing data". BMC Bioinformatics. 11 (1): 485. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-11-485. PMC 2956736. PMID 20875133.
^ Murray, TH (January 1991). "Ethical issues in human genome research". FASEB Journal. 5 (1): 55–60. PMID 1825074.
^ abc Robertson, John A. (August 2003). "The $1000 Genome: Ethical and Legal Issues in Whole Genome Sequencing of Individuals". The American Journal of Bioethics. 3 (3): 35–42. doi:10.1162/152651603322874762. PMID 14735880.
^ ab Henderson, Mark (2013-09-09). "Human genome sequencing: the real ethical dilemmas". The Guardian. Retrieved 20 May 2015.
^ Harmon, Amy (24 February 2008). "Insurance Fears Lead Many to Shun DNA Tests". The New York Times. Retrieved 20 May 2015.
^ Statement of Administration policy, Executive Office of the President, Office of Management and Budget, 27 April 2007
^ National Human Genome Research Institute (21 May 2008). "President Bush Signs the Genetic Information Nondiscrimination Act of 2008". Retrieved 17 Feb 2014.
^ Baker, Monya. "US ethics panel reports on DNA sequencing and privacy". Nature New Blog. Retrieved 20 May 2015.
^ "Privacy and Progress in Whole Genome Sequencing" (PDF). Presidential Commission for the Study of Bioethical Issues. Retrieved 20 May 2015.
^ Goldenberg, Aaron J.; Sharp, Richard R. (1 February 2012). "The Ethical Hazards and Programmatic Challenges of Genomic Newborn Screening". JAMA. 307 (5): 461–2. doi:10.1001/jama.2012.68. PMC 3868436. PMID 22298675.
^ Hughes, Virginia (2013-01-07). "It's Time To Stop Obsessing About the Dangers of Genetic Information". Slate Magazine. Retrieved 22 May 2015.
^ ab Bloss, Cinnamon S.; Schork, Nicholas J.; Topol, Eric J. (10 February 2011). "Effect of Direct-to-Consumer Genomewide Profiling to Assess Disease Risk". New England Journal of Medicine. 364 (6): 524–34. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1011893. PMC 3786730. PMID 21226570.
^ Rochman, Bonnie (25 October 2012). "What Your Doctor Isn't Telling You About Your DNA". Time.com. Retrieved 22 May 2015.
External links
Library resources about DNA sequencing |
|
| Wikibooks has a book on the topic of: Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) |
- A wikibook on next generation sequencing
- A free didactic directory for DNA sequencing analysis.
- A The path to DNA sequencing: The life and work of Fred Sanger
- A US Map of New Generation Sequencers
- A Introduction of Sequencing History: Sequencing in 20th Century

Comments
Post a Comment