British Overseas Territories
British Overseas Territories | |
|---|---|
 Flag of the United Kingdom | |
 Location of the United Kingdom and the British Overseas Territories | |
| Largest settlements | George Town, Gibraltar, Road Town |
| Official language | English |
| Demonym(s) | British, Briton |
| Territories | 14 territories
|
| Leaders | |
• Monarch | Elizabeth II |
• Foreign Secretary | Jeremy Hunt |
• Minister of State | Tariq Ahmad |
• Minister of State | Alan Duncan |
| Area | |
• Total | 1,727,570 km2 (667,020 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• 2010 estimate | 250,020 |
| Date format | dd/mm/yyyy (AD) |
The British Overseas Territories (BOTs) or United Kingdom Overseas Territories (UKOTs) are 14 territories under the jurisdiction and sovereignty of the United Kingdom.[1][2] They are remnants of the British Empire that have not been granted independence or have voted to remain British territories. These territories do not form part of the United Kingdom and, with the exception of Gibraltar, are not part of the European Union. Most of the permanently inhabited territories are internally self-governing, with the UK retaining responsibility for defence and foreign relations. Three are inhabited only by a transitory population of military or scientific personnel. They all share the British monarch (Elizabeth II) as head of state.
As of April 2018[update] the Minister responsible for the Territories excluding the Falkland Islands, Gibraltar and the Sovereign Base Areas on Cyprus, is the Minister of State for the Commonwealth and the UN. The other three territories are the responsibility of the Minister of State for Europe and the Americas[3].
Contents
1 Current overseas territories
1.1 Map
2 Collective titles
3 Population
4 History
5 Government
5.1 Head of state
5.2 Local government
5.3 Legal system
5.4 Joint Ministerial Council
6 Relations with the United Kingdom
6.1 Foreign affairs
6.2 Citizenship
6.3 Military
7 Languages
8 Currencies
9 Symbols and insignia
10 Sports
11 Biodiversity
12 See also
13 References
14 Further reading
15 External links
Current overseas territories
The fourteen British Overseas Territories are:[4]
| Flag | Arms | Name | Location | Motto | Area | Population | Capital |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Akrotiri and Dhekelia | Cyprus, Mediterranean Sea | 255 km2 (98 sq mi)[5] | 7,700 (Cypriots; estimate) 8,000 non-permanent (UK military personnel and their families; estimate) | Episkopi Cantonment | |||
Anguilla | Caribbean, North Atlantic Ocean | "Strength and Endurance" | 91 km2 (35.1 sq mi)[6] | 13,500 (2006 estimate)[7] | The Valley | ||
Bermuda | North Atlantic Ocean between the Azores, the Caribbean, Cape Sable Island and Canada | "Quo fata ferunt" (Latin; "Whither the Fates carry [us]") | 54 km2 (20.8 sq mi)[8] | 64,000 (2007 estimate)[9] | Hamilton | ||
British Antarctic Territory | Antarctica | "Research and discovery" | 1,709,400 km2 (660,000 sq mi)[6] | 0 50 non-permanent in winter, over 400 in summer (research personnel)[10] | Rothera (main base) | ||
British Indian Ocean Territory | Indian Ocean | "In tutela nostra Limuria" (Latin; "Limuria is in our charge") | 60 km2 (23 sq mi)[11] | 0 3,000 non-permanent (UK and US military and staff personnel; estimate)[12] | Diego Garcia (base) | ||
British Virgin Islands | Caribbean, North Atlantic Ocean | "Vigilate" (Latin; "Be watchful") | 153 km2 (59 sq mi)[13] | 27,000 (2005 estimate)[13] | Road Town | ||
Cayman Islands | Caribbean | "He hath founded it upon the seas" | 264 km2 (101.9 sq mi)[14] | 64,420 (2018 estimate)[14] | George Town | ||
Falkland Islands | South Atlantic Ocean | "Desire the right" | 12,173 km2 (4,700 sq mi)[8] | 2,955 (2006 census)[15] 1,350 non-permanent (UK military personnel; 2012 estimate) | Stanley | ||
Gibraltar | Iberian Peninsula, Continental Europe | "Nulli expugnabilis hosti" (Latin; "No enemy shall expel us") | 6.5 km2 (2.5 sq mi)[16] | 28,800 (2005 estimate)[17] 1,250 non-permanent (UK military personnel; 2012 estimate) | Gibraltar | ||
Montserrat | Caribbean, North Atlantic Ocean | "A people of excellence, moulded by nature, nurtured by God" | 101 km2 (39 sq mi)[18] | 4,655 (2006 estimate)[18] | Plymouth (abandoned due to volcano—de facto capital is Brades) | ||
Pitcairn, Henderson, Ducie and Oeno Islands | Pacific Ocean | 47 km2 (18 sq mi)[19] | 49 (2014 estimate)[20] 6 non-permanent (2014 estimate)[21] | Adamstown | |||
Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha, including: | South Atlantic Ocean | 420 km2 (162 sq mi) | 5,530 (total; estimate) | Jamestown | |||
Saint Helena | "Loyal and Unshakeable" (Saint Helena) | 4,255 (Saint Helena; 2008 census)[22] | |||||
Ascension Island | 880 (Ascension; estimate)[23] 1,000 non-permanent (Ascension; UK military personnel; estimate)[23] | ||||||
Tristan da Cunha | "Our faith is our strength" (Tristan da Cunha) | 300 (Tristan da Cunha; estimate)[23] 9 non-permanent (Tristan da Cunha; weather personnel) | |||||
South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands | South Atlantic Ocean | "Leo terram propriam protegat" (Latin; "Let the lion protect his own land") | 4,066 km2 (1,570 sq mi)[24] | 0 99 non-permanent (officials and research personnel)[25] | King Edward Point | ||
Turks and Caicos Islands | Lucayan Archipelago, North Atlantic Ocean | 430 km2 (166 sq mi)[26] | 32,000 (2006 census)[26] | Cockburn Town | |||
| Overall | 1,727,570 km2 | c. 250,000 |
Map
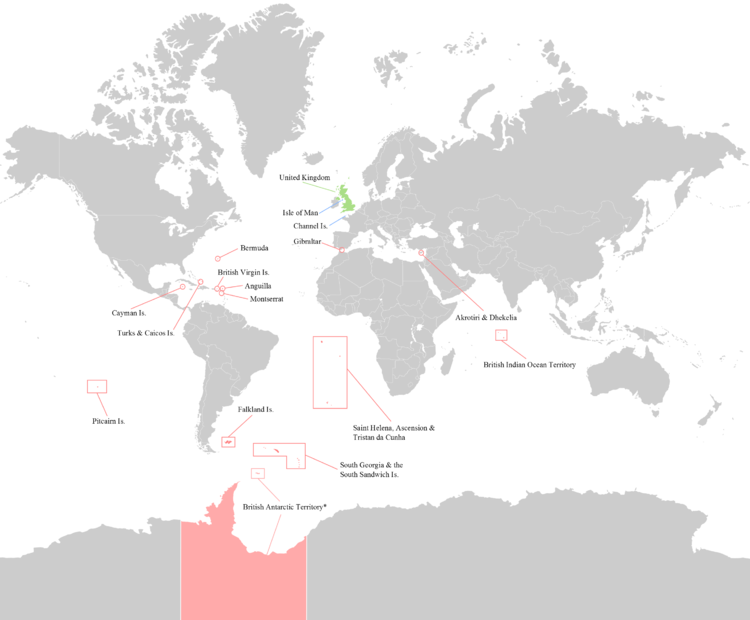
British Overseas Territories
United Kingdom
Crown dependencies
Collective titles

Unofficial flag for the overseas territories used by Friends of the British Overseas Territories, a charitable organisation.[27]
United Kingdom |
|---|
 |
This article is part of a series on the politics and government of the United Kingdom |
Constitution
|
The Crown British Monarchy
|
Executive HM Government
Privy Council
|
Legislature Parliament (57th Parliament) Crown-in-Parliament
House of Lords
House of Commons
|
Judiciary Supreme Court
|
Devolution
Scotland
Wales
Northern Ireland
England
|
Administrative geography
|
Elections
General Elections
Referendums
|
Crown Dependencies
|
Overseas Territories
|
Foreign relations
|
|
The term "British Overseas Territory" was introduced by the British Overseas Territories Act 2002, replacing the term British Dependent Territory, introduced by the British Nationality Act 1981. Prior to 1 January 1983, the territories were officially referred to as British Crown Colonies.
Although the Crown dependencies of Jersey, Guernsey, and the Isle of Man are also under the sovereignty of the British monarch, they are in a different constitutional relationship with the United Kingdom.[28][29] The British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies are themselves distinct from the Commonwealth realms, a group of 16 independent countries (including the United Kingdom) each having Elizabeth II as their reigning monarch, and from the Commonwealth of Nations, a voluntary association of 53 countries mostly with historic links to the British Empire (which also includes all Commonwealth realms).
Population
With the exceptions of the British Antarctic Territory and South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands (which host only officials and research station staff) and the British Indian Ocean Territory (used as a military base), the Territories retain permanent civilian populations. Permanent residency for the approximately 7,000 civilians living in the Sovereign Base Areas of Akrotiri and Dhekelia is limited to citizens of the Republic of Cyprus.
Collectively, the Territories encompass a population of about 250,000 people and a land area of about 1,727,570 square kilometres (667,020 sq mi). The vast majority of this land area, 1,700,000 square kilometres (660,000 sq mi), constitutes the almost uninhabited British Antarctic Territory, while the largest territory by population, Bermuda, accounts for almost a quarter of the total BOT population. At the other end of the scale, three territories have no civilian population; the Antarctic territory, the British Indian Ocean Territory (from which the Chagos Islanders were controversially removed) and South Georgia. Pitcairn Islands, settled by the survivors of the Mutiny on the Bounty, is the smallest settled territory with 49 inhabitants, while the smallest by land area is Gibraltar on the southern tip of the Iberian peninsula.[30][31] The United Kingdom participates in the Antarctic Treaty System[32] and, as part of a mutual agreement, the British Antarctic Territory is recognised by four of the six other sovereign nations making claims to Antarctic territory.
History

St. George's town, in the Islands of Bermuda, or "The Somers Isles". The colony was founded by the wrecking of the flagship of the Virginia Company in 1609. The Company's charter was extended to include Bermuda in 1612, and it has remained a British colony ever since. Since the rebellion of Virginia, it has been the oldest-remaining British colony, and the town of St. George's is the oldest continuously inhabited British settlement in the New World.[33]
Early colonies, in the sense of English subjects residing in lands hitherto outside the control of the English government, were generally known as "Plantations".
The first, unofficial, colony was Newfoundland, where English fishermen routinely set up seasonal camps in the 16th century.[34] It is now a province of Canada known as Newfoundland and Labrador. It retains strong cultural ties with Britain.
English colonisation of North America began officially in 1607 with the settlement of Jamestown, the first successful permanent colony in Virginia (a term that was then applied generally to North America). Its offshoot, Bermuda, was settled inadvertently after the wrecking of the Virginia company's flagship there in 1609, with the Virginia Company's charter extended to officially include the archipelago in 1612. St. George's town, founded in Bermuda in that year, remains the oldest continuously inhabited British settlement in the New World (with some historians stating that – its formation predating the 1619 conversion of "James Fort" into "Jamestown" – St. George's was actually the first successful town the English established in the New World). Bermuda and Bermudians have played important, sometimes pivotal, but generally underestimated or unacknowledged roles in the shaping of the English and British trans-Atlantic Empires. These include maritime commerce, settlement of the continent and of the West Indies, and the projection of naval power via the colony's privateers, among other areas.[35][36]
The growth of the British Empire in the 19th century, to its territorial peak in the 1920s, saw Britain acquire nearly one quarter of the world's land mass, including territories with large indigenous populations in Asia and Africa. From the mid-nineteenth century to the early twentieth century, the larger settler colonies – in Canada, Australia, New Zealand and South Africa – first became self-governing colonies and then achieved independence in all matters except foreign policy, defence and trade. Separate self-governing colonies federated to become Canada (in 1867), Australia (in 1901), South Africa (in 1910), and Rhodesia (in 1965). These and other large self-governing colonies had become known as Dominions by the 1920s. The Dominions achieved almost full independence with the Statute of Westminster (1931).

Many of the overseas territories are in the Caribbean, as shown on the map.
Through a process of decolonisation following the Second World War, most of the British colonies in Africa, Asia and the Caribbean gained independence. Some colonies became Commonwealth realms, retaining the British monarch as their own head of state.[37] Most former colonies and protectorates became member states of the Commonwealth of Nations, a non-political, voluntary association of equal members, comprising a population of around 2.2 billion people.[38]
After the independence of Southern Rhodesia (now Zimbabwe) in Africa in 1980 and British Honduras (now Belize) in Central America in 1981, the last major colony that remained was Hong Kong, with a population of over 5 million.[39] With 1997 approaching, the United Kingdom and China negotiated the Sino-British Joint Declaration, which led to the whole of Hong Kong becoming a "special administrative region" of China in 1997, subject to various conditions intended to guarantee the preservation of Hong Kong's capitalist economy and its way of life under British rule for at least 50 years after the handover. George Town in the Cayman Islands has consequently become the largest city in the Overseas Territories.
In 2002, the British Parliament passed the British Overseas Territories Act 2002. This reclassified the UK's dependent territories as overseas territories and, with the exception of those people solely connected with the Sovereign Base Areas of Cyprus, restored full British citizenship to their inhabitants.[40]
Government

McKeeva Bush, Premier of the Cayman Islands in 2012
Head of state
The head of state in the overseas territories is the British monarch, Elizabeth II. The Queen's role in the territories is in her role as Queen of the United Kingdom, and not in right of each territory.[citation needed] The Queen appoints a representative in each territory to exercise her executive power. In territories with a permanent population, a Governor is appointed by the Queen on the advice of the British Government, usually a retired senior military officer,[citation needed] or a senior civil servant. In territories without a permanent population, a Commissioner is usually appointed to represent the Queen. Exceptionally, in the oversea territory of Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha, an Administrator is appointed to be the Governor's representative in each of the two distant parts of the territory, namely Ascension Island and Tristan da Cunha.
The role of the Governor is to act as the de facto head of state, and they are usually responsible for appointing the head of government, and senior political positions in the territory. The Governor is also responsible for liaising with the UK Government, and carrying out any ceremonial duties. A Commissioner has the same powers as a Governor, but also acts as the head of government.[citation needed]
Local government
All the overseas territories have their own system of government, and localised laws. The structure of the government appears to be closely correlated to the size and political development of the territory.[citation needed]
| Territories | Government |
|---|---|
| There is no native or permanent population; therefore there is no elected government. The Commissioner, supported by an Administrator, run the affairs of the territory. |
| There is no elected government, as there is no native settled population. The Chagos Islanders – who were forcibly evicted from the territory in 1971 – won a High Court Judgement allowing them to return, but this was then overridden by an Order in Council preventing them from returning. The final appeal to the House of Lords (regarding the lawfulness of the Order in Council) was decided in the government's favour, exhausting the islanders' legal options in the United Kingdom at present. |
| There is no elected government. The Commander British Forces Cyprus acts as the territory's Administrator, with a Chief Officer responsible for day-to-day running of the civil government. As far as possible, there is convergence of laws[clarification needed] with those of the Republic of Cyprus. |
| There are an elected Mayor and Island Council, who have the power to propose and administer local legislation. However, their decisions are subject to approval by the Governor, who retains near-unlimited powers of plenary legislation on behalf of the United Kingdom Government. |
| The Government consists of an elected Legislative Assembly, with the Chief Executive and the Director of Corporate Resources as ex officio members.[41] |
| The Government consists of an elected Legislative Council. The Governor is the head of government and leads the Executive Council, consisting of appointed members made up from the Legislative Council and two ex-officio members. Governance on Ascension Island and Tristan da Cunha is led by Administrators who are advised by elected Island Councils.[42] |
| These territories have a House of Assembly, Legislative Assembly (Cayman Islands and Montserrat), with political parties. The Executive Council is usually called a cabinet and is led by a Premier or a Chief Minister (in Anguilla), who is the leader of the majority party in parliament. The Governor exercises less power over local affairs and deals mostly with foreign affairs and economic issues, while the elected government controls most "domestic" concerns.[citation needed] |
| Under the Gibraltar Constitution Order 2006 which was approved in Gibraltar by a referendum, Gibraltar now has a Parliament. The Government of Gibraltar, headed by the Chief Minister, is elected. Defence, external affairs and internal security vest in the Governor.[43] |
| Bermuda, settled in 1609, and self-governed since 1620, is the oldest and most populous of the Overseas Territories. The bicameral Parliament consists of a Senate and a House of Assembly, and most executive powers have been devolved to the head of government, known as the Premier.[44] |
| The Turks and Caicos Islands adopted a new constitution effective 9 August 2006; their head of government now also has the title Premier, their legislature is called the House of Assembly, and their autonomy has been greatly increased.[citation needed] |
Legal system
British Overseas Territories Joint Ministerial Council | |
|---|---|
| Type | |
| Type | Dialogue forum |
| Seats | 28-30 |
| Elections | |
Voting system | All members elected either as MPs in the UK cabinet or as heads of Government or Ministers in Overseas Territories. |
| Meeting place | |
Westminster, London | |
| Website | |
| www.gov.uk/government/topical-events/overseas-territories-joint-ministerial-council | |
Each overseas territory has its own legal system independent of the United Kingdom. The legal system is generally based on English common law, with some distinctions for local circumstances. Each territory has its own attorney general, and court system. For the smaller territories, the UK may appoint a UK-based lawyer or judge to work on legal cases. This is particularly important for cases involving serious crimes and where it is impossible to find a jury who will not know the defendant in a small population island.[citation needed]
The Pitcairn sexual assault trial of 2004 is an example of how the UK may choose to provide the legal framework for particular cases where the territory cannot do so alone.
Joint Ministerial Council
A joint ministerial council of UK ministers, and the leaders of the Overseas Territories has been held annually since 2012 to provide representation between UK Government departments and Overseas Territory Governments.[45]
Relations with the United Kingdom

Leaders of the Overseas Territories with former Prime Minister David Cameron in 2012.

Tristan da Cunha on 6 February 2013, as seen from space. The population was temporarily evacuated to the UK in 1961 because of an eruption. Postal code TDCU 1ZZ

Coastline at Little Bay, the site of the new capital of Montserrat replacing Plymouth. The project is funded by the[46] UK's Department for International Development.
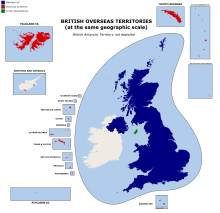
British Overseas Territories at the same geographic scale as the UK.
The Foreign and Commonwealth Office (FCO) has the responsibility of looking after the interests of all overseas territories except the Sovereign Base Areas of Akrotiri and Dhekelia, which comes under the jurisdiction of the Ministry of Defence.[47][48] Within the FCO, the general responsibility for the territories is handled by the Overseas Territories Directorate.[49]
In 2012, the FCO published The Overseas Territories: security, success and sustainability which set out Britain's policy for the Overseas Territories, covering six main areas:[50]
- Defence, security and safety of the territories and their people
- Successful and resilient economies
- Cherishing the environment
- Making government work better
- Vibrant and flourishing communities
- Productive links with the wider world
Britain and the overseas territories do not have diplomatic representations, although the governments of the overseas territories with indigenous populations all retain a representative office in London. The United Kingdom Overseas Territories Association (UKOTA) also represents the interests of the territories in London. The governments in both London and territories occasionally meet to mitigate or resolve disagreements over the process of governance in the territories and levels of autonomy.[51]
Britain provides financial assistance to the overseas territories via the Department for International Development. Currently[when?] only Montserrat and Saint Helena receive budgetary aid (i.e. financial contribution to recurrent funding).[citation needed] Several specialist funds are made available by the UK, including:
- The Good Government Fund which provides assistance on government administration;
- The Economic Diversification Programme Budget which aim to diversify and enhance the economic bases of the territories.
The territories have no official representation in the UK Parliament, but have informal representation through the All-Party Parliamentary Group,[52] and can petition the UK Government through the Directgov e-Petitions website.[53] Only Gibraltar has representation in the European Parliament and it shares its Member with the region of South West England.
Two national parties, UKIP and the Liberal Democrats, have endorsed calls for direct representation of overseas territories in the UK Parliament, as well as backbench members of the Conservative Party and Labour Party.[54][55][56][57]
Foreign affairs

Map showing the portion of Antarctica claimed by the UK as British Antarctic Territory.

Gibraltar is the only overseas territory included in the European Union
Foreign affairs of the overseas territories are handled by the FCO in London. Some territories maintain diplomatic officers in nearby countries for trade and immigration purposes. Several of the territories in the Americas maintain membership within the Organisation of Eastern Caribbean States, the Caribbean Community, the Caribbean Development Bank, Caribbean Disaster Emergency Management Agency, and the Association of Caribbean States. The territories are members of the Commonwealth of Nations through the United Kingdom. The inhabited territories compete in their own right at the Commonwealth Games, and three of the territories (Bermuda, the Cayman Islands and the British Virgin Islands) sent teams to the 2008 Summer Olympics.
Gibraltar is the only overseas territory that is part of the European Union (EU), although it is not part of the European Customs Union, the European Tax Policy, the European Statistics Zone or the Common Agriculture Policy. Gibraltar is not a member of the European Union in its own right. The Sovereign Base Areas in Cyprus are not part of the European Union, but they are the only British overseas territory to use the euro as official currency. None of the other Overseas Territories are members of the EU, the main body of EU law does not apply and, although certain slices of EU law are applied to those territories as part of the EU's Association of Overseas Countries and Territories (OCT Association), they are not commonly enforceable in local courts. The OCT Association also provides overseas territories with structural funding for regeneration projects.
Since the return of full British citizenship[58] to most 'belongers' of overseas territories (mainly since the British Overseas Territories Act 2002), the citizens of those territories hold concurrent European Union citizenship, giving them rights of free movement across all EU member states.
Five nations dispute the UK's sovereignty in the following overseas territories:
British Antarctic Territory – Territory overlaps Antarctic claims made by Chile and Argentina
British Indian Ocean Territory – claimed by Mauritius and Seychelles
Falkland Islands – claimed by Argentina
Gibraltar – claimed by Spain
South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands – claimed by Argentina
Citizenship
None of the overseas territories has its own nationality status, and most residents hold two forms of British nationality: British Overseas Territories citizenship (BOTC) and British citizenship. Only the latter grants the right of abode in a specific country or territory, namely, the United Kingdom proper which includes its three Crown Dependencies. Individual overseas territories have legislative independence over immigration, and consequently, BOTC status does not automatically grant the right of abode in any of the territories, as it depends on the territory's immigration laws. A territory may issue belonger status to allow a person to reside in the territory that they have close links with. The governors of the territories may also allow naturalization of non-BOTCs as BOTCs.

Thousands of Gibraltarians dress in their national colours of red and white during the 2013 Gibraltar National Day celebrations. Gibraltarians were the only group of overseas territories residents who could apply for full British citizenship without restrictions before 2002.
From 1949 to 1983, the nationality status of Citizenship of UK and Colonies (CUKC) was shared by residents of the UK proper and residents of overseas territories, although most residents of overseas territories lost their automatic right to live in the UK after the ratification of Commonwealth Immigrants Act 1968 that year unless they were born in the UK proper or had a parent or a grandparent born in the UK.[59] In 1983, CUKC status of residents of overseas territories without the right of abode in the UK was replaced by British Dependent Territories citizenship (BDTC) in the newly-minted British Nationality Act 1981, a status that does not come with it the right of abode in the UK or any overseas territory. For these residents, registration as full British citizens then required physical residence in the UK proper. There were only two exceptions: Falkland Islanders, who were automatically granted British citizenship and was treated as a part of the UK proper through the enactment of British Nationality (Falkland Islands) Act 1983 due to the Falklands War with Argentina, and Gibraltarians who were given the special entitlement to be registered as British citizens upon request without further conditions because of its individual membership in the European Economic Area and the European Community.[60]
5 years after the handover of Hong Kong to China in 1997, the British government amended the 1981 Act to give British citizenship without restrictions to all BDTCs (the status was also renamed BOTC at the same time) except for those solely connected with Akrotiri and Dhekelia (whose residents already held Cypriot citizenship).[61]. This restored the right of abode in the UK to residents of overseas territories after a 34-year hiatus from 1968 to 2002.
Military

RAF Mount Pleasant, Falkland Islands
Defence of the Overseas Territories is the responsibility of the UK. Many of the overseas territories are used as military bases by the UK and its allies.
Ascension Island (part of Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha) – the Base known as RAF Ascension Island is used by both the Royal Air Force and the United States Air Force.
Bermuda – became the primary Royal Navy base in North America, following US independence. The Naval establishment included an admiralty, a dockyard, and a naval squadron. A considerable military garrison was built up to protect it, and Bermuda, which the British Government came to see as a base, rather than as a colony, was known as Fortress Bermuda, and the Gibraltar of the West (Bermudians, like Gibraltarians, also dub their territory "The Rock").[62] Canada and the USA also established bases in Bermuda during the Second World War, which were maintained through the Cold War. Four air bases were located in Bermuda during the Second World War (operated by the Royal Air Force, Royal Navy, US Navy, and US Army/Army Air Force). Since 1995, the military force in Bermuda has been reduced to the local territorial battalion, the Royal Bermuda Regiment.
British Indian Ocean Territory – the island of Diego Garcia is home to a large naval base and airbase leased to the United States by the United Kingdom until 2036 (unless renewed). There are British forces in small numbers in the BIOT for administrative and immigration purposes.
Falkland Islands – the British Forces Falkland Islands includes commitments from the British Army, Royal Air Force and Royal Navy, along with the Falkland Islands Defence Force.
Gibraltar – British Forces Gibraltar includes a Royal Navy dockyard (also used by NATO), RAF Gibraltar – used by the RAF and NATO and a local garrison – the Royal Gibraltar Regiment.- The Sovereign Base Areas of Akrotiri and Dhekelia in Cyprus – maintained as strategic British military bases in the eastern Mediterranean Sea.
Montserrat – the Royal Montserrat Defence Force, historically connected with the Irish Guards, is a body of twenty volunteers, whose duties are primarily ceremonial.[63]
Languages

Cliffs at Gough and Inaccessible Islands.
Most of the languages other than English spoken in the territories contain a large degree of English, either as a root language, or in codeswitching, e.g. Llanito. They include:
Llanito or Yanito and Spanish (Gibraltar)
Cayman Creole (Cayman Islands)
Turks-Caicos Creole (Turks and Caicos Islands)
Pitkern (Pitcairn Islands)
Greek and Turkish (Akrotiri and Dhekelia)
Forms of English:
Bermudian English (Bermuda)- Falkland Islands English
Currencies
The many British overseas territories use a varied assortment of currencies, including the euro, pound, US dollar, NZ dollar, or their own currencies, which may be pegged to one of these.
| Location | Native currency | Issuing authority |
|---|---|---|
| Euro | European Central Bank |
| Pound sterling | Bank of England |
| Falkland Islands pound (parity with pound sterling) | Government of the Falkland Islands |
| Gibraltar pound (parity with pound sterling) | Government of Gibraltar |
| Saint Helenian pound (parity with pound sterling) | Government of Saint Helena |
| United States dollar | US Federal Reserve |
| Eastern Caribbean dollar (pegged to US dollar at 2.7ECD=1USD) | Eastern Caribbean Central Bank |
| Bermudian dollar (parity with US dollar) | Bermuda Monetary Authority |
| Cayman Islands dollar (pegged to US dollar at 1KYD=1.2USD) | Cayman Islands Monetary Authority |
| New Zealand dollar | Reserve Bank of New Zealand |
| United States dollar (de facto)[66][67] | US Federal Reserve |
1 Part of the British Overseas Territory of Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha.
Symbols and insignia

Overseas Territories flags in Parliament Square in 2013
Each overseas territory has been granted its own flag and coat of arms by the British monarch. Traditionally, the flags follow the Blue Ensign design, with the Union Flag in the canton, and the territory's coat of arms in the fly. Exceptions to this are Bermuda which uses a Red Ensign; British Antarctic Territory which uses a White Ensign; British Indian Ocean Territory which uses a Blue Ensign with wavy lines to symbolise the sea; and Gibraltar which uses a banner of its coat of arms (the flag of the city of Gibraltar).
Akrotiri and Dhekelia and Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha are the only British overseas territories without their own flag. The Union Flag is used in these territories.
Sports
Bermuda, the British Virgin Islands and the Cayman Islands are the only British Overseas Territories with recognised National Olympic Committees (NOCs); the British Olympic Association is recognised as the appropriate NOC for athletes from the other territories, and thus athletes who hold a British passport are eligible to represent Great Britain at the Olympic Games.[70]
Shara Proctor from Anguilla, Delano Williams from the Turks and Caicos Islands, Jenaya Wade-Fray from Bermuda[71] and Georgina Cassar from Gibraltar strived to represent Team GB at the London 2012 Olympics. Proctor, Wade-Fray and Cassar qualified for Team GB, with Williams missing the cut, however wishing to represent the UK in 2016.[72][73]
The Gibraltar national football team was accepted into UEFA in 2013 in time for the 2016 European Championships. It has been accepted by FIFA and went into the 2018 FIFA World Cup qualifying, where they achieved 0 points.
Biodiversity

The World Heritage Sites of the UK (Overseas Territories): The natural sites of Gough and Inaccessible Islands and Henderson Island are marked green, the cultural sites of the Historic Town of St George and Related Fortifications, Kourion, and Gorham's Cave are marked red.
The British Overseas Territories have more biodiversity than the entire UK mainland.[74] There are at least 180 endemic plant species in the overseas territories as opposed to only 12 on the UK mainland. Responsibility for protection of biodiversity and meeting obligations under international environmental conventions is shared between the UK Government and the local governments of the territories.[75]
Two areas, Henderson Island in the Pitcairn Islands as well as the Gough and Inaccessible Islands of Tristan Da Cunha are listed as UNESCO World Heritage Sites, and two other territories, the Turks and Caicos Islands, and Saint Helena are on the United Kingdom's tentative list for future UNESCO World Heritage Sites.[76][77] Gibraltar's Gorham's Cave Complex is also found on the UK's tentative UNESCO World Heritage Site list.[78]
The three regions of biodiversity hotspots situated in the British Overseas Territories are the Caribbean Islands, the Mediterranean Basin and the Oceania ecozone in the Pacific.[75]
The UK created the largest continuous marine protected areas in the world, the Chagos Marine Protected Area, and announced in 2015 funding to establish a new, larger, reserve around the Pitcairn Islands.[79][80][81]
In January 2016, the UK government announced the intention to create a marine protected area around Ascension Island. The protected area would be 234,291 square kilometers, half of which would be closed to fishing.[82]

A Stoplight Parrotfish in Princess Alexandra Land and Sea National Park, Providenciales, Turks and Caicos Islands

Penguins in South Georgia, 2010.
Henderson Island in the Pitcairn Islands

Rothera Research Station.
See also
Depopulation of Chagossians from the Chagos Archipelago to enable building of a UK-US military base in the British Indian Ocean Territory
- List of postcodes
- List of leaders of Overseas Territories
- List of British Army installations
- British overseas territory citizens in the mainland United Kingdom
- Colonial Department
- Secretary of State for the Colonies
- Colonial Office
- Universities in British Overseas Territories
United Kingdom Overseas Territories Association (UKOTA)- UK Overseas Territories Conservation Forum
- List of stock exchanges in the United Kingdom, the British Crown Dependencies and United Kingdom Overseas Territories
- Tax haven lists
References
^ "Supporting the Overseas Territories". UK Government. Retrieved 8 November 2014.There are 14 Overseas Territories which retain a constitutional link with the UK. .... Most of the Territories are largely self-governing, each with its own constitution and its own government, which enacts local laws. Although the relationship is rooted in four centuries of shared history, the UK government's relationship with its Territories today is a modern one, based on mutual benefits and responsibilities. The foundations of this relationship are partnership, shared values and the right of the people of each territory to choose to freely choose whether to remain a British Overseas Territory or to seek an alternative future.
.mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ "What is the British Constitution: The Primary Structures of the British State". The Constitution Society. Archived from the original on 6 October 2014. Retrieved 15 November 2014.The United Kingdom also manages a number of territories which, while mostly having their own forms of government, have the Queen as their head of state, and rely on the UK for defence and security, foreign affairs and representation at the international level. They do not form part of the UK, but have an ambiguous constitutional relationship with the UK.
^ "New ministerial appointments at the Foreign and Commonwealth Office" (Press release). Foreign and Commonwealth Office. 19 July 2016. Retrieved 20 September 2016.
^ "Overseas Territories". UK Overseas Territories Foreign & Commonwealth Office. Archived from the original on 23 June 2012. Retrieved 8 December 2010.
^ "SBA Cyprus". Jncc.gov.uk. Retrieved 8 December 2010.
^ ab "British Antarctic Territory". Jncc.gov.uk. Retrieved 8 December 2010.
^ "Commonwealth Secretariat – Anguilla". Thecommonwealth.org. Archived from the original on 17 December 2010. Retrieved 8 December 2010.
^ ab "UNdata | record view | Surface area in km2". United Nations. 4 November 2009. Retrieved 8 December 2010.
^ "Bermuda". Jncc.gov.uk. Retrieved 8 December 2010.
^ "Commonwealth Secretariat – British Antarctic Territory". Thecommonwealth.org. Archived from the original on 5 June 2011. Retrieved 8 December 2010.
^ "British Indian Ocean Territory". Jncc.gov.uk. Retrieved 8 December 2010.
^ "Commonwealth Secretariat – British Indian Ocean Territory". Thecommonwealth.org. Archived from the original on 5 June 2011. Retrieved 8 December 2010.
^ ab "British Virgin Islands (BVI)". Jncc.gov.uk. Retrieved 8 December 2010.
^ ab "Economics and Statistics Office - Labour Force Survey Report Spring 2018" (PDF). www.eso.ky. Cayman Islands Economics and Statistics Office. August 2018. Retrieved 26 November 2018.
^ "Commonwealth Secretariat – Falkland Islands". Thecommonwealth.org. 14 June 1982. Archived from the original on 13 May 2011. Retrieved 8 December 2010.
^ "Gibraltar". Jncc.gov.uk. Retrieved 8 December 2010.
^ "Commonwealth Secretariat – Gibraltar". Thecommonwealth.org. 7 November 2002. Archived from the original on 6 March 2010. Retrieved 8 December 2010.
^ ab "Montserrat". Jncc.gov.uk. Retrieved 8 December 2010.
^ "Pitcairn Island". Jncc.gov.uk. Retrieved 8 December 2010.
^ Rob Solomon and Kirsty Burnett (January 2014) Pitcairn Island Economic Review. government.pn. Retrieved 7 September 2016.
^ "Pitcairn Residents". puc.edu. Retrieved 7 September 2016.
^ "UN Statistics – St Helena census 2008" (PDF). United Nations. Archived from the original (PDF) on 29 June 2014. Retrieved 4 January 2011.
^ abc "St Helena, Ascension, Tristan da Cunha profiles". BBC. 16 March 2016. Retrieved 25 June 2016.
^ Vital Statistics – SOUTH GEORGIA AND THE SOUTH SANDWICH ISLANDS. 22 January 1993. CIA WORLD FACTBOOK 1992 via the Libraries of the Univ. of Missouri-St. Louis.
^ "Population of Grytviken, South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands". Population.mongabay.com. 31 March 2009. Archived from the original on 17 July 2011. Retrieved 8 December 2010.
^ ab "Turks and Caicos Islands". Jncc.gov.uk. 1 November 2009. Retrieved 8 December 2010.
^ "Fotbot.org". sites.google.com.
^ "States of Guernsey: About Guernsey". Gov.gg. Archived from the original on 12 October 2010. Retrieved 8 December 2010.
^ "Government – Isle of Man Public Services". Gov.im. Archived from the original on 18 December 2010. Retrieved 8 December 2010.
^ [1] Archived 1 October 2009 at the Wayback Machine
^ "CIA – The World Factbook 2002 – South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands". Faqs.org. Retrieved 8 December 2010.
^ "CIA – The World Factbook". Cia.gov. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
^ "Bermuda – History and Heritage". Smithsonian.com. 6 November 2007. Archived from the original on 24 May 2012. Retrieved 3 December 2008.
^ "Newfoundland History – Early Colonization and Settlement of Newfoundland". Faculty.marianopolis.edu. Retrieved 8 December 2010.
^ Copyright 2015 The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. "UNC Press - In the Eye of All Trade".
^ "In the Eye of All Trade: Bermuda, Bermudians, and the Maritime Atlantic World, 1680-1783". Archived from the original on 9 January 2012.
^ Statute of Westminster 1931 (UK) CHAPTER 4 22 and 23 Geo 5
^ The Commonwealth – About Us; Online September 2014
^ "Population". Census and Statistics Department. Hong Kong Statistics. Retrieved 12 July 2013.
^ British Overseas Territories Act 2002 (text online): S. 3: "Any person who, immediately before the commencement of this section, is a British overseas territories citizen shall, on the commencement of this section, become a British citizen."
^ "Falkland Islands Legislative Assembly". Falklands.gov.fk. Retrieved 8 December 2010.
^ "Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha Constitution Order 2009 (at OPSI)". Opsi.gov.uk. 16 July 2010. Retrieved 8 December 2010.
^ Press Release No. 133/2007 Archived 24 February 2010 at WebCite. Government of Gibraltar Press Office.
^ "Bermuda Parliament". parliament.bm.
^ "Overseas Territories Joint Ministerial Council 2015 Communique and Progress Report - Publications - GOV.UK". Retrieved 15 September 2016.
^ "Little Bay Development". Projects.dfid.gov.uk. Archived from the original on 25 April 2013. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
^ British Overseas Territories Law, Ian Hendry and Susan Dickson, Hart Publishing, Oxford, 2011, p. 340
^ "Sovereign Base Areas, Background". Sovereign Base Areas, Cyprus. Retrieved 7 October 2011.
^ "UK Overseas Territories".
^ "The Overseas Territories: security, success and sustainability" (PDF). Foreign & Commonwealth Office. 28 June 2012. Retrieved 15 November 2014.
^ British financial officials in the region for talks with dependent territories Archived 25 March 2009 at the Wayback Machine – By Oscar Ramjeet, CaribbeanNetNews, (Published on Saturday, 21 March 2009)
^ "MP proposes British Overseas Territories be represented in Westminster – MercoPress". En.mercopress.com. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
^ "HM Government e-petitions". Epetitions.direct.gov.uk. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
^ "Lib Dems would create an MP for Gibraltar". Gibraltar News Olive Press. 18 May 2017.
^ "UKIP leader defends call for Gibraltar to become part of Britain - Xinhua - English.news.cn". news.xinhuanet.com.
^ "Spain must treat Gibraltar as an equal part of the British family, says Rosindell". www.gibraltarpanorama.gi.
[permanent dead link]
^ "gibraltar". gibraltar.
^ [2] Any person who, immediately before the commencement of this section, is a British overseas territories citizen shall, on the commencement of this section, become a British citizen.
^ "Section 1 of the 1968 Act" (PDF).
^ Section 5 of British Nationality Act 1983
^ British Overseas Territories Act 2002
^ Bermuda[permanent dead link] at avalanchepress.com
^ "UK Government White Paper on Overseas Territories, June, 2012. Page 23" (PDF).
^ "demtullpitcairn.com" (PDF). www.demtullpitcairn.com. Archived from the original (PDF) on 9 May 2016. Retrieved 3 January 2018.
^ Asia and Pacific Review 2003/04 p.245
ISBN 1862170398
^ FCO country profile Archived 10 June 2010 at the Wayback Machine
^ "The World Factbook".
^ "British Indian Ocean Territory Currency". Wwp.greenwichmeantime.com. 6 March 2013. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
^ Commemorative UK Pounds and Stamps issued in GBP have been issued. Source:[3], [4]
^ Overseas Territories. House of Commons Foreign Affairs Select Committee.
^ Stephen Wright (28 July 2012). "Representing Britain...and Bermuda | Bermuda Olympics 2012". Royalgazette.com. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
^ "Williams' Olympic hopes on hold for 4 more years". Fptci.com. 29 June 2012. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
^ Purnell, Gareth (27 July 2012). "At last! Phillips Idowu tracked down... in Team GB photo – Olympic News". The Independent. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
^ "About the Biodiversity of the UK Overseas Territories". UKOTCF. Retrieved 17 June 2016.
^ ab "Science: UK Overseas Territories: Biodiversity". Kew. Archived from the original on 2 May 2013. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
^ "Turks and Caicos Islands – UNESCO World Heritage Centre". Whc.unesco.org. 27 January 2012. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
^ "Island of St Helena – UNESCO World Heritage Centre". Whc.unesco.org. 27 January 2012. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
^ "Gorham's Cave Complex". UNESCO. UNESCO World Heritage Centre. 27 January 2012. Retrieved 30 June 2016.
^ "World's Largest Single Marine Reserve Created in Pacific". National Geographic. World's Largest Single Marine Reserve Created in Pacific. 18 March 2015. Retrieved 19 March 2015.
^ "Pitcairn Islands get huge marine reserve". BBC. 18 March 2015. Retrieved 19 March 2015.
^ "Pitcairn Islands to get world's largest single marine reserve". The Guardian. London. 18 March 2015. Retrieved 19 March 2015.
^ "Ascension Island to become marine reserve". 3 January 2016. Retrieved 3 January 2016.
Further reading
- Charles Cawley. Colonies in Conflict: The History of the British Overseas Territories (2015) 444pp
- Harry Ritchie, The Last Pink Bits: Travels Through the Remnants of the British Empire (London: Hodder & Stoughton, 1997)
Simon Winchester, Outposts: Journeys to the Surviving Relics of the British Empire (London & New York, 1985)- George Drower, Britain's Dependent Territories (Dartmouth, 1992)
- George Drower, Overseas Territories Handbook (London: TSO, 1998)
- Ian Hendry and Susan Dickson, "British Overseas Territories Law" (London: Hart Publishing, 2011)
Ben Fogle, The Teatime Islands: Adventures in Britain's Faraway Outposts (London: Michael Joseph, 2003)
Bonham C. Richardson (16 January 1992). The Caribbean in the Wider World, 1492–1992. Cambridge University Press. Retrieved 8 December 2010.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to British overseas territories. |
- Foreign and Commonwealth Office – UK Overseas Territories
- United Kingdom Overseas Territories Association
- British Overseas Territories Act 2002 – Text of the Act








Comments
Post a Comment