间脑
| 間腦 | |
|---|---|
 從間腦浮現三中央大腦結構——視丘(thalamus)、下視丘(hypothalamus)和腦垂腺(pituitary gland),大腦呈現矢狀切面。 | |
| 细节 | |
| 拉丁语 | diencephalon |
| 识别标示 | |
| Gray's | p.807 |
| MeSH | A08.186.211.730.385 |
| Code | TH H3.11.03.5.00001 |
| NeuroNames | hier-271 |
NeuroLex ID | Diencephalon |
| TA | A14.1.03.007、A14.1.08.001 |
| TH | H3.11.03.5.00001 |
| FMA | FMA:62001 |
解剖学术语 | |
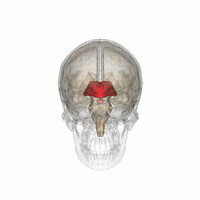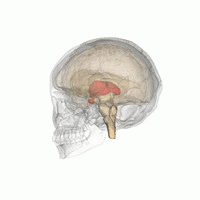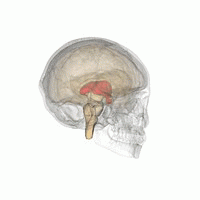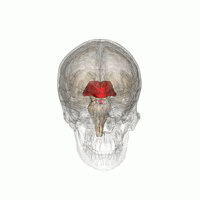
間腦(紅色)的位置。
间脑(diencephalon)位於端脑与中脑之间,大部份被大脑两侧半球所遮盖,间脑呈楔形,下部与中脑相连。间脑主要分为丘脑和下丘脑,细分可分为背侧丘脑、上丘脑、后丘脑、下丘脑和底丘脑。[1][2]
目录
1 功能
2 間腦症候群
3 相關圖片
4 參考資料
4.1 書籍、網站資源
4.2 醫學資源
功能
间脑是脊椎动物胚胎神经管中,产生后前脑结构的部分,包括丘脑、下丘脑、垂体后部和松果体。下丘脑执行大量的重要功能,其中大部分直接或间接与通过其他脑区和自主神经系统调节與内脏活动有关[2]。
間腦症候群

間腦症候群影響的範圍包含丘腦、底丘腦、下丘腦以及上丘腦。
間腦症候群的特徵是一種天生罕見擁有發育停滯神經系統的疾病。儘管身理正常或略有減少熱量攝入、運動機能亢進、和亢奮感,皆有嚴重消瘦的現象。皮膚蒼白不太常見,無貧血、低血糖和低血壓[醫學 1]。間腦症候群可能會影響到自身的成長,也可能導致致命的原因,未能成長茁壯的幼兒平均只有七個月的年齡[醫學 1]。值得注意的是該症狀不與發育遲緩有關,而是與腦積水有關[醫學 2]。
間腦症候群於1951年由罗素首次介紹[3]。雖然因為有過多的β促脂解素的分泌[醫學 1]和代謝需求整體上升[醫學 3],使不適當高的生長激素釋放已被提出[醫學 4],但是位於下丘腦 - 光視交叉區,通常會引起如低級別膠質瘤或星形細胞瘤的腦腫瘤,然而尚未了解到如何影響到食慾和新陳代謝所引起的間腦症候群。
相關圖片

圖片描繪脊椎動物胚胎大腦的主要結構的細節。這些區域分成大腦、中腦和後腦的結構。
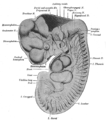
10.2毫米人類周圍神經的構造(標籤間腦位於左側)。
參考資料
書籍、網站資源
^ Jacobson & Marcus. Neuroanatomy for the Neuroscientist. Springer. 2008: 147. ISBN 978-0-387-70970-3.
^ 2.02.1 中樞神經系統. 香港體育教學網. 2013年5月10日 [2015年8月21日].
^ Russell A. A diencephalic syndrome of emaciation in infancy and childhood. Arch Dis Child. 1951, 26: 274.
醫學資源
^ 1.01.11.2 Kim A, Moon JS, Yang HR, Chang JY, Ko JS, Seo JK. Diencephalic syndrome: a frequently neglected cause of failure to thrive in infants. Korean J Pediatr. Jan 2015, 58 (1): 28–32. PMID 25729396.
^ Fleischman A1, Brue C, Poussaint TY, Kieran M, Pomeroy SL, Goumnerova L, Scott RM, Cohen LE. Diencephalic syndrome: a cause of failure to thrive and a model of partial growth hormone resistance. Pediatrics. June 2005, 115 (6): 724–6. PMID 15930202.
^ Vlachopapadopoulou E, Tracey KJ, Capella M, Gilker C, Matthews DE. Increased energy expenditure in a patient with diencephalic syndrome. J Pediatr. June 1993, 112 (6): 922–4. PMID 8501572.
^ Drop SL, Guyda HJ, Colle E. Inappropriate growth hormone release in the diencephalic syndrome of childhood: case report and 4 year endocrinological follow-up. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). August 1980, 13 (2): 181–7. PMID 7438472.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||



Comments
Post a Comment